The place on an enzyme where it meets the substrate to complete a chemical reaction
What is the active site?
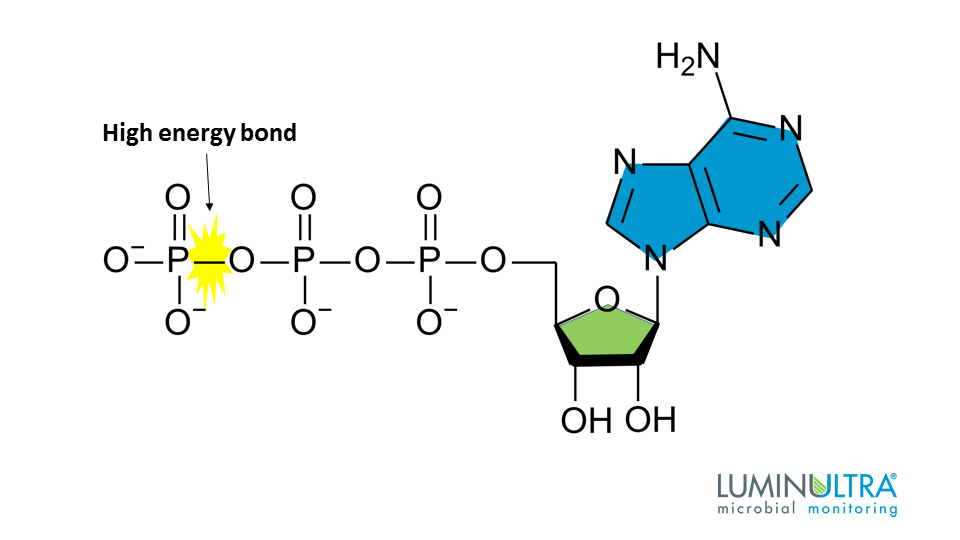
This molecule is the primary source of useable cellular energy
What is adenosine triphosphate?
The sac-like structures inside of a chloroplast where the light-dependent reaction occurs
What are thylakoids?

This organelle is where in the cell the majority of ATP is produced
What is the mitochondrion?

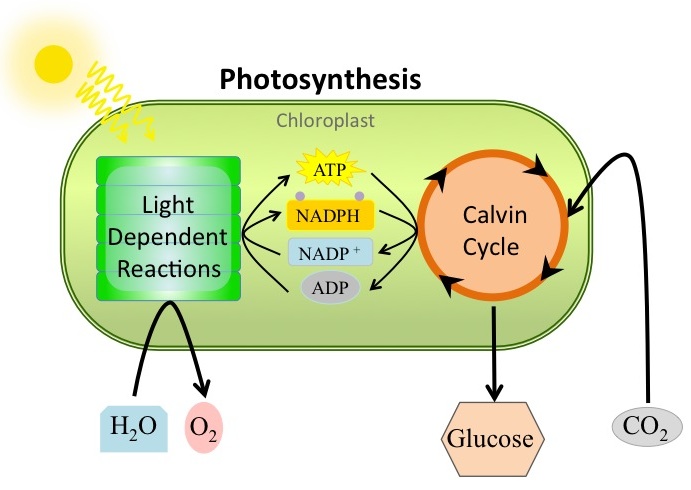
This molecule, which stores energy for later use, is the main product of photosynthesis and the main reactant of cellular respiration
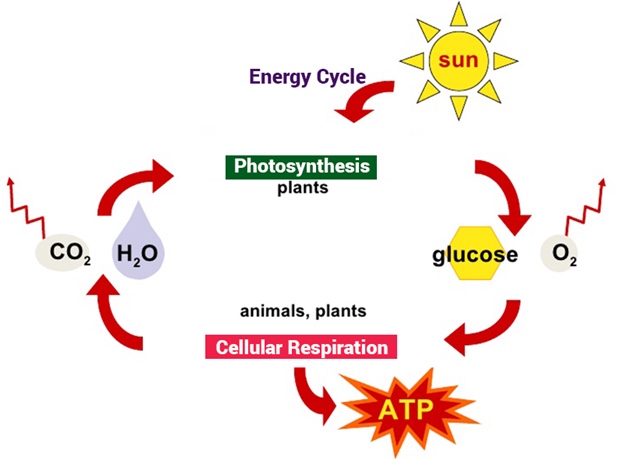 What is glucose?
What is glucose?
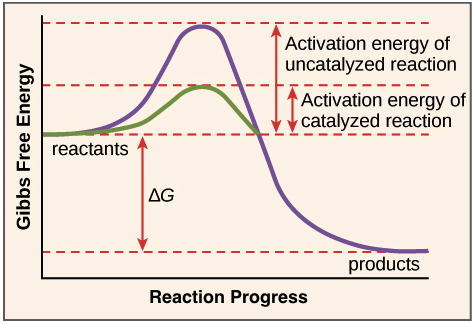
Enzymes act as a catalyst by lowering this
What is activation energy?
These types of organisms are able to store their own energy in the form of sugar by using sunlight and carbon dioxide
What are autotrophs?

These membrane-embedded proteins are responsible for absorbing sunlight and transforming it into energy in the form of excited electrons
What are photosystems (I & II)?

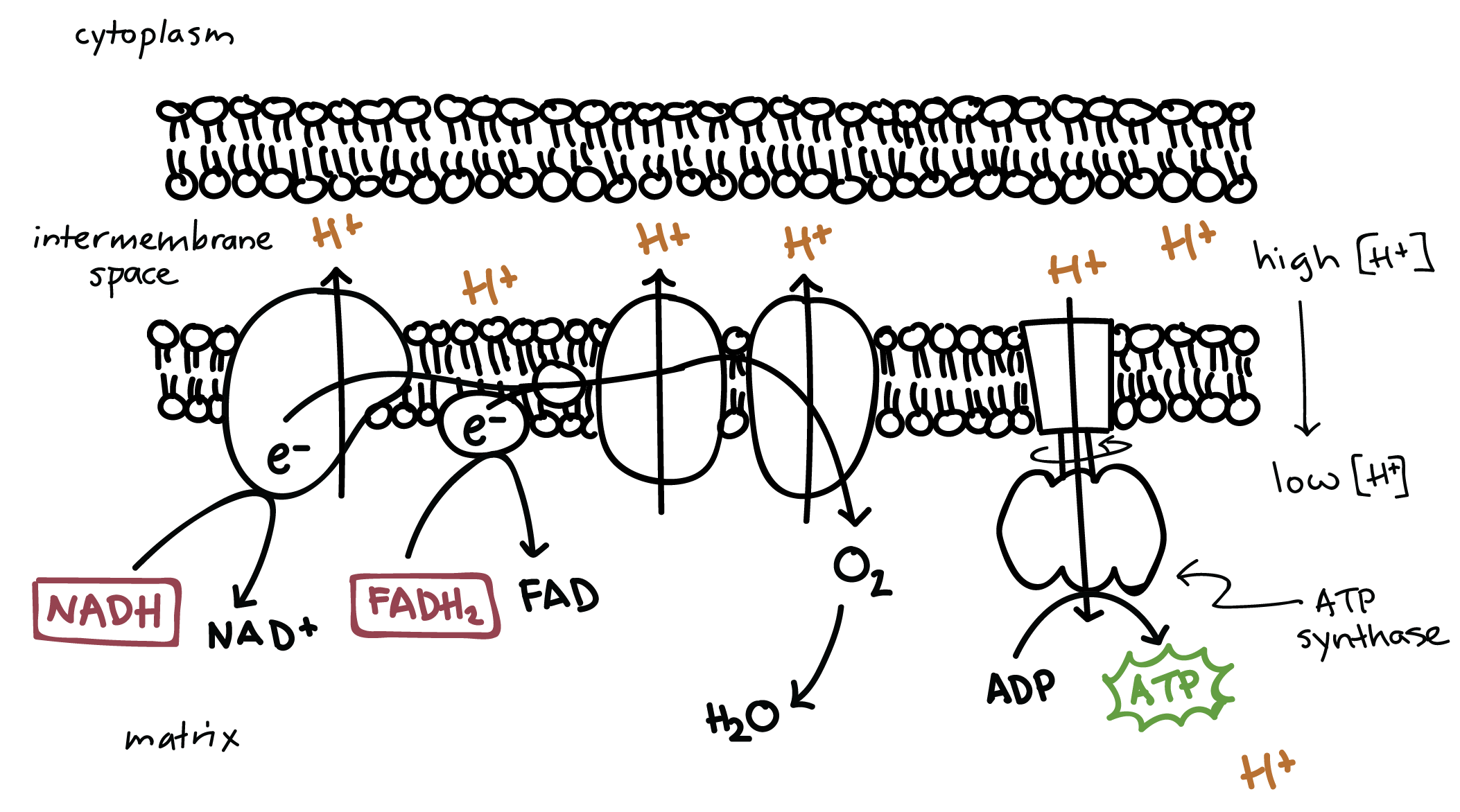
This is the only process in cellular respiration that does NOT occur in the mitochondrion
What is glycolysis? 
The movement of this molecule across the inner mitochondrial membrane via passive transport powers the creation of ATP
What are hydrogen ions?
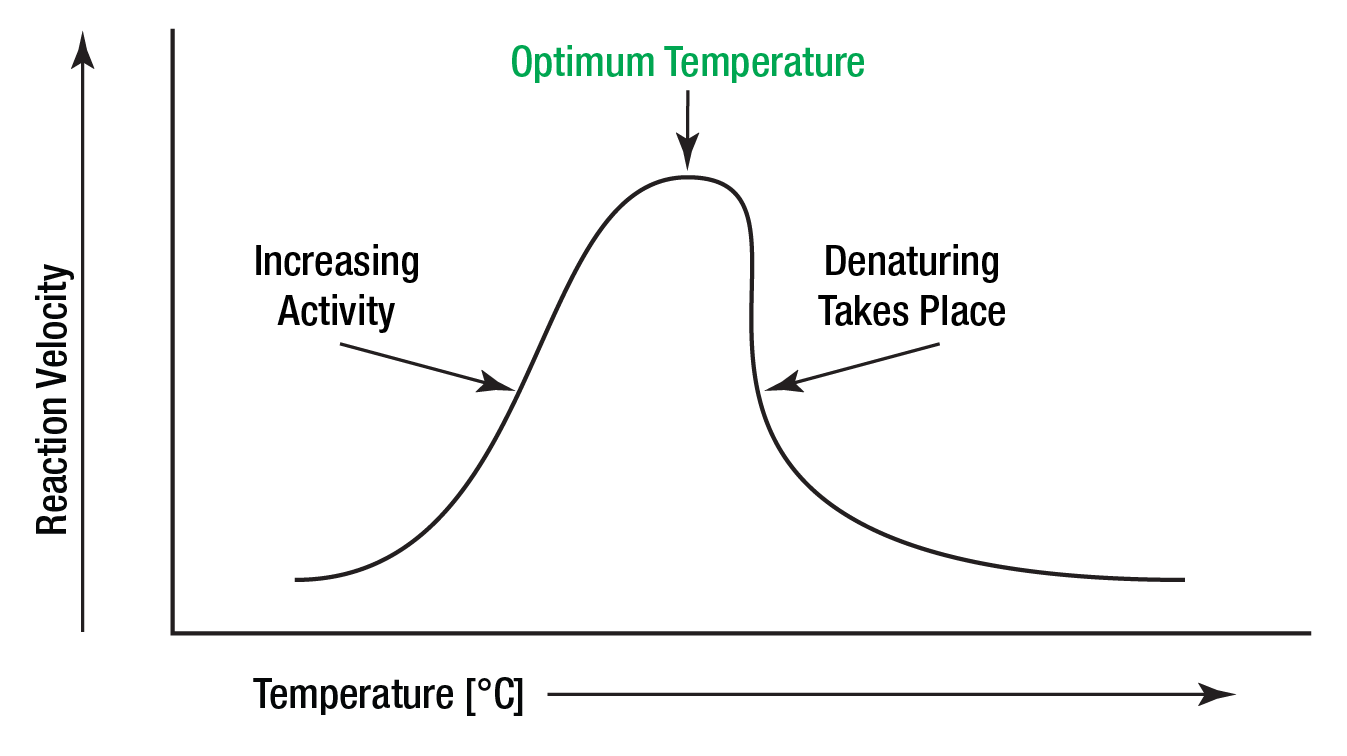
The amount of heat in the environment that allows an enzyme to have the highest rate of function
What is the optimal temperature?
The combination of all chemical reactions, both synthesis and digestion, in an organism
What is metabolism?

This molecule provides the electrons to move through the electron transport chain during the light-dependent reaction
What is water (H2O)?
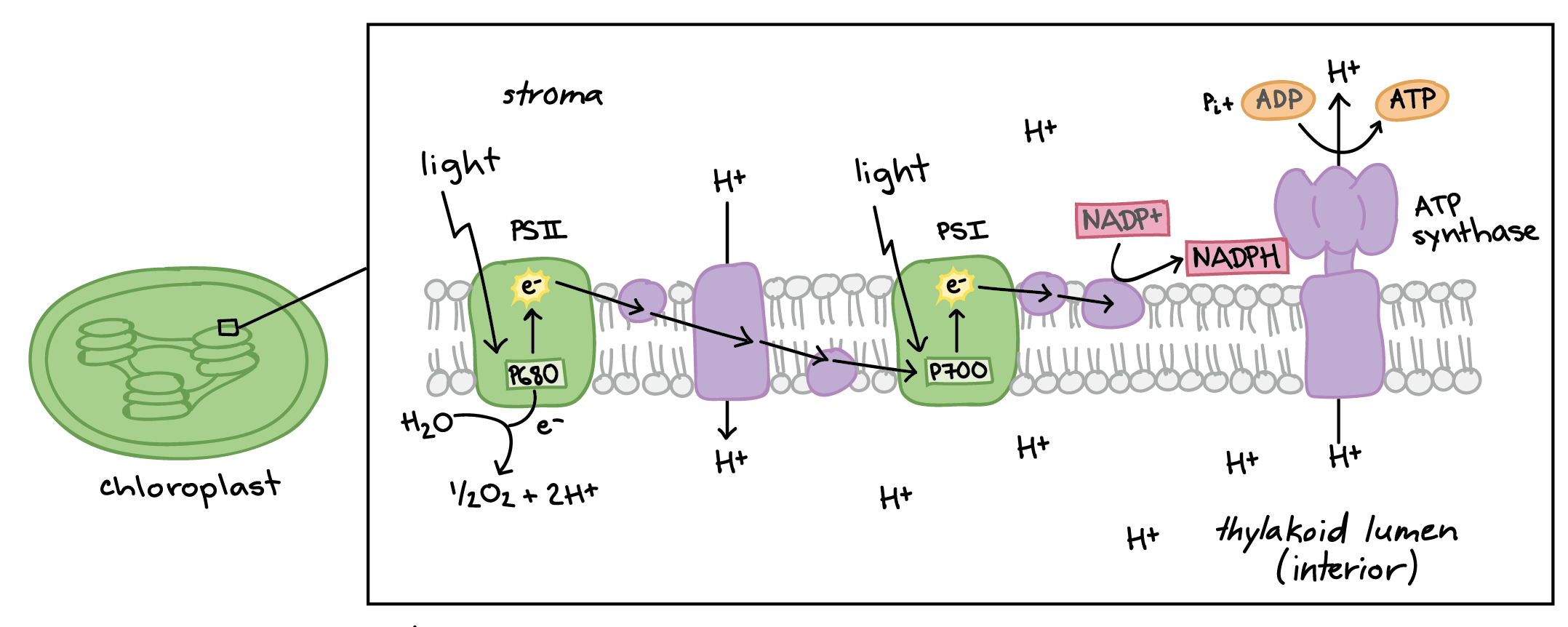
The enzyme that is responsible for the creation of ATP at the end of the electron transport chain
What is ATP synthase?
Along with ATP, this molecule carries energy from excited electrons in the light-dependent reaction to be used to create glucose in the light-independent reaction
What is NADPH (NADP+)?
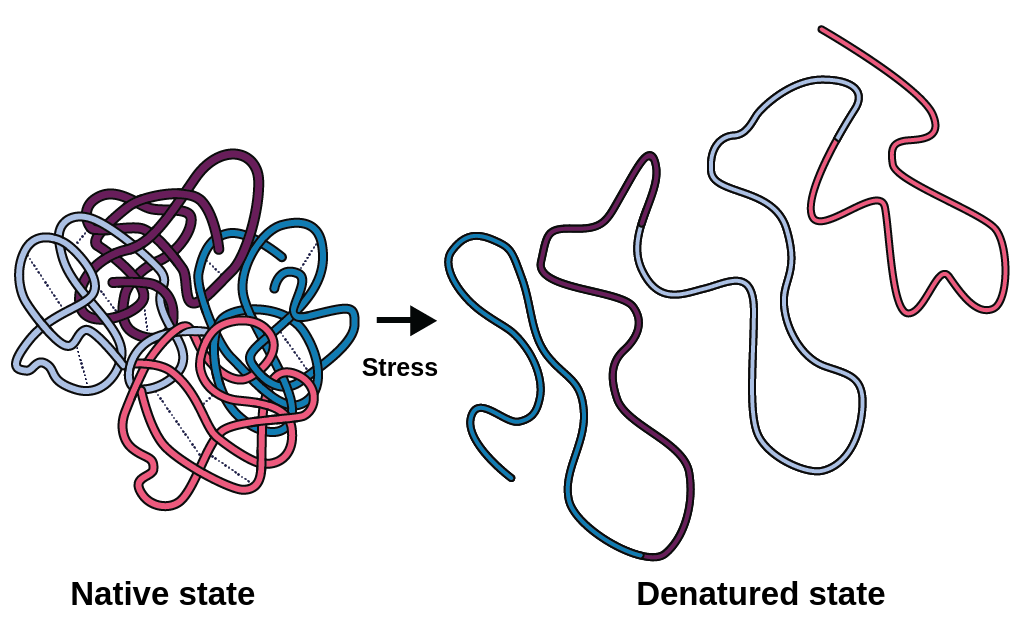
When an enzyme becomes less active (or inactive) due to the tertiary protein structure becoming unfolded
What is denaturation?

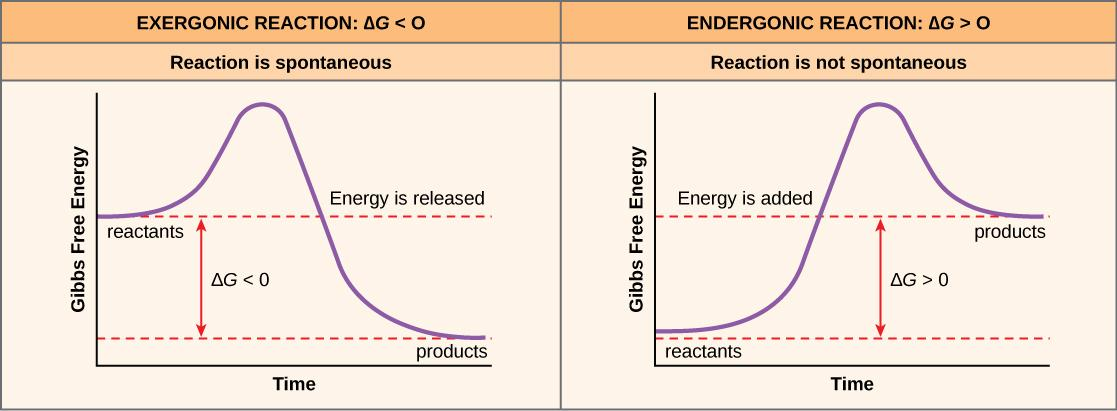
This type of reaction requires the input of energy
What is an endergonic reaction?
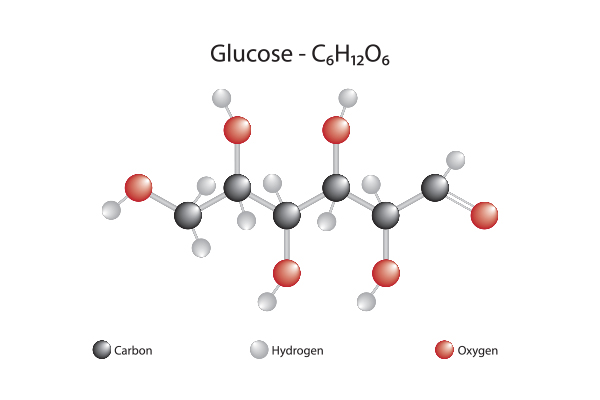
This is the chemical formula for the carbohydrate which stores energy in cells
What is C6H12O6?
The step in cellular respiration in which carbon dioxide is released as a waste product
What is the Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid cycle)?

This molecule is the final electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration
What is oxygen?
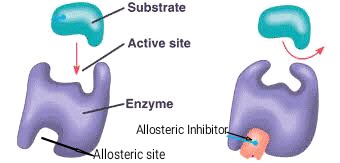
A molecule which does not bond to the active site of an enzyme but can still alter the shape of the active site by binding elsewhere on the molecule
What is a non-competitive inhibitor (allosteric inhibitor)?
The area in the molecule ATP where the majority of useable energy is stored
What is the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups?
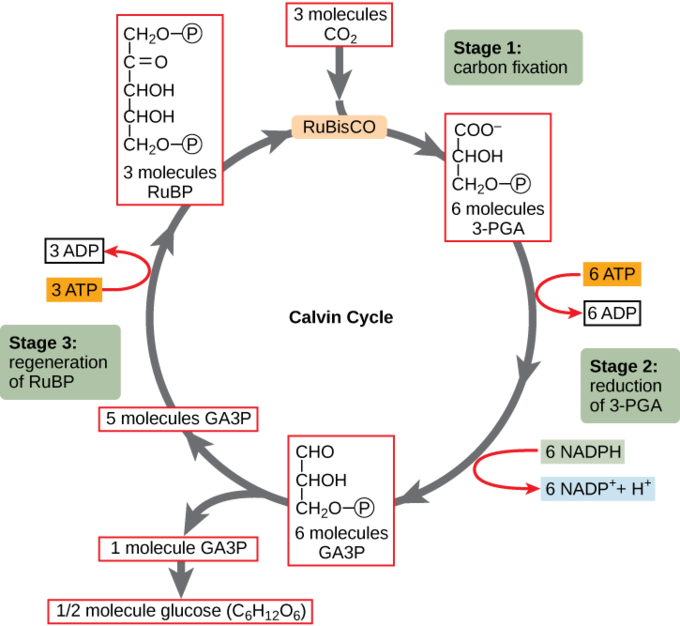
This enzyme takes carbon dioxide to a form of carbon that can be used by cells in the process known as carbon fixation
What is RuBisCO?
These two molecules are the electron carriers which transport energy from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle to the electron transport chain
What is NADH and FADH2?
These two molecules are the possible products of the different types of anaerobic respiration
What are lactic acid and ethanol(alcohol)?

