What is the general formula for magnification?
M=I/A
Energy (ATP) synthesis in animal cells
Mitochondria
one example of a prokaryotic organism
any type of bacteria
name any organelle from any eukaryotic cell
mitochondria, chromosome, ribosome, centriole, nucleus, nucleolus, RER SER, Golgi apparatus, etc
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
What is the general formula for Actual size?
A=I/M
do not have a cell wall
animal cells
main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
the presence or absence of a membrane bound nucleus and organelles
what is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
presence or absence of nucleus and membranous organelles
What is the function of the of the organelle in the picture?

to carry out photosynthesis
how much is 5,33cm in µm?
53300 µm
DNA is contained here
Nucleus
many prokaryotic organisms have a long, tail-like structure called
Flagella
where is DNA located in eukaryotic organisms?
Nucleus
What type of cell is pictured?

Plant Cell
How many mm is in a cm?
10 mm in a cm
They come in two sizes: 70s for Prokaryotic and 80s for Eukaryotic
Ribosomes
typical size for prokariotes ranges from...
0.1µm to 5.0µm
typical size for prokariotes ranges from...
10μm to 100 μm
What type of cell is pictured?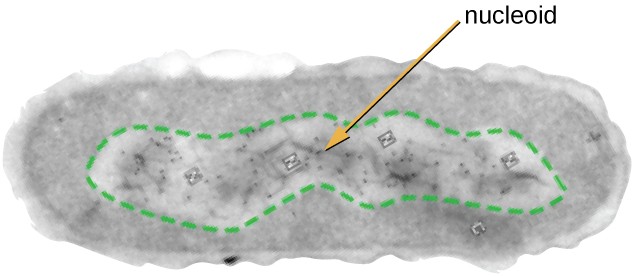
Prokaryotic
list two differences between LM and SEM/TEM?

they have chlorophyll, they have stroma, they have thylakoids
chloroplasts
is this a prokaryotic organism?
No. That is a mitochondria
Is this "organism" a prokaryotic or an eukaryotic one?

Apparently, eukaryotic. More research is needed
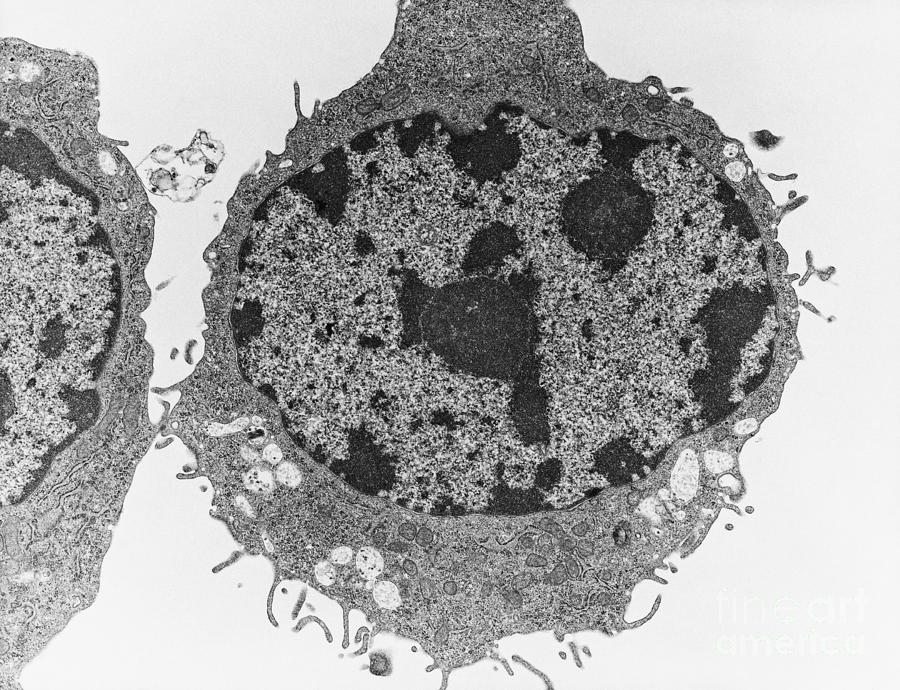
What type of cell is pictured? How do you know? (2 reasons)
Animal Cell-
no cell wall
no chloroplast