Does like That
This organelle can be free floating or attached to another organelle, and manufactures proteins.
What is the ribosome?
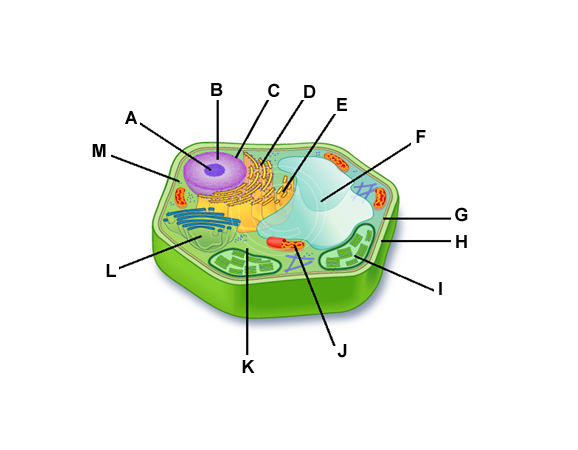
The Structure that number 2 is pointing at.

What is the nucleus?
The control center for the cell.
What is the nucleus?
The function of letter I.
What is photosynthesis?
The purpose of DNA.
What is to store genetic information/code for proteins?
I can maintain the shape of the cell and protect it from harm.
What is the cell wall?
The structure that number 5 is pointing at.

What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Produces energy for the cell, aka the powerhouse of the cell.
What is the mitochondrion?
The Function of Letter G.

What is control what comes into and out of the cell?
A liquid environment filled with organelles that helps with chemical reactions.
What is the cytoplasm?
This controls what comes into and out of the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
The structure number 9 is pointing at.

What is the mitochondria?
A membrane sac found in cells that is used to store food, water, wastes and enzymes. Is very large in plant cells.
What is the vacuole?
The function of letter J.

What is produce energy for the cell?
The UPS/post office/shipping station of the cell.
What is the golgi apparatus?
I'm made of protein fibers and provide internal support for the cell.
What is the cytoskeleton?
The Structure that number 6 is pointing at.

What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
An internal membrane system that is used to manufacture carbohydrates and lipids.
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
The function of letter H.

What is protect and provide shape for the cell?
Organelles that have their own DNA.
What is the chloroplast and the mitochondria?
A small bag of membrane used to transport materials around, into and out of the cell.
What is the vesicle?
The structure that number 1 is pointing at.

What is the nucleolus?
I digest invaders and old cell parts, aiding in cell renewal.
What is the lysosome?
The function of letter F.

What is to store water, food, waste and enzymes?
The three organelles that would eventually result in zero protein production if any of them stopped working.
What are the DNA, nucleolus and ribosomes?