What is the geometry of the carbon in CH4?
Tetrahedral
What is the hybridization around the carbon in CH4?
2sp3
Rank in electronegativity:
Cs, Br, Se, Hg
Br > Se > Hg > Cs
How do electronegativity values help us determine the polarity of a bond?
the higher electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms suggests a more polar bond.
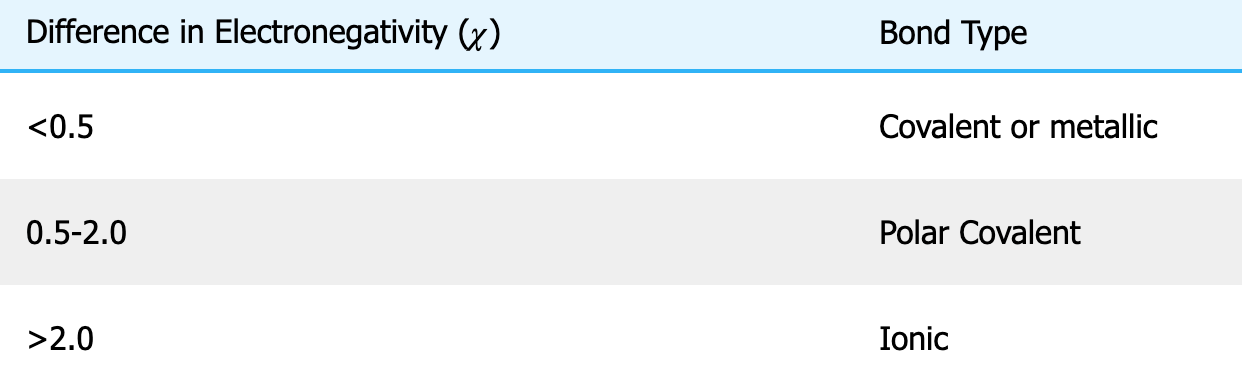
In the best Lewis structure of SO42-
there are ___ pi bonds and the formal charge on sulfur is ___
A) 4, -2
B) 2, 0
C) 0, +2
D) 2, -1
E) 4, 0
B) 2, 0
What is the geometry of the Oxygen in CH3CH3CH2OH? What is the shape?
Geometry: Tetrahedral
Shape: Bent
What is the hybridization around each carbon C2H4?
2sp2
Which lattice energy is greater?
NaF or NaCl
NaF
remember magnitude + charge: the energy of the attraction decreases with distance.
A higher charge increases the force
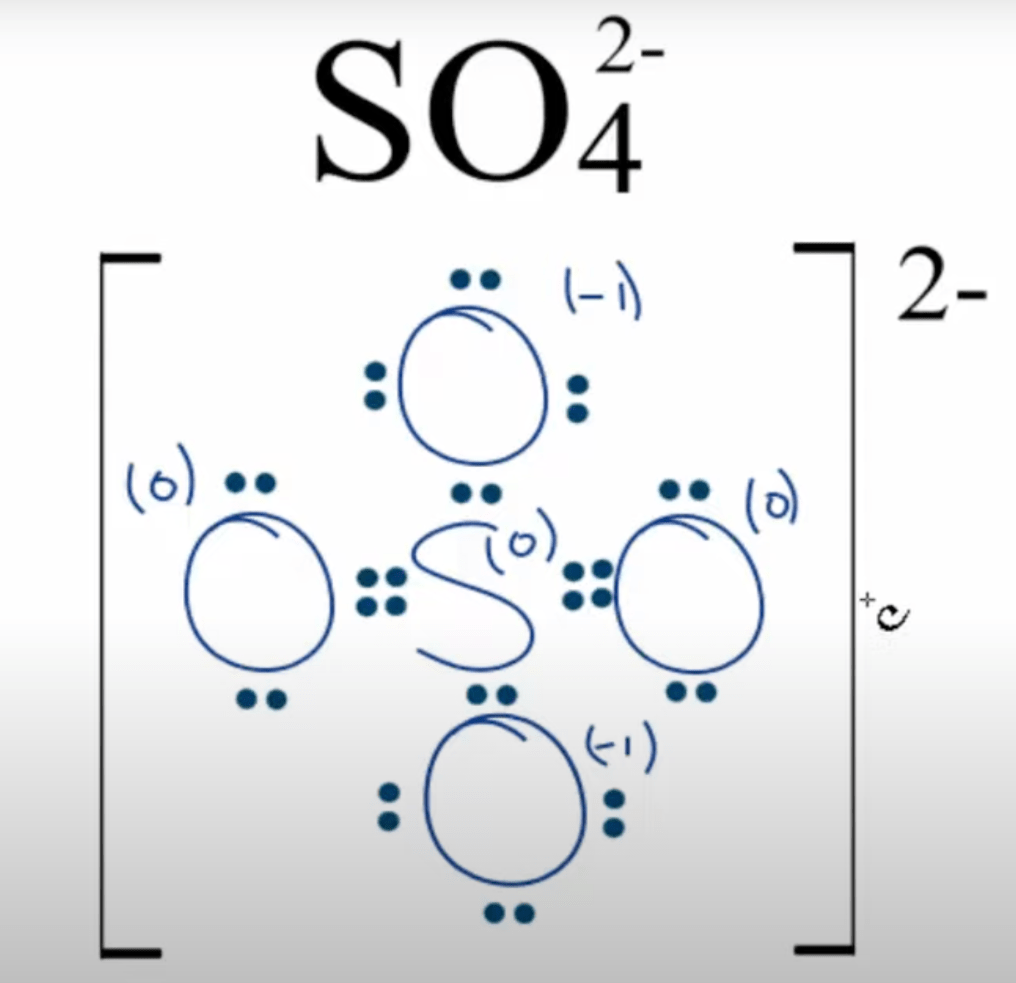
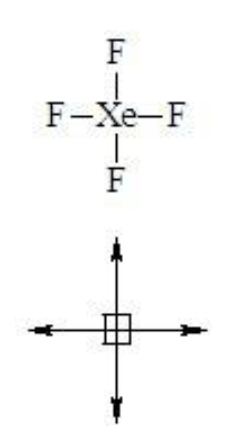
Which of the following is a polar compound: draw the structure and all dipoles including the net dipole moment
XeF4
SF4
SF4 = polar!
XeF4 = non polar compound, remember it still has polar bonds however, no net dipole making it non-polar
Rank the following regarding bond length: (longest to shortest)
NO2+, NO3-, NO+
NO3- > NO2+ > NO+
What is the geometry and ideal bond angle of NF3?
Geometry: Tetrahedral
Ideal Bond angle: 109.5°
What orbital do lone pairs reside in?
p-orbital
Which compound will have the higher melting point:
MgO or NaI
MgO = greater lattice energy = higher melting point
NaI = lower lattice energy
remember: need to overcome lattice energy, the more you have the more energy you need to overcome giving rise to a higher melting point
You are conducting a reaction in the laboratory and require a solvent that exhibits nonpolar characteristics to facilitate the process. Which molecule would be the most suitable choice for a nonpolar solvent?
HCN
NI3
CS2
COF2
CS2
Why: it is a linear molecule
determine the enthalpy of the reaction:
C2H4(g)+Cl2(g)→C2H3Cl(l)+HCl(g)
C-H = 413 kJ/mol, H-H 432 kJ/mol
Cl-Cl 243 kJ/mol, C-C 347 kJ/mol
C=C 614 kJ/mol, H-Cl 427 kJ/mol,
C-Cl 339 kJ/mol
(broken - formed) *remember to balance the equation
= -110 kJ/mol
What is the geometry and ideal bond angle of SF6?
Geometry: Octahedral
Ideal Bond Angle: 90°
How many pi bonds and how many sigma bonds are in benzene? (C6H6)
Sigma: 12
Pi:3
Which compound will have the highest melting point:
KCl, KF, CaF2 or CaCl2
CaF2
K+ Cl-, K+ F-
Ca2+ F-, Ca2+ Cl-
Why: Lattice energy is dependent on size + magnitude 
Which compound has the highest ΔEN, what does this mean?
H3CLi, H3CMgBr, H3CZn
C = 2.6
Mg = 1.3
Li = 1.0
Zn = 1.7
H3CLi ΔEN = 1.6 highest!
H3CMgBr ΔEN = 1.3
H3CZn ΔEN = 0.9
range ΔEN 0.5-2.0 = Polar Covalent
Draw the molecular orbital for CN-
is CN paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
diamagnetic
What is the shape of CH3- and angle between 2 hydrogens in CH3-?
Shape: Tetrahedral
Angle: <109.5°
Draw C2H2 using the molecular orbital theory we have learned. Then identify the number of pi and sigma bonds present.
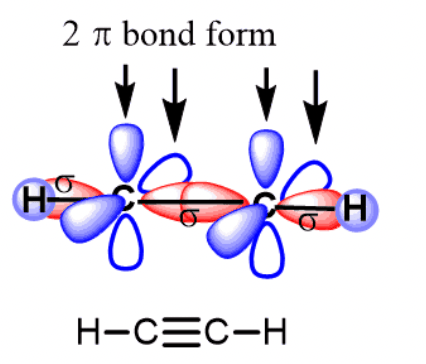
Pi:2
Sigma:3
Which compound has the strongest bond?
CO2, H2O, N2
N2, Triple bond! (shortest & strongest)
The carbon-hydrogen bonds in benzene result from the overlap of:
a. sp2 hybrid orbital of carbon and sp hybrid orbital of hydrogen
b. sp2 hybrid orbital of carbon and sp2 hybrid orbital of hydrogen
c. sp2 hybrid orbital of carbon and 1s atomic orbital of hydrogen
c. sp2 hybrid orbital of carbon and 1s atomic orbital of hydrogen