-What is bias?
-When a method systematically favors one outcome over another.
-Anything that affects the actual truth.
-What is the difference between a population and a sample?
-population: an entire group of individuals
-sample: a subset of individuals in the population
-What is an experiment?
-Experiment: It deliberately imposes some treatment on individuals to measure their responses.
-What are the steps to a well designed experiment?
1.Comparison
2. Random assignment
3. Control
4. Replication
-What is a census?
-Census: Collects data from every individual in the population.
-Is the following prompt an example of interviewer bias?
- The interviewer (who has multi-colored hair.) come up to you and explains that he's conducting a survey on hair color and trust. He asks you do you trust people with multi-colored hair? You responded yes.
- Yes, it's an example of interviewer bias.
-With the interviewer having multi-colored hair it forces the interviewee to give a non-truthful response.
-What two types of sampling can lead to bias?
-Convenience sampling: This sampling chooses individuals who are easiest to reach
-Voluntary response sampling: individuals choose to join the sample in response to an open invitation.
-What is the difference between an observational study and an experiment?
-Observational study: observes individuals and measures variables of interest but does not attempt to influence the responses.
-Experiment: It deliberately imposes some treatment on individuals to measure their responses.
-What experimental design does this represent?
-Completely randomized design.
-What is lack of realism?
-Lack of realism: can limit our ability to apply the conclusions of an experiment to the settings of greatest interest.
-What is wording bias?
-Wording that can affect a person's answer.
-What is a simple random sample and what ways can you do and SRS?
- An SRS gives every possible sample of a given size the same chance to be chosen.
- Table D of random digits, technology, slips of paper.
-What is the difference between lurking variable and confounding variable?
-Lurking variable: influencing a response that is unknown.
-Confounding variable: occurs when two variable are associated in such a way that their effects on a response variable cannot be distinguished from each other.
-What type of experimental design does the image show?

-Randomized Block design
-What does it mean for something to be statistically significant?
-Statistically significant: An observed effect so large that it would rarely occur by chance.
-What is the difference between under-coverage bias and non-response?
-Under-coverage: left an entire group of people out.
-Non-response: person chose not to respond.
-What is a stratified random sample and what is strata?
-Stratified random sample: start by classifying the population into groups of similar individuals called strata. Then choose a separate SRS in each stratum and combine these SRS's to form the sample.
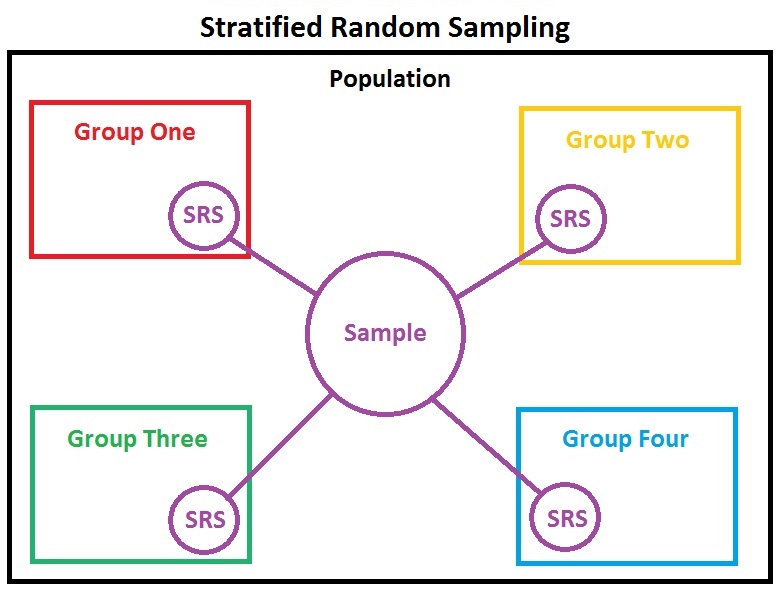
-Fill in the blank.....
-The experimental unit get's the ________, while the control group usually gets the __________.
-The experimental unit get's the treatment, while the control group usually gets the placebo.
What type of experimental design does the diagram show?
-Matched pairs design
-What is a factor and a level?
-Factor: The treatment(s)
-Level: Different levels of the treatments
Have two out of the three members in your group perform a bias given to you and the third group member will guess the bias being performed.
-Wording bias/ interviewer bias
-What is a cluster sample and clusters?
-To get a cluster sample, start by classifying the population into groups of individuals that are located near each, called clusters. Then choose an SRS of the clusters. All individuals in the chosen clusters are included in the sample.

-What the difference between a double-blind experiment and a single-blind experiment.
-Double-blind: Neither the researchers or the subjects know who gets the treatment or the placebo.
-Single-blind: The subjects don't know whether they receive the placebo or the treatment.
-Have one of your group members come up to the board and make an experimental design based on the prompt given.
-Prompt: An experimenter wants to conduct an experiment of a new drug in testing. There 100 (50 of each gender) willing subjects to test the drug. The drug has different effects on both men and women. Help the experimenter make an experimental design based on his situation.
- Randomized block design.
-What are the criteria for establishing causation?
- The association is strong
- The association is consistent
- Larger values of the explanatory variable are associated with stronger responses
- The alleged cause precedes the effect in time
- The alleged caused is plausible