It's the meaning of the two stem words that make up the name of the category.
What are "light" and "make/produce"?
Red blood cells are equipped with hemoglobin proteins that can each accomodate and deliver up to 4 molecules of this gaseous waste product.
What is carbon dioxide?
It's the common suffix that many enzymes contain.
What is a-s-e?
It's the name of the phases that make up interphase, the longest part of the cell cycle.
What are G1, S, and G2?
It's what this zygote will do for several days as it eventually becomes an embryo.
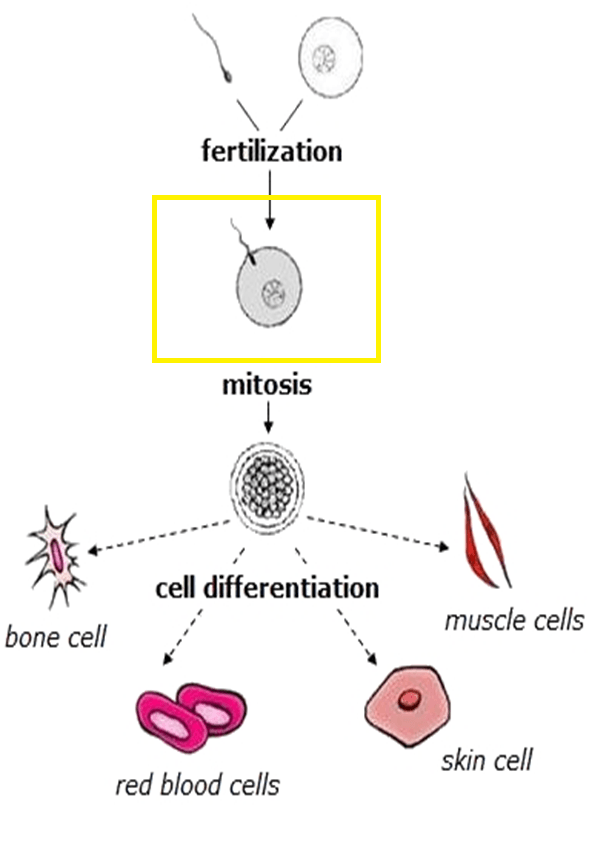
What is divide?
It's the name of the gas used in photosynthesis and released in cellular respiration.
What is carbon dioxide?
These organelles are the site of photosynthesis in eukaryotic cells.
What are chloroplasts?
These organelles are the primary sites of cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells.
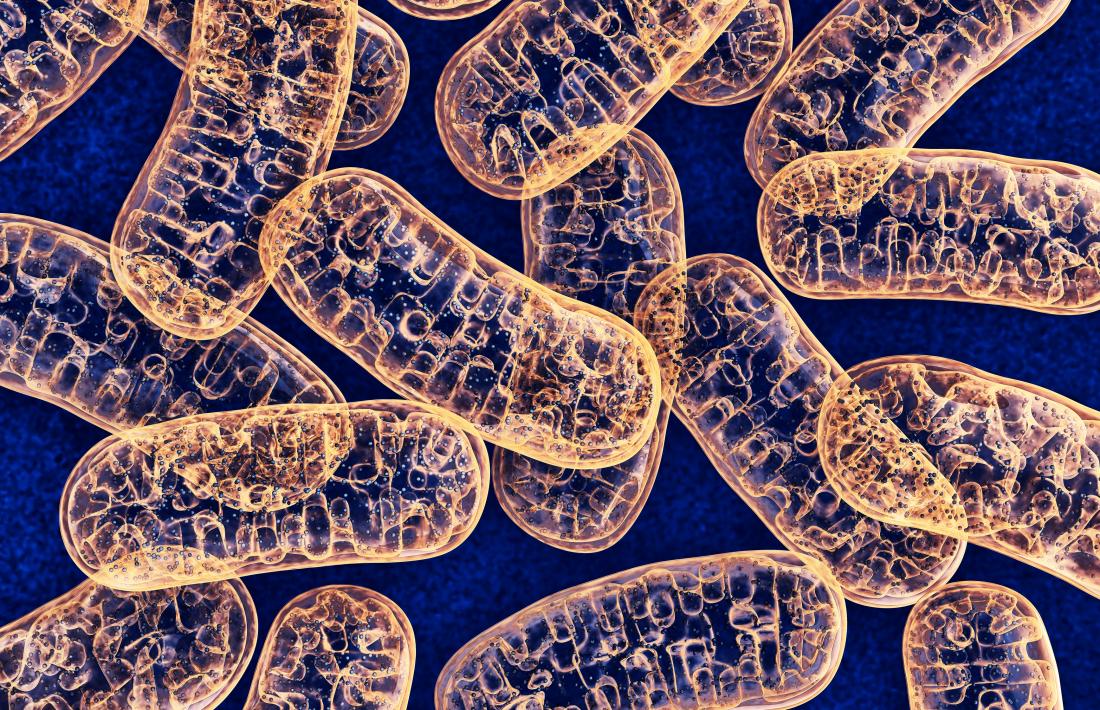
What are mitochondria?
It's the location where an enzyme binds with its substrate.
What is an active site?
It's what gets synthesized during the S-phase.
What is DNA? (or chromosomes)
Embryonic stem cells divide & give rise to more specialized ones, like neurons for the brain, in this process.
What is differentiation?
The products of photosynthesis are these two main reactants of cellular respiration.
What are glucose and oxygen?
The carbons from six CO2 molecules are incorporated into a single molecule of this sweet product of photosynthesis.
What is glucose?
A chief reactant of cellular respiration, this gaseous molecule serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
What is oxygen?
Enzymes function by lowering this vital requirement of chemical reactions.
What is activation energy?
A damaged cell that cannot be repaired may undergo this process that has been defined as "programmed cellular death".
What is apoptosis?
Requiring no ATP, it's the process by which these CO2 molecules are crossing the cell membrane.
What is diffusion?
P is for photosynthesis, but it's also for this word that describes members of the plant kingdom for their ability to create glucose that is at the heart of every food chain and food web across the globe.
What is producer?
Besides light and carbon dioxide, this abiotic environmental factor is crucial to carrying out photosynthesis.
What is water?
It's the complete name of the energy currency of the cell that which is a primary product of cellular respiration.
What is adenosine triphospate? (Simply stating ATP does not earn any points, but doesn't lose any either)
Enzymes can be classified as catabolic if they break substances down into smaller parts, or this type if they build bigger molecules from smaller ones.
What is anabolic?
Chromosomes are still visible, nuclear membranes are re-forming around them and spindle fibers have broken down during this stage of mitosis.

What is telophase?
At around 50°C the enzyme for this reaction becomes less effective. At even higher temperatures, it may become this.
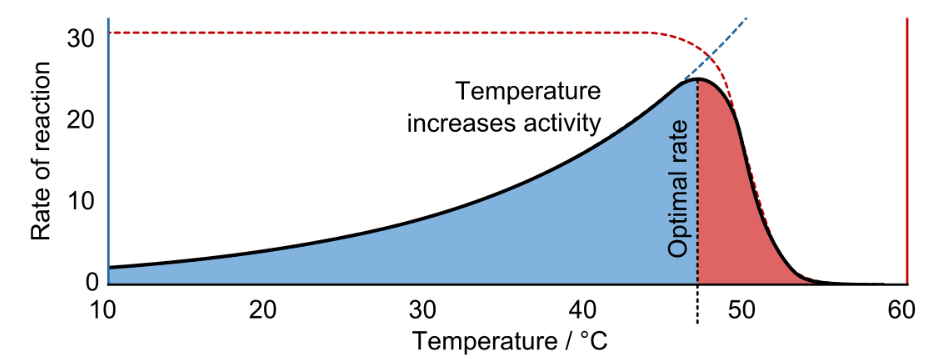
What is denatured?
Most plant leaves take in more carbon dioxide as light increases, but they will give off more if light intensity is too low as seen in the graph.
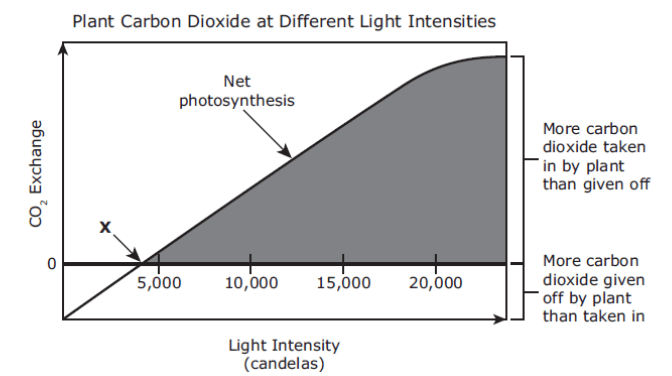
At point X, the rate of which process is equal to the rate of photosynthesis?
What is cellular respiration?
To conserve precious resources some plants have evolved to only open these small gas-exchanging pores in their leaves during times when sunlight is available for photosynthesis.
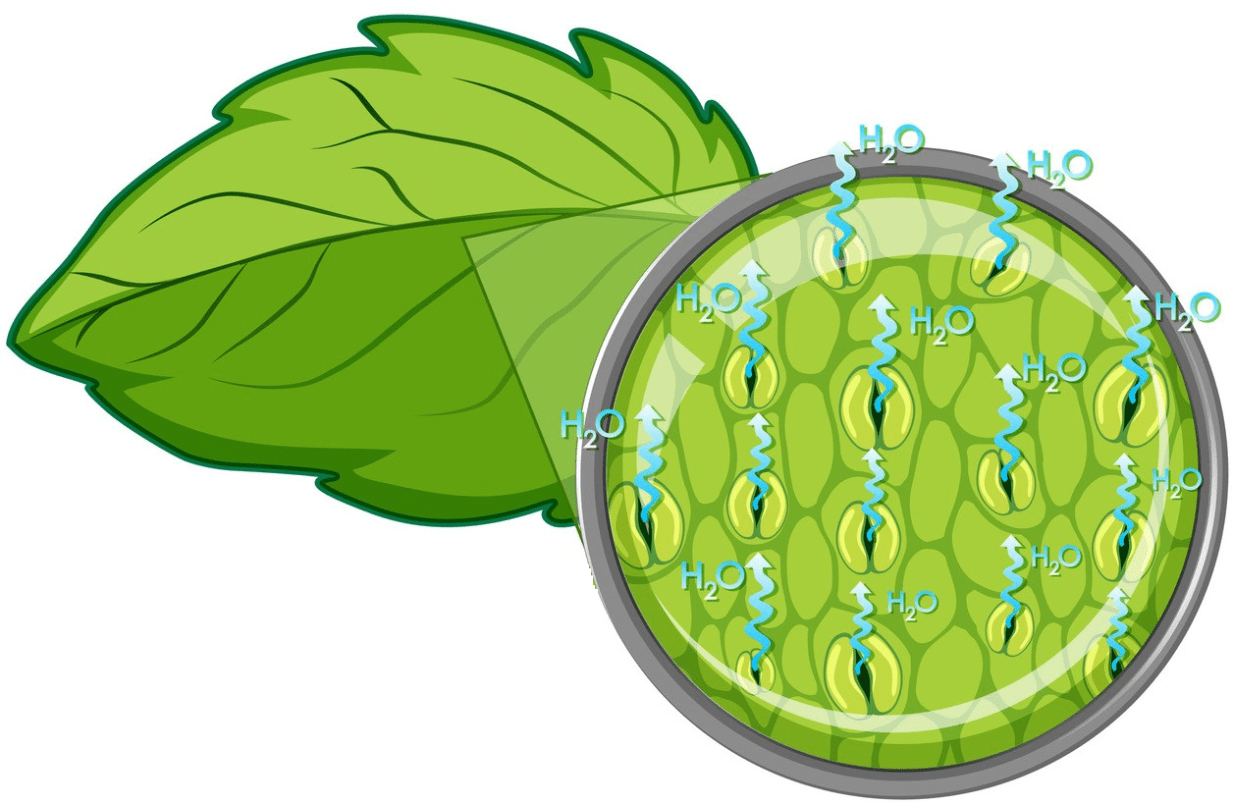
What are stomata?
While some organisms like yeast depend on it exclusively, eukaryotic cells can still generate small amounts of energy via this "no-oxygen" method of cellular respiration.
What is anaerobic respiration (or fermentation)?
Because they do not undergo any chemical change themselves and are re-usable in the reactions they speed up, enzymes are said to be this type of compound.
What is a catalyst?
Need a break? Some cells do to, sometimes for the rest of their lives. They'll spend it in this less common stage of the cell cycle.
What is G0?
Knowing what the D in DNA stands for should tell you this noun, the sugar found in DNA.
What is deoxyribose?
Diatoms like the one pictured here are the most common types of photosynthetic protists found in marine habitats. Like plants they contain this green, light-absorbing pigment that is critical for producing glucose.
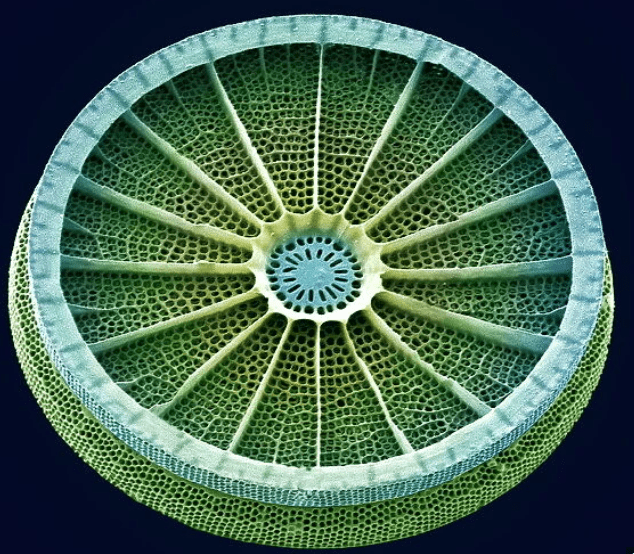
What is chlorophyll?
