What is the frequency, in Hz, associated with a wavelength of 3.7m?
8.1 x 107 Hz
What is the relationship between wavelength and energy?
Inverse relationship
What do n, l, ml and ms stand for in terms of quantum numbers?
n = principal quantum number
l = angular quantum number
ml = magnetic quantum number
ms = spin quantum number
How many particles are in 1.50 moles of CO₂?
9.03×1023 molecules CO₂
What is the atomic trend of each:
Atomic Size
Ionization Energy
Electron Affinity
Atomic Size: Increases down and decreases across
Ionization Energy: Decreases down and increases across
Electron Affinity:Decreases down and increases across
What is the wavelength, in nm, of a frequency of 375 Hz?
8 x 1014 nm
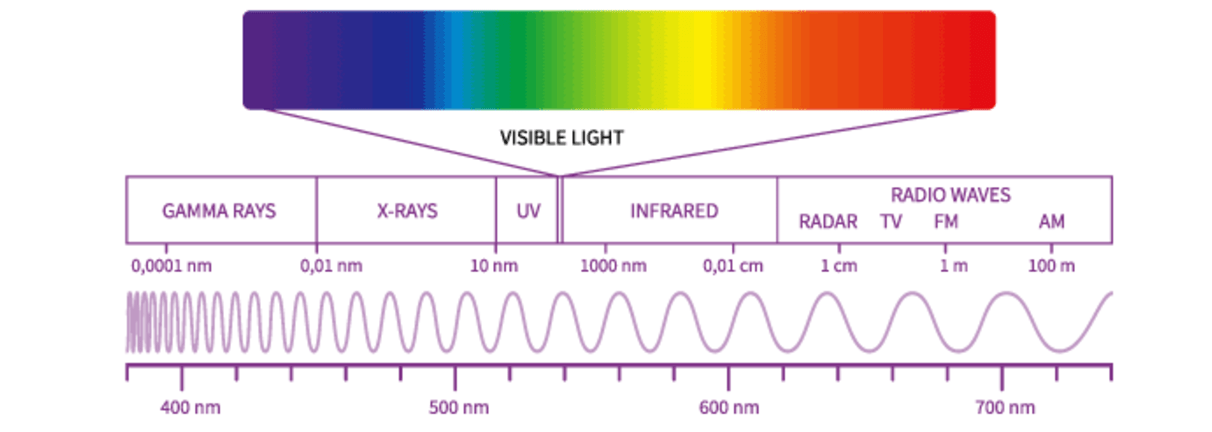
Draw/List the electromagnetic spectrum
Give all possible quantum number sets for electrons in the 2p subshell.
(2,1,−1,±1/2),(2,1,0,±1/2),(2,1,+1,±1/2)
How many grams of calcium are required to produce 5.00 moles of calcium chloride (CaCl₂)?
203.9 g
Arrange the following elements in increasing ionization energy:
Na, Cl, S, Mg
Na < Mg < S < Cl
What is the frequency, in s-1, associated with a wavelength of 227 nm?
1.32 s-1
Is an electron going from n=1 to n=3 an emission or an absorption? Explain in terms of energy.
Absorption. Electrons are gaining energy, so energy must be taken in from the surroundings, meaning it is absorbed.
How many unpaired electrons are in nitrogen (N)?
1s22s22p3 → 3 unpaired
A compound is 70% iron and 30% oxygen by mass. What is its empirical formula?
Fe₂O₃
Rank the following ions by increasing ionic radius, and explain your reasoning:
O²⁻, F⁻, Na⁺, Mg²⁺, and Al³⁺
O²⁻ > F⁻ > Na⁺ > Mg²⁺ > Al³⁺.
What is the wavelength, in m, associated with an energy of 8.7 J?
2.3 x 10-26
The wave property of light allows for what?
Diffraction and constructive interferenace
Can two electrons in the same atom have identical three quantum numbers but opposite spins? Explain using the Pauli Exclusion Principle.
Yes. Two electrons can share n,l, and ml (same orbital) only if ms differs; Pauli forbids all four being identical.
If 10.0 g of aluminum reacts with excess oxygen, how many moles of Al₂O₃ will form?
0.185 mol
Why does fluorine have a higher electron affinity than oxygen, even though both are in the same period?
Both want to complete their p orbitals, but F has a higher nuclear charge.
F’s smaller size → incoming electron feels a stronger attraction.
What is the wavelength, in nm, of a frequency of 865 GHz?
3.46 x 105 nm
Would there be a larger wavelength of light associated with an electron going from n=5 to n=3 or n=2 to n=1?
Electron going from n=5 to n=3
What is the expected electron configuration for the Fe²⁺ ion, and why does it differ from the neutral atom?
[Ar]3d6
Reason: When an atom forms a positive ion, electrons are always removed from the orbital with the highest principal quantum number first, as these are the outermost electrons and thus the most exposed to the influence of the nucleus. For iron, the 4s orbital has a higher principal quantum number than the 3d orbital.
A hydrocarbon sample contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen. When burned, 0.100 moles of it produce 0.400 moles of CO₂. Determine the empirical formula.
CH₂
Why do ionization energy and electron affinity decrease down the periodic table and increase across it?
Ionization energy - The more protons in the nucleus, as you go across, the stronger the attraction of the nucleus to electrons. Makes it harder to remove electrons.
Electron Affinity: Elements are more likely to want to gain an electron to fill out their shells as we go across, so the energy change from that transfer would be higher.