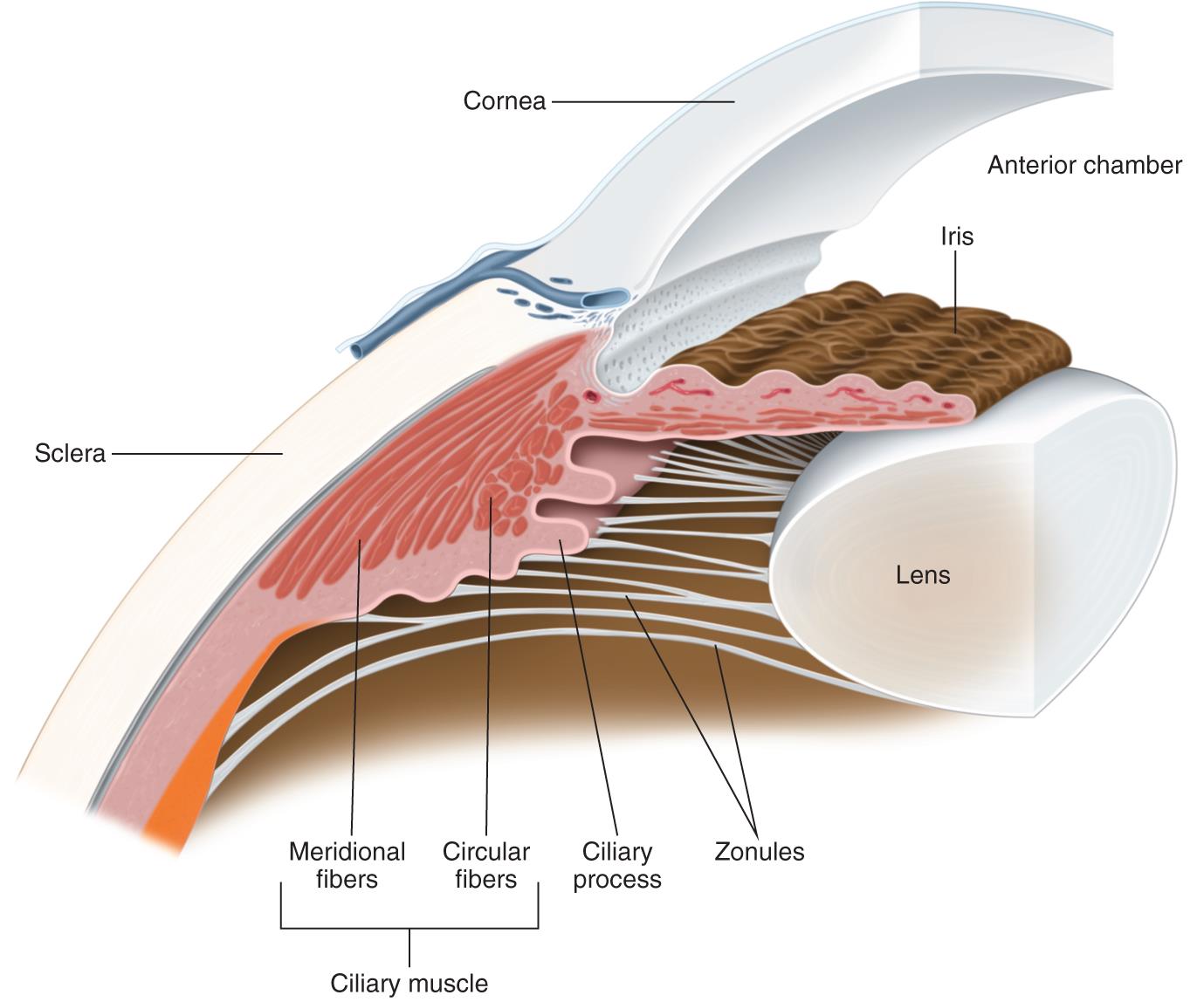
What does the ciliary body have hanging off its ciliary processes and attached to the lens?
ciliary zonules/suspensory ligaments
What is the correct order of the layers of the eye including the retina?
retina-->choroid-->sclera

What type of light do rods detect?
dim light because they are sensitive to bright light

What structure has the primary job of refracting light?
lens

How do the inner segments connect to the cell bodies of rods?
via an outer fiber
Where do we find the most cones in the eye?
fovea centralis
Where are the photoreceptors embedded?
outermost pigmented layer of retina

What happens to rhodopsin when it absorbs light?
It changes from 11-cis to all-trans retinal

What is the position of the image that lands in the primary visual cortex?
upside down mirror image

How do the inner segments connect to the cell bodies of cones?
via a direct connection
What division of the ANS controls the sphincter pupillae muscle?
the parasympathetic division

What part of the neural layer forms the optic nerve?
axons of ganglion cells in the innermost layer of the retina

What ion channels close as a result of light-activated rhodopsin?
cGMP gated Na+ and Ca+ channels

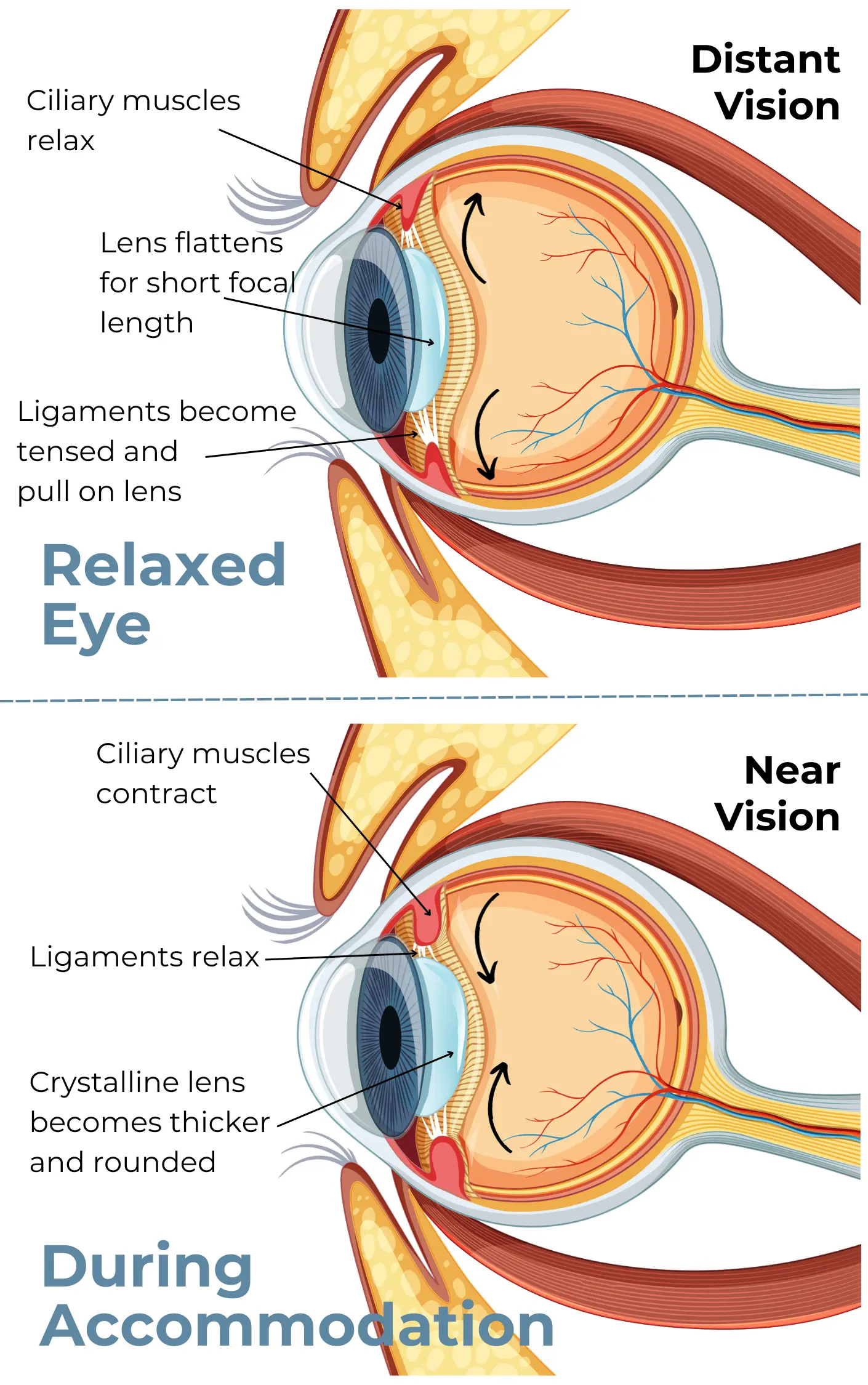
What is the purpose of accommodation?
when the lens becomes more convex/"chubby" to increase refractory power.
How are we able to perceive a variety of colors?
blending of photoreceptor stimulus

what supports the shape and structure of the eye?
vitreous humor
What wavelengths do cones respond to?
Red, blue, and green; each cone is specific to one wavelength

What G-protein is activated by rhodopsin during phototransduction?
Transducin

What are some other adjustments besides accommodation of the lens?
pupil constriction and medial convergence

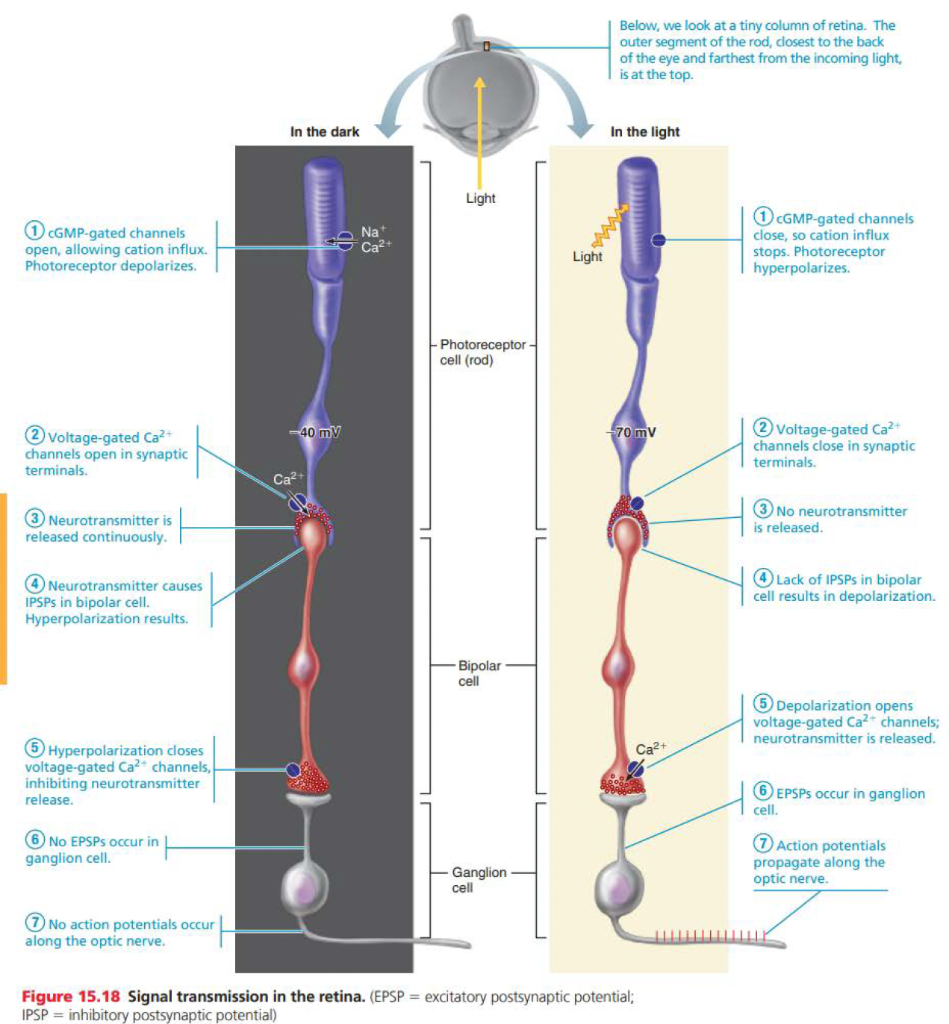
in the dark, rods release _______ onto___________
glutamate onto bipolar cells

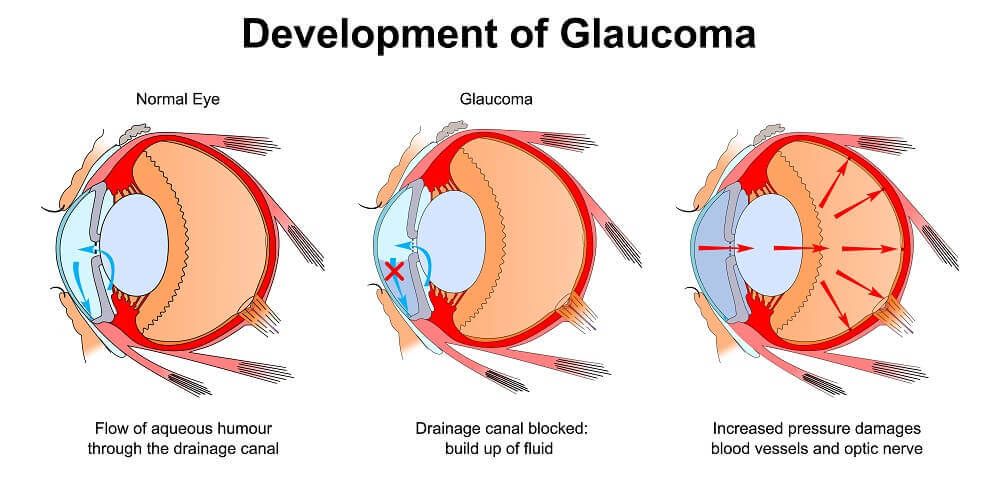
What causes the increase of intraocular pressure in glaucoma?
Aqueous humor flowing out of the anterior chamber back into the posterior segment
How many bipolar cells are cones connected to?
only one which is what gives them such visual acuity (area being stimulated is more specific)

Under what conditions are rods hyperpolarized v, depolarized?
Hyperpolarized in light conditions v depolarized in dark conditions

How is accommodation physically achieved?
the ciliary muscle contracts and tension on the zonules decreases.

stimulation of bipolar cells lead to what?
inhibitory post synaptic potential