The formula for cellular respiration is
What is Glucose + Oxygen + Water ---> 36 ATP, Carbon Dioxide and Water.
Homeostasis is defined as
What is the state of internal stability.
A stimulus in a feedback look is first received by this type of cell.
What is a neuron?
Anaerobic respiration can be done by these two processes.
What are lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation?
The nervous system is split into two parts, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. This part of the CNS is generally the control center in a feedback loop,
What is the brain?
Cellular respiration occurs in this organelle
What is the mitochondria.
The maintenance of homeostasis fall under this life function
What is regulation?
What is continue and increase?
During fermentation this gas is produced.
What is carbon dioxide?
This type of neuron connects the stimulus to the control center of the brain.
What is a sensory neuron?
Cellular respiration without the presence of oxygen is known as
What is anaerobic respiration
An example of maintaining homeostasis is
what is sweating, shivering blood, vasoconstriction or dilation, healing, hunger etc.
In a negative feedback look the goal is for the stimulus to do this.
What is decrease and stop.
This organism uses alcoholic fermentation to produce ATP.
What is yeast?
This part of the neuron receives chemical signals known as neurotransmitters.

What is 2: dendrites?
The 3 steps in the process of cellular respiration in order of occurrence are
What are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and the Electron transport chain.
When a person cannot regulate their blood sugar it is called
Diabetes
An example of a positive feedback loop is
What is Childbirth and/or healing?
The formula for alcoholic fermentation results in carbon dioxide, 2 ATP, and this.
What is ethanol?
This area, labeled C on the diagram, is the gap chemical signals must cross to reach the next neuron in the chain.

What is synapse?
The step of cellular respiration that produces the greatest amount of ATP is
What is the electron transport chain
Cyanide is a poison disrupts homeostasis by stopping the ETC leading to death because
what is stops production of ATP
A feedback mechanism is comprised of a stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector. Arranged in a loop, they should look like this.
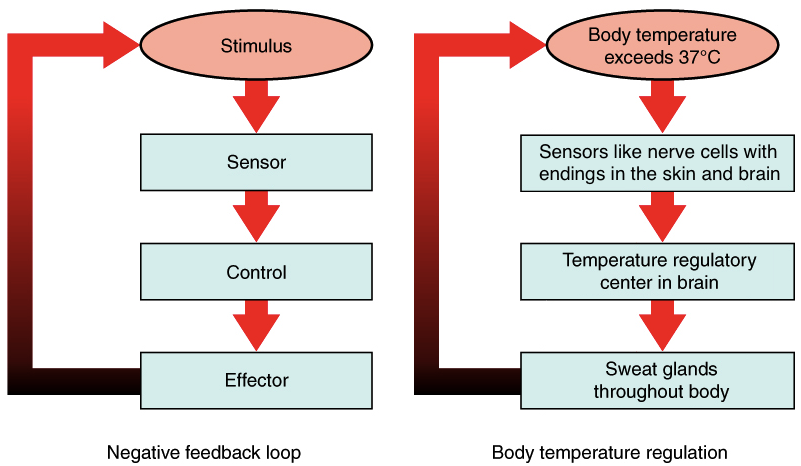
Without oxygen present humans will do this type of respiration.
What is lactic acid fermentation?
Three types of neurons are
Sensory, motor, and interneurons.