What is the area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone in a child? What is it called in an adult?
Epiphyseal Plate/Line
Muscle tissue has the ability to shorten when adequately stimulated, a characteristic known as ________.
Contractility
The 'metabolic center' of the neuron is known as the
cell body
Describe the difference between the aqueous and vitreous humor
Aqueous Humor - water-like fluid housed in the anterior segment of the eye (supports the lens)
Vitreous Humor - gel-like substance housed in the posterior segment of the eye
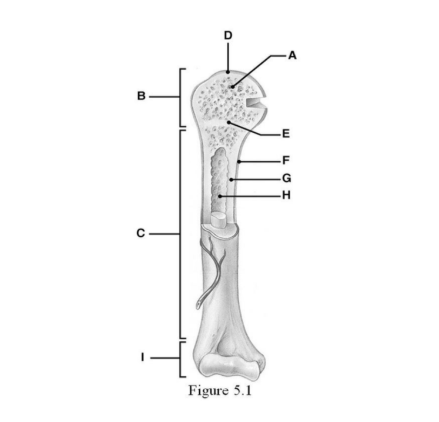
The diaphysis is indicated by ________.
C
Where is fat stored in the long bone?
Yellow marrow
Striated involuntary muscle tissue is classified as ________ muscle.
Cardiac muscle
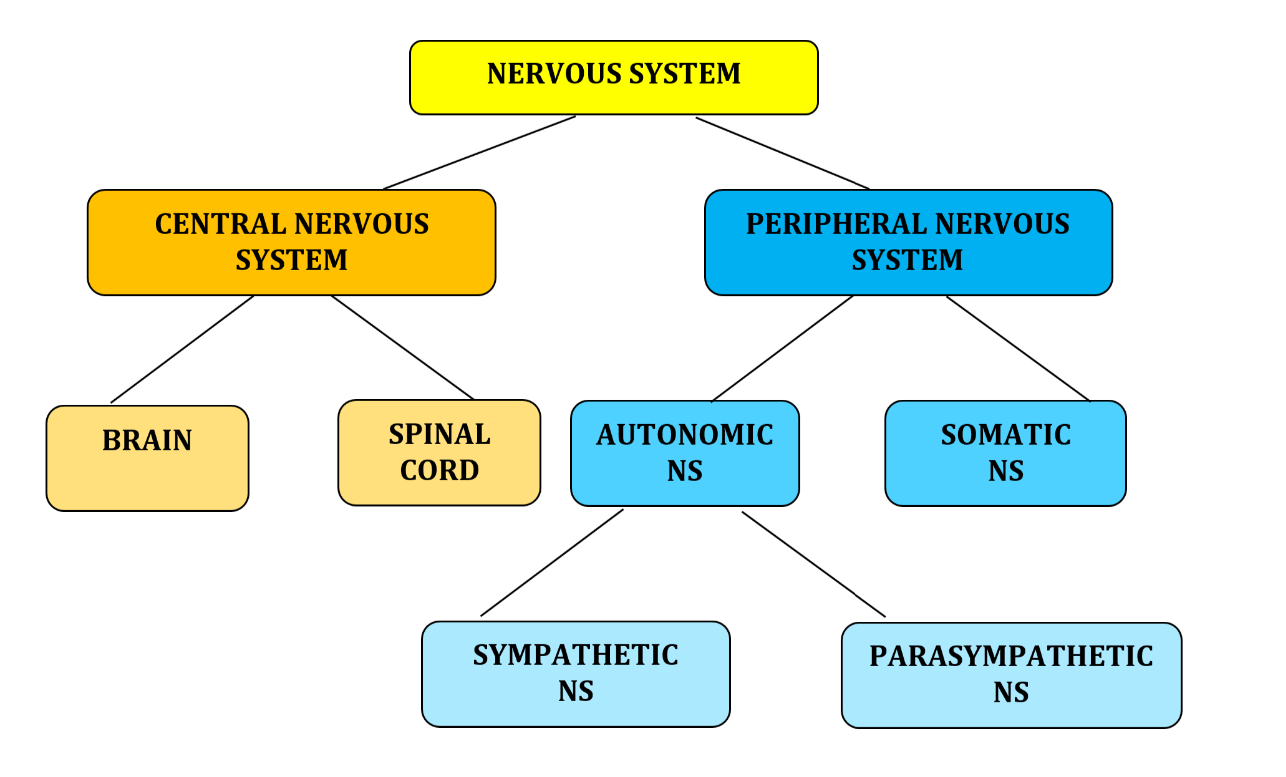
What are the divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system?
Explain how the function of rods and cones differ.
Rods and cones are photoreceptor cells because they respond to light. Rods allow us to see gray tones in dim light, and they provide our peripheral vision. By contrast, cones allow us to see color under bright light conditions. Three varieties of cones are sensitive to particular wavelengths of visible light.
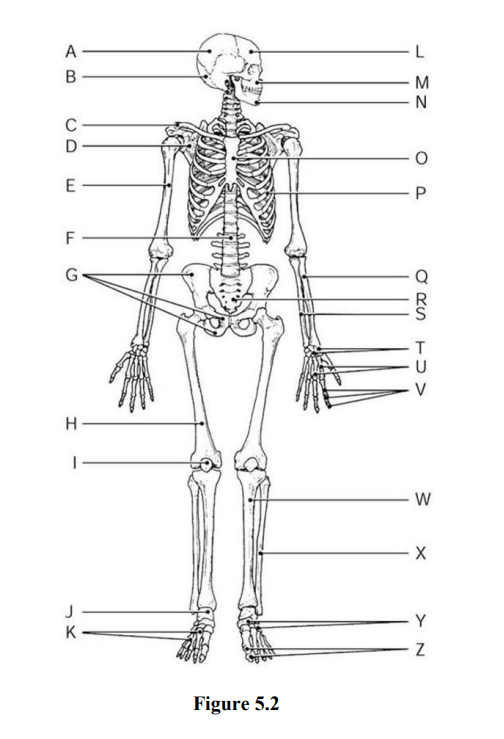
Find the mandible and the maxilla
Maxilla - M
Mandible - N
Where is blood produced in the long bone?
Red bone marrow
One neuron and all the skeletal muscles it stimulates is known as a ________.
Motor Unit
Myelinated fibers (tracts) form ________ matter while unmyelinated fibers form ________ matter.
Myelinated - white
Unmyelinated - gray
True or False:
The ability of the eye to focus on objects closer than 20 feet away is known as accommodation.
True
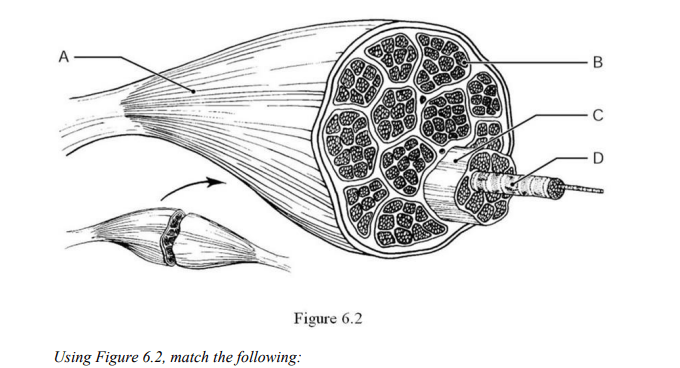
The muscle fiber (cell) is indicated by ________.
B
From superior to inferior, what is the correct order of the vertebrae? How many of each are there?
C-7
T-12
L-5
What is the unstoppable electrical current that travels down the length of the entire surface of a sarcolemma?
Action Potential
What cells form the myelin sheaths around the nerve fibers in the PNS?
Schwann cells
Identify the pathway of vibrations as they travel from one ossicle to the next (bones of the ear)
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
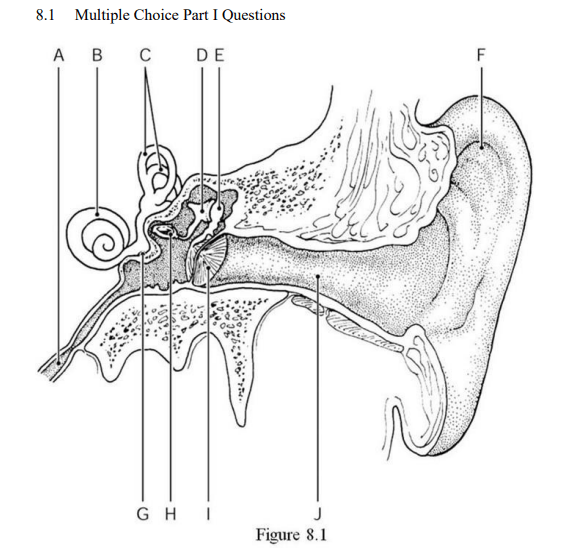
The auricle (pinna) is indicated by ________.
Label F
What type of bone cell is primarily active when bone growth occurs? What type of cells are active for old damaged bone destruction?
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
Which of the following is not a function of the muscular system?
A) Production of movement B) Maintenance of posture C) Stabilization of joints D) Generation of heat E) Blood cell formation
E.) Blood Cell Formation
The gaps between Schwann cells found at regular intervals in peripheral system neurons are called ________.
Nodes of Ranvier
What type of chemoreceptor is responsible for our sense of smell?
A) Static equilibrium receptor B) Olfactory receptor C) Dynamic equilibrium receptor D) Photoreceptor
B) Olfactory receptor
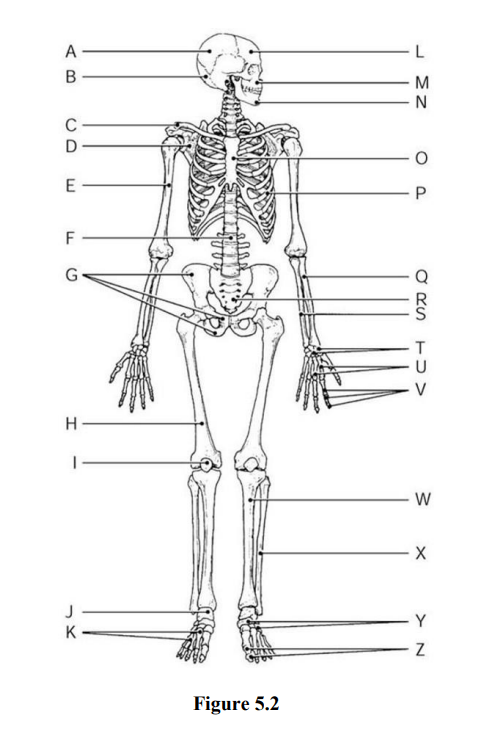
Find the Radius and the Ulna
Radius - Q
Ulna - S
Which type of rib connects directly to the sternum by way of costal cartilage?
Which movement is antagonistic to extension?
Flexion
What is the primary role of the interneuron (association neuron)?
A) Carry information from the central nervous system to muscles and/or the viscera B) Form a lipid-protein (lipoprotein) cell membrane on the outside of axons C) Transmit nerve impulses from the skin and organs to the central nervous system D) Connect motor and sensory neurons in their pathways
D) Connect motor and sensory neurons in their pathways
The small, peglike projections of the tongue's surface are called ________.
Papillae
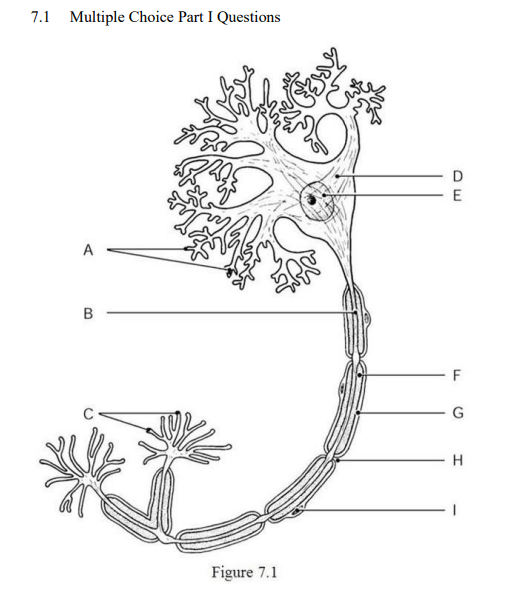
The axon terminals are indicated by ________.
Label C
What bones are involved in the axial skeleton? What bones are involved in the appendicular skeleton?
Your axial skeleton is made up of the bones in your head, neck, back and chest. Your appendicular skeleton is made up of everything else — the bones that attach (append) to your axial skeleton.
The state of continuous partial muscle contractions is known as ________.
Muscle Tone
Name cranial nerve X and its function(s)
Vagus nerve (CN X): Regulating several automatic bodily processes, including your digestion, blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, mood, saliva production and more. It's the main nerve of your parasympathetic nervous system.
The five taste sensations are ________.
sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami
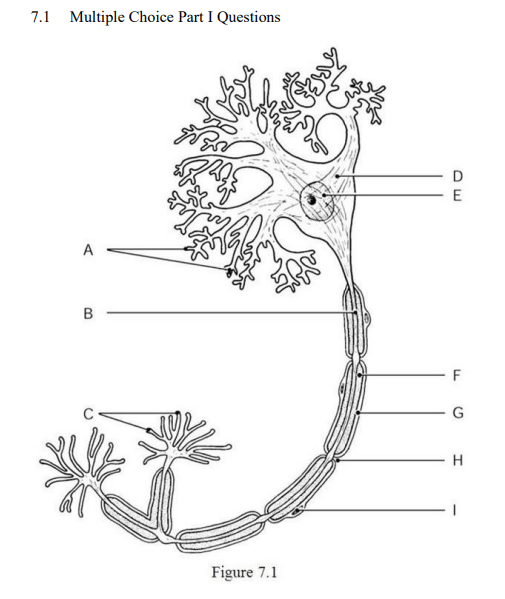
The axon is indicated by ________.
Label B
Name 4 different types of bone fractures and what they look like
Open - through skin
Closed- not through skin
Greenstick - partial bone break (children)
Comminuted - shatter
Spiral - twist
Compression - collapse (usually vertebrae)
True or False: The neurotransmitter used by the nervous system to activate skeletal muscle cells is acetylcholine.
TRUE:
Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the sarcolemma to open sodium channels, which trigger the skeletal muscle to generate an action potential and contract
Mr. Warren has spinal cord damage that prevents nerve impulses from being carried from the CNS to muscles or glands. What specific type of neuron has been damaged?
A) Afferent neurons B) Sensory neuron C) Motor neuron D) Axon terminals
C.) Motor Neuron
What separates the outer ear from the inner ear.
tympanic membrane (ear drum)
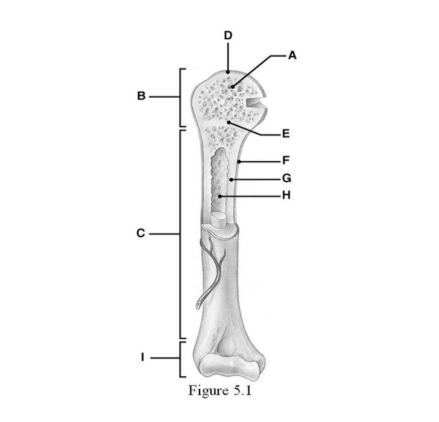
Name B & I
B - proximal epiphysis
I - distal epiphysis