Olfactory receptors are examples of
chemoreceptors
If you enter a room and smell a strong odor, but shortly there after, the smell fades away, this is called
Sensory adaptation
What is the function of the auricle?
Collects sound waves
Which part of the inner ear functions in hearing
The cochlea + vestibule
Name the SPECIAL senses (4) and their location
Smell/ Taste/ Hearing/ Sight
IN THE HEAD
The mechanoreceptors of the ear (hair cells) are located where?
Organ of Corti
How are the senses of taste and smell related?
Smell and taste function together.
75-80% of flavor is actually the sense of smell
What is the function of the tympanic membrane?
Opaque thin tissue that vibrates in response to sound waves
Which part of the inner ear functions in equilibrium
The Semi-circular canals + vestibule
The tympanic reflex is designed to do what?
Protect hearing from loud sounds by transmitting the sound LESS EFFECTIVELY to the inner ear
Describe Conductive hearing loss
-Name a possible cause
-Name a possible treatment
Sound is not transmitted efficiently through the outer or middle ear
- Ear infections/ Perforated eardrum/ tumors/ Impacted earwax/ Deformation of outer or middle ear
- Hearing aides
What is the main function of the auditory tube?
Mains equal pressure on each side of the tympanic membrane.
Describe Static equilibrium
-Include location of hair cells and what makes the hair cells move
1. Senses the position of the head, maintaining stability and posture when STILL
2. Hair cells located in vestibule
3. Hair cells move due to gravity when head moves
What is the proper order of vibrations through the MIDDLE ear?
Malleus-->
Incus-->
Stapes
Describe sensorineural deafness
Name a possible cause
Name a possible treatment
SNHL occurs due to damage of the cochlea or to the vestibulocochlear nerve
- Illnesses/ Drugs/ Aging/ Head trauma/ Exposure to loud sounds
-Cochlear implants are a common treatment
Describe Dynamic equilibrium
-Include location of hair cells and what makes the hair cells move
1. Detects motions when your head/body suddenly move allowing you to maintain balance while in MOTION
2. Hair cells are located in semicircular canals
3. Hair cells move when endolymph flows through the semicircular canals
Movement of the hair cells in semicircular canals signals
the direction of the motion of the head
Olfactory receptors are the ONLY neurons that do what two things?
1. Have DIRECT contact with the outside environment
2. Only neurons in the body that are regularly replaced
Name the proper order of operations of the sound vibrations through the inner ear *Hint remember the acronym

Oval Window -->
Scala Vestibuli-->
Vestibular Membrane-->
Cochlear Duct-->
Basilar Membrane-->
Organ of Corti-->
Tectorial Membrane-->
Vestibulocochlear Nerve-->
Scala Tympani-->
Round Window
Why do children have a greater prevalence of ear infections than adults? (2)
- Their auditory tubes are SHORTER and more HORIZONTAL
-Short--> bacteria can more easily make its way up the auditory tube to the middle ear from throat
-Horizontal--> makes it difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear, creating a perfect breeding ground for bacteria
You need to be able to name all of the major parts of the outer, middle and inner ear
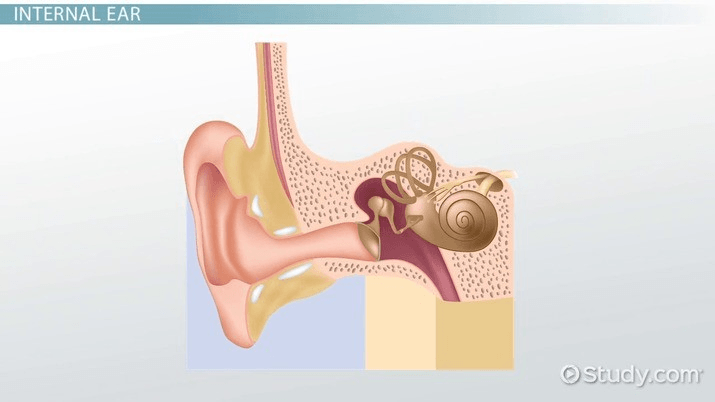
External ear: Auricle/ External Acoustic Meatus/ Tympanic membrane
Middle ear: Malleus/ Incus/ Stapes
Inner ear: Oval window/ Semicircular canals/ cochlea/ vestibulocochlear nerve/Round window