Types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage, Elastic cartilage, and Fibrocartilage
What is four of the bones' function?
Support, Protection, Movement, Blood cell formation, Triglyceride (fat) storage, Hormone production, and Mineral and growth factor storage.
Gross anatomy type?
Compact and spongy bone.
What are the five major cell bone tissue types?
1. Osteogenic cells
2. Osteoblasts
3. Osteocytes
4. Bone-lining cells
5. Osteoclasts
What does Interstitial growth require?
Epiphyseal Cartilage in the Epiphyseal Plate.
Which cartilage provides support, flexibility, and resilience?
Hyaline cartilage 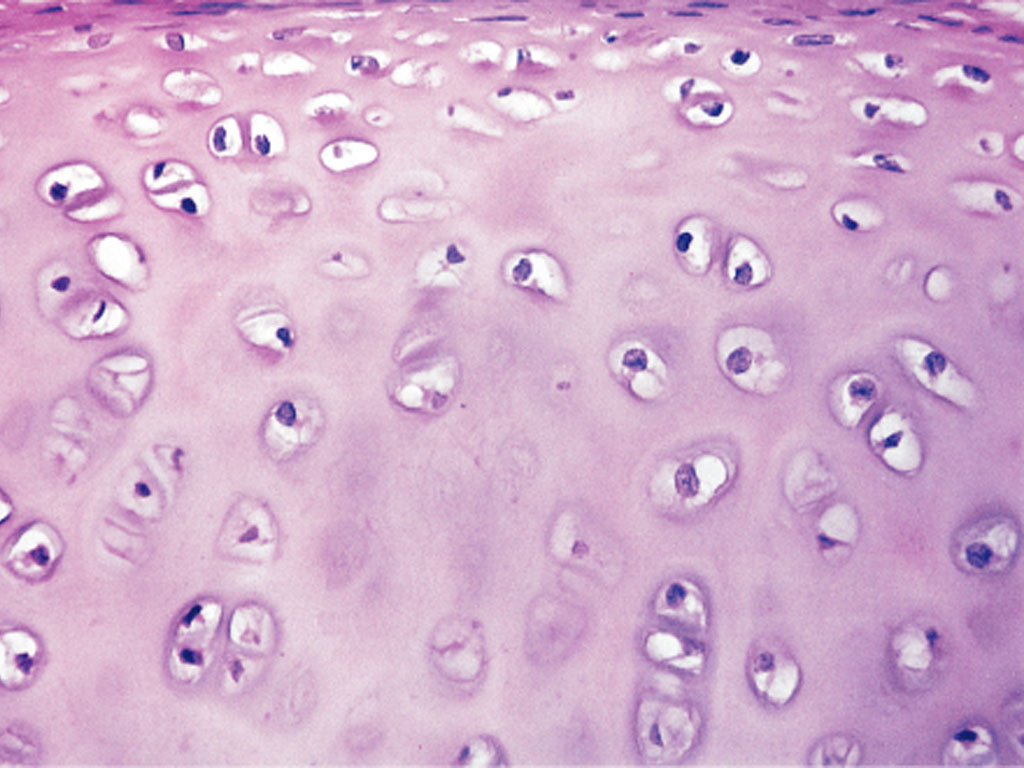
Axial skeleton and Appendicular skeleton: This is because of their location.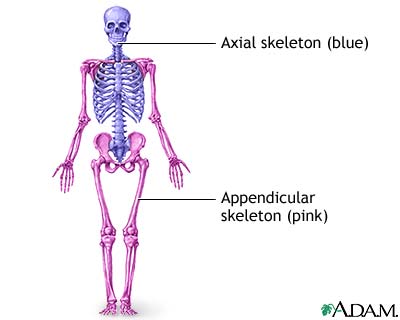
What are the two membranes and give a brief description of the function.
Periosteum: Helps bone growth
Endosteum: Bone development and remodeling of the bone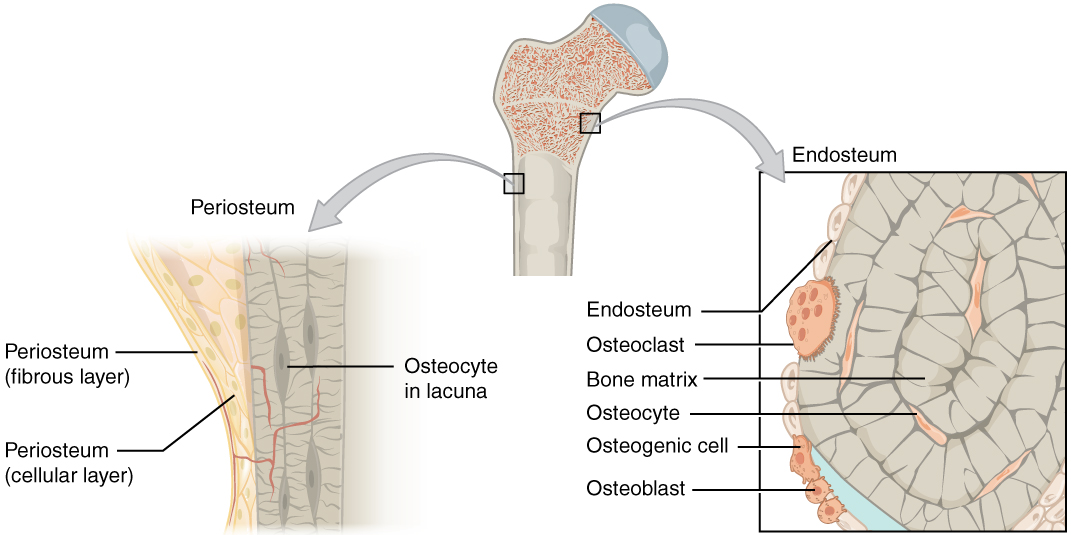
What does the compact bone consist of?
Osteon (Haversian system)
Canals and canaliculi
Interstitial and circumferential lamellae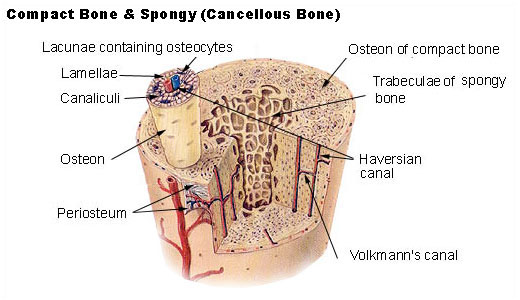
What is the Epiphyseal plate five zones?
1. Resting (quiescent) zone
2. Proliferation (growth) zone
3. Hypertrophic zone
4. Calcification zone
5. Ossification (osteogenic) zone
What is the difference between Appositional growth and Interstitial growth?

Appositional growth is like growing and getting taller, while interstitial is growing to heal bones or internal injuries.
What are the classifications of bones and give an example. (answers may vary)
Long bone: Humerus
Irregular bone: Vertebra
Short bone: Talus
Flat bone: Sternum
What is the structure of long bone and where is it?
Diaphysis and Epiphyses.

What is the spongy bone function?
The spongy bone helps to reduce the weight of bones and helps to transmit forces across joints without damaging the bone.
What are the two hormonal controls and what do they produce?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH): produced by parathyroid glands in response to low blood calcium levels.
Calcitonin: produced by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland in response to high levels of blood calcium levels.

Which cartilage is similar?
Hyaline cartilage and Elastic cartilage
What are the bone structure levels?
Gross, Microscopic, and Chemical
What are the three types of Bone Marking?
Projection: the outward bulge of bone
Depression: bowl- or groove-like cut-outs that can serve as passageways for vessels and nerves, or play a role in joints
Opening: hole or canal in a bone that serves as the passageway for blood vessels and nerves
What organic and inorganic components are found in bones?
Organic components
-Includes osteogenic cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, bone-lining cells,
osteoclasts, and osteoid.
Inorganic components
– Hydroxyapatites (mineral salts).
What are the common types of fractures and describe them?
Comminuted: Bone fragments into three or more pieces.
Compression: Bone is crushed.
Spiral: A ragged break occurs when excessive twisting forces are applied to a bone.
Epiphyseal: Epiphysis separates from the diaphysis along the epiphyseal plate.
Depressed: The broken bone portion is pressed inward.
Greenstick: Bone breaks incompletely, much in the way a green twig breaks. Only one side of the shaft breaks; the other side bends.
Which cartilage is the Larynx?
Hyaline cartilage
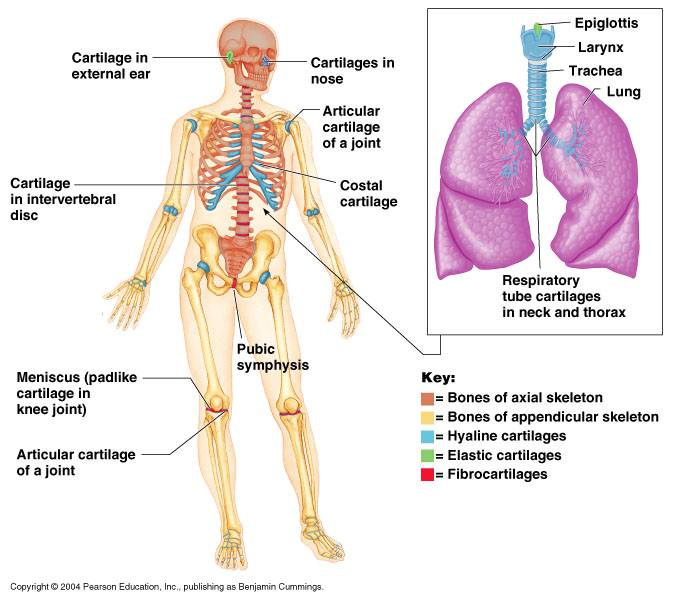
How many bones are named in the body and which group is the rib cage part of?
206 and Axial skeleton
What bone marking is the Femur and Humenus a part of?
Epicondyle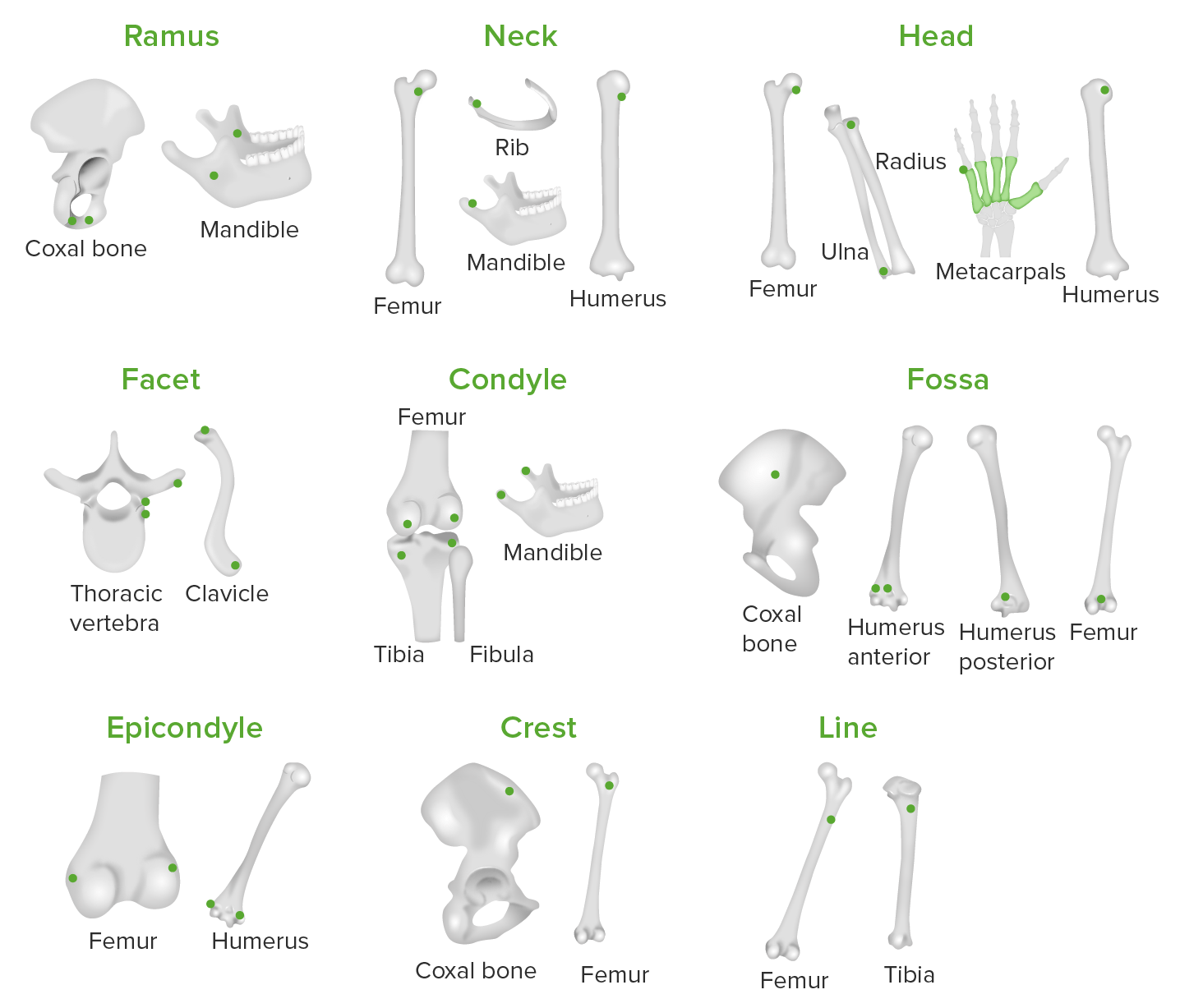
Do inorganic components last after death?
Yes
What are the four major stages of bone repair?
1. Hematoma formation
2. Fibrocartilaginous callus formation
3. Bony callus formation
4. Bone remodeling 