The name and type of tissue.
Simple Squamous and Epithelial Tissue
Function: Thick protective layer
Stratified Squamous ET
Location: Bones in the skeleton, the outside/ hard portion
Bone (Compact)
1) Skeletal
2) Cardiac
3) Smooth
Muscle Tissue
Characteristics:
-Covers organs and body surfaces
-Lines cavities, and hollow organs
-Makes glands -NO Blood Vessels
-Highly Mitotic -Cells are tightly packed
Epithelial Tissue
What is the name and type of connective tissue?
Adipose and Loose connective tissue
Function: Binding Organs
Areolar (Loose CT)
Location: Dermis
Dense Irregular CT
1) Tight
2) Desmosomes
3) Gap
Junctions between the cells
Characteristics:
-Levers for movement
-Supports Tissues
-Protects vital organs
-Stores minerals
-Houses hematopoietic cells
Functions of the Bone
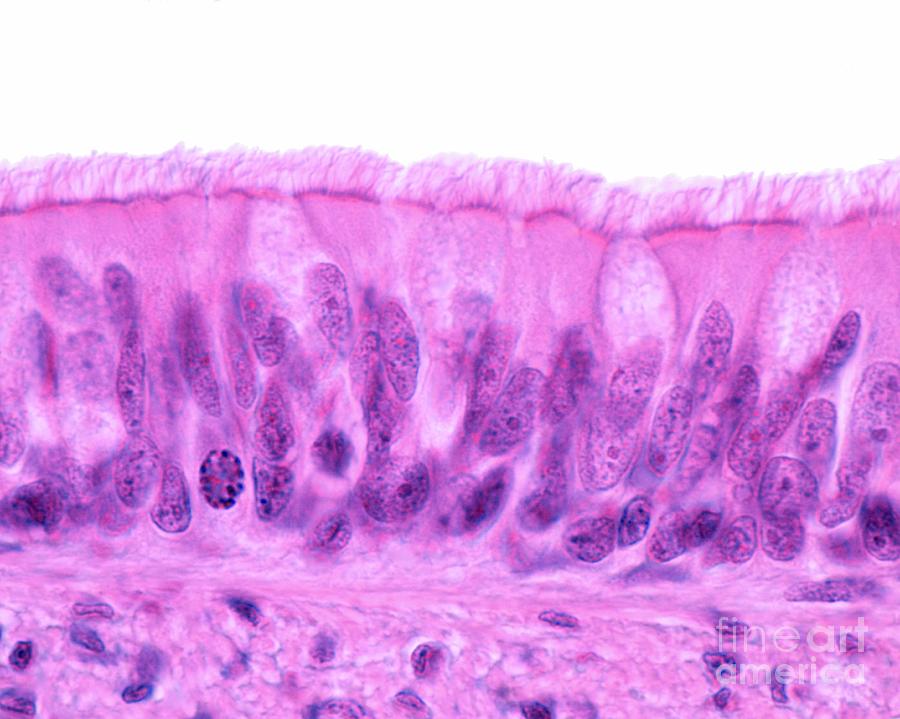 What is the name and the type of tissue?
What is the name and the type of tissue?
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar and Epithelial Tissue
Function: Binds body parts
Dense regular CT
Location: thyroid gland
Simple Cuboidal ET
1) Mucous
2) Serous
3) Cutaneous
4) Synovial
Body Membranes
Characteristics:
-Most abundant type
-good blood supply
-very mitotic
-surrounded by an extracellular matrix between cell spaces
Connective Tissues

What is the name and type of tissue?
Elastic and Dense Connective Tissue
Function: Supports
Reticular (Loose CT)
Location: Epiglottis
Elastic Cartlidge
1) Merocrine
2) Apocrine
3) Holocrine
Classification of Exocrine Glands
Characteristics:
-rigid specialized CT
-contains collagen ground substance
-located in the lacunae
-covered by the perichondrium
Cartildge

What is the name and type of Connective Tissue?
Hyaline and it is Cartlidge
Function: Stretch and recoil
Elastic (Dense CT)
Location: Parts of the knee
Fibrocartilage
1) Fibroblasts
2) Adiocytes
3) Mast Cells
4) Macrophages
Resident Cells
-Does NOT transmit nerve impulses
-is responsible for protection, nourishment, and supporting neurons
-part of nervous tissue
Glial Cells