What does it mean when an atom is more electronegative than another atom?
The more electronegative atom has a stronger attraction to/pull on electrons.
Is a hydrogen bond an intramolecular or intermolecular bond? Explain.
A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular bond, meaning that it is a bond that forms between two different molecules. For example, the attraction that forms between the partially positive Hydrogen of one water molecule and the partially negative Oxygen of another water molecule is a hydrogen bond.
What is the name of the monomer, polymer, and bond that is specific to proteins?
Monomer: Amino acid
Polymer: Polypeptide
Bond: Peptide bond
What is the name of the monomer, polymer, and bond that is specific to nucleic acids?
Monomer: nucleotide
Polymer: polynucleotide (DNA and RNA)
Bond: Phosphodiester bond
What is the name of the monomer, polymer, and bond that is specific to carbohydrates?
Monomer: monosaccharide (like glucose)
Polymer: polysaccharide (like starch or glycogen)
Bond: Glycosidic linkage
What is the name of the bond when two atoms share electrons?
Covalent bond
What level of protein structure is it when the R groups (side chains) of different amino acids interact?
Tertiary.

What are the three components of a nucleotide, and where does a phosphodiester bond form between them?
Name examples of storage polysaccharides and structural polysaccharides.
Storage: Starch (plants), and glycogen (animals)
Structural: Cellulose (plants), and chitin (fungi and some animals)
What are valence electrons?
Electrons in the outermost electron shell/orbital. These electrons are the ones that can form bonds.
In the picture below in which water is dissolving a solute, what charge must the black ion in the center of the image have?
Since we know the oxygen (bigger atom in a water molecule) is partially negative, it must be attracted to something that has a positive charge.
How do hydrophilic amino acids behave/fold in a protein? How do hydrophobic amino acids behave in a protein?
Hydrophilic arrange themselves on the outside of the protein (toward water).
Hydrophobic arrange themselves on the inside of the protein (away from water).
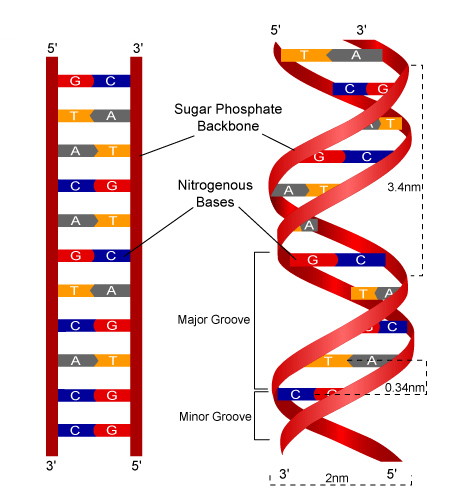
What does antiparallel mean?
The two strands of a DNA double helix run opposite of each other. If one runs 5' at the top to 3' at the bottom, the other runs 3' at the top to 5' at the bottom.
What is unique about the Lipid class of macromolecules?
It is the only group that is classified by a physical property (all lipids are hydrophobic), rather than having a set monomer and polymer.
How many bonds can 1 carbon atom make?
What is cohesion? What kind of bond makes cohesion possible?
Cohesion is the attraction of water molecules to each other. Hydrogen bonds cause cohesion.
What are the 4 parts of an amino acid (besides the central alpha carbon)? Where does the bond form between two amino acids (which 2 parts)?
1. Amino group
2. Hydrogen
3. Carboxyl group
4. R group (side chain)
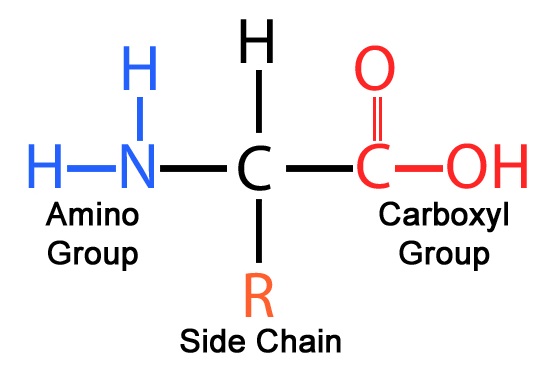
The peptide bond forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
Which bases are purines and which are pyrimidines?
Purines = Adenine, Guanine
Pyrimidines = Cytosine, Thymine (and Uracil in RNA)
What are the three types of lipids we learned about?
Fats (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids (like cholesterol).
What is the difference between a polar and a nonpolar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is when two atoms share electrons UNEVENLY (because of a difference in electronegativity). A nonpolar covalent bond is when two atoms share electrons EVENLY.
In a water molecule, which atom(s) is more electronegative? Does this atom then have a partial positive or partial negative charge?
The oxygen is more electronegative, which gives it a partial negative charge.
This difference in electronegativity makes the covalent bond within a water molecule polar.
What is it called when a protein loses its shape due to unfavorable conditions and can no longer function properly?
Denaturing (denaturation)
DNA: double stranded, sugar=deoxyribose, ATCG
RNA: single stranded, sugar=ribose, AUCG
Name each of the following with both its macromolecule group (nucleic acid, protein, carbohydrate, or lipid) and the specific name of the monomer or polymer.
a.
b.
A. carbohydrate, disaccharide
B. protein, polypeptide