1
2
3
This man observed cork with his microscope and called the tiny boxes 'cells'.
Who was Robert Hooke?
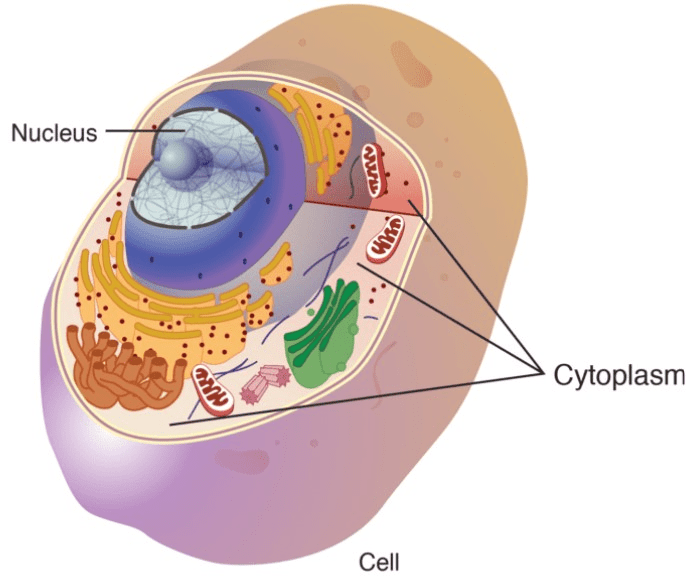
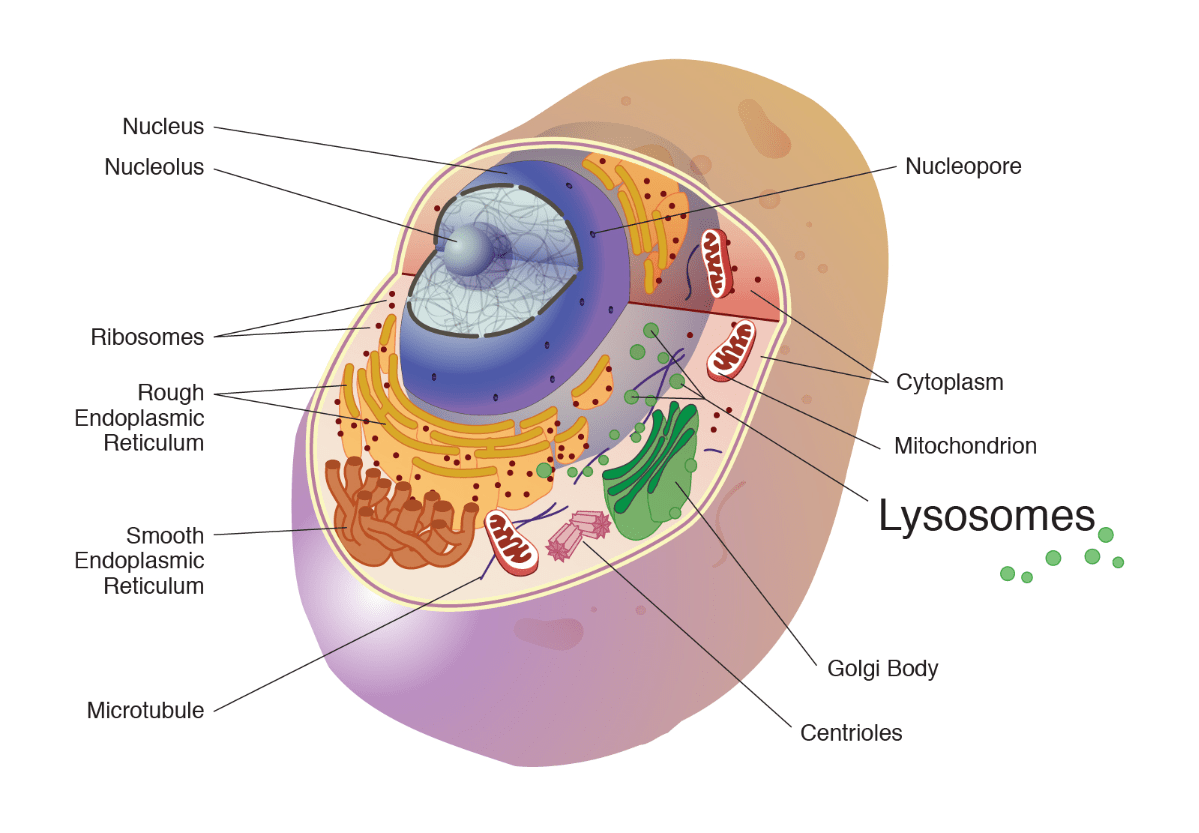
This fills the space inside a cell. It is a gel-like substance that surround cell organelles inside of a cell. It is semi-fluid and is composed of water and dissolved materials.
What is cytoplasm?
This organelle provides the cell with the ENERGY (ATP) it needs to perform its functions and activities for an organism.
What is the mitochondria?
A flexible semi-permeable barrier outside of a cell that controls what comes into and goes out of the cell. It is found in all types of cells.
What is a cell membrane?
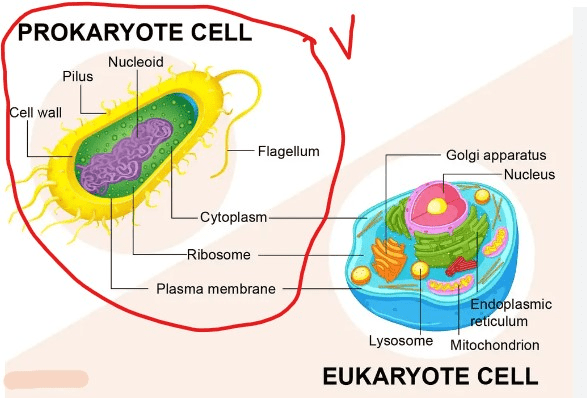
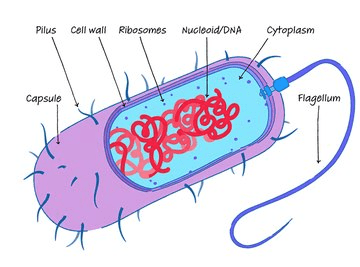
This cell category has no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. They are more ancient and more simple intheir structure. They are unicellular. Bacteria and archaea are the examples of this cell category.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
He saw the first living microorganisms. He called them "animalcules".
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
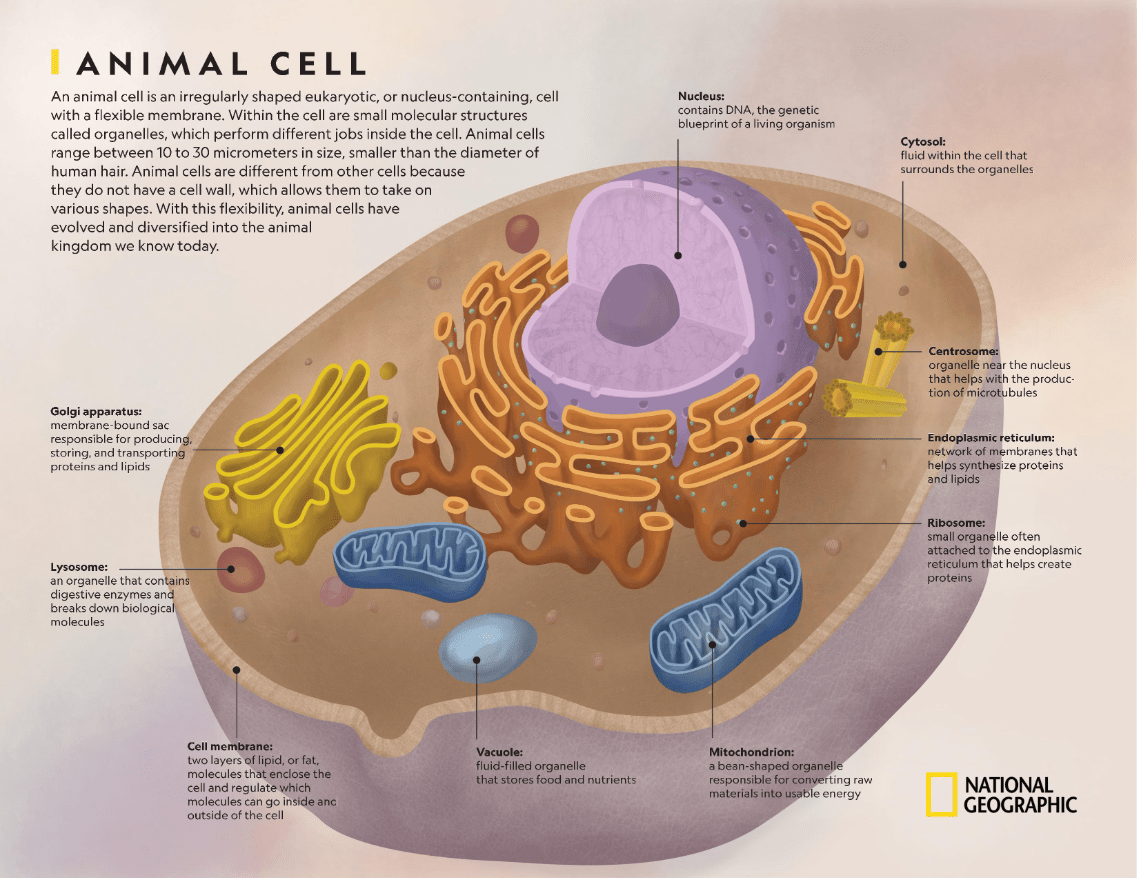
This organelle is the control center of a cell. It directs cell processes by providing DNA instructions. It is surrounded by its own membrane and is covered with pores.
What is the nucleus?
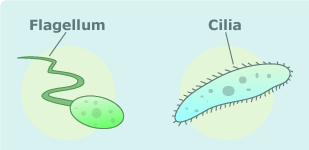
These structures are used for cell movement. The first is long and there are usually very few of them. The second are short and there are usually many of them.
What flagella and cilia?
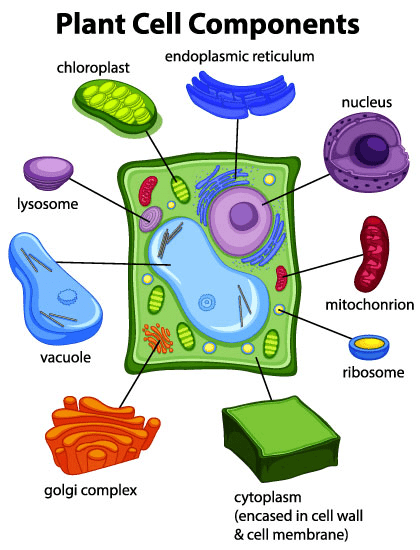
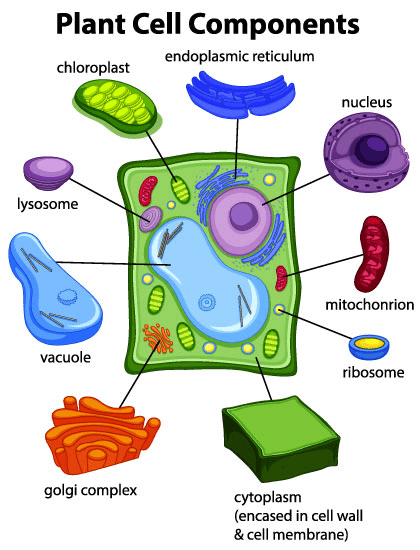
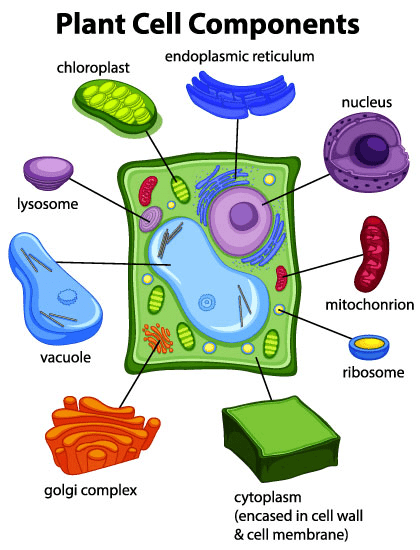
The plant organelle that captures the sun’s energy and uses it for photosynthesis.
What is chloroplast?
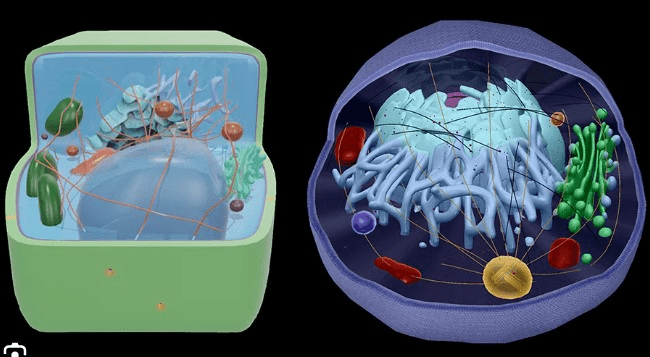
This cell type contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (such as mitochondria).
What are eukaryotic cells?
Simple, compound, light, electron and transmission are all terms that relate to:
What are Microscopes?
This organelle modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) for transport to their final destinations inside or outside the cell. It looks like a stack of pancakes.
What is the Golgi Body (apparatus)?
This organelle digests worn out cell parts and also plays a role to defend the cell from infection and impuritis. It's like a cleaning agent for a cell.
What is a lysosome?
Rigid layer that surrounds plant, fungi, and bacteria cells.
What is a cell wall?
Prokaryotic cells have these organelles in its structure.
What is cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes AND DNA without nucleus.
He studied plants. He looked at lots of plants under the microscope; their leaves, flowers, roots and stems. He decided that "All plants are made of cells".
Mattias Schleiden
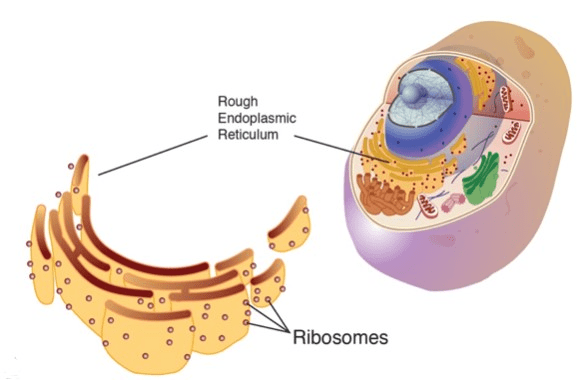
This organelle is a series of interconnected passageways (outside of the nucleus). Proteins and lipids are synthesized (put together) here. There are two varieties 'Smooth' and 'Rough'.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
These are made by the nucleolus and their function is to follow DNA instructions to make PROTEINS. They are free-floating or may be found attached to the rough ER.
What are ribosomes?
Storage area of the cell that contains food, water, and waste.
What is a vacuole?
Describe how prokaryotic cells divide compared to eukaryotic cell.
What is binary fission?
Three principles of the Cell Theory are.....
1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of life. 3. Cells only come from pre-existing cells.
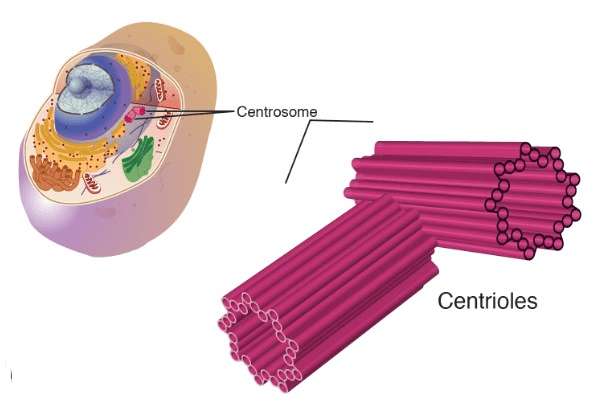
This organelle is found only in animal cells. It is made of microtubules and is thought to play a role in cell division.
What are centrioles?
The three differences between plant and animal cells are:
3Cs in a plant cell: 1. Cell walls. 2. Chloroplasts 3. Central Vacuole. 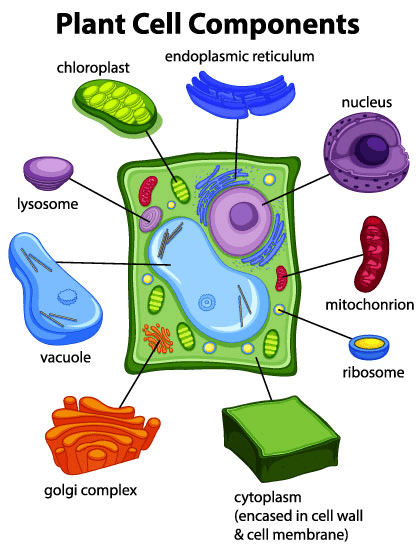
Animal cells have centrioles (for cell division).
The cell organelle that primarily helps in cell division.
What is a Centriole?
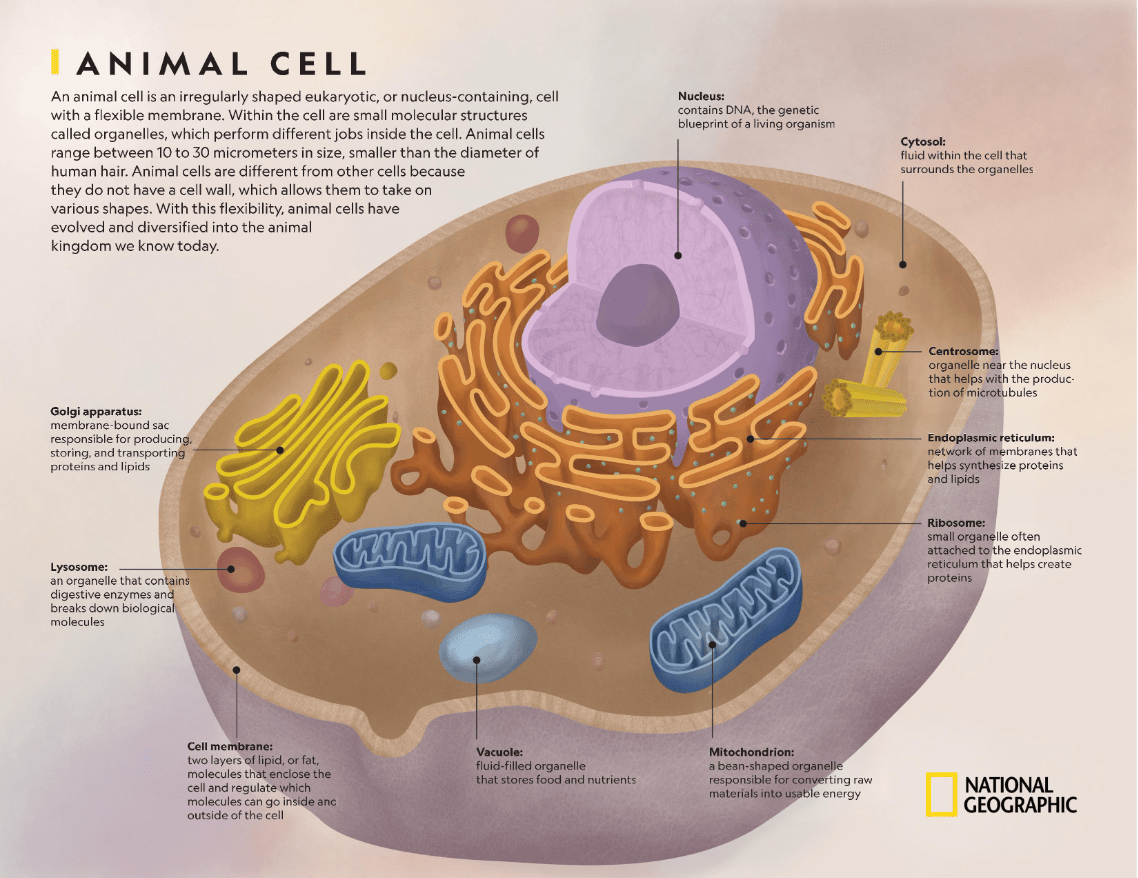
The following structures are involved in energy production in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells.
What is mitochondria?