What is scarcity?
An organization that produces a good or service to earn a profit.
What is a firm?
Trade that benefits all participants because it was agreed to freely by all parties.
What is voluntary exchange?
A curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two goods that can be produced with available resources and current technology.
What is a Production Possibilities Frontier?
The rights of individuals and firms to have exclusive use of physical property and intellectual property.
What are private property rights?
People generally make decisions after considering the known costs and benefits of an action.
What is rationality?
Activities performed for others, such as cleaning or providing investment advice.
What is a service?
When good are distributed throughout society in a way that is fair.
What is equity?
The highest-valued alternative that must be given up to make a decision.
An economy where decisions about production and allocation are primarily made by a central planner, usually the government.
What is a centralized economy?
The economic costs and benefits of an action which people respond to when making decisions.
What are economic incentives?
Someone who takes risks to start a new business.
What is an entrepreneur?
A model showing how firms and households are linked in the market system through factor and product markets.
What is the circular flow diagram?
The ability to produce more of a good or service using the same amount of resources.
What is absolute advantage?
An evaluative statement about the world. For example - The cost of eggs is too high.
What is a normative statement?
The golden rule of marginal decisions making.
What is MB=MC?
Manufactured goods that are used to produce other goods and services.
What is capital?
When a good or service is produced at the lowest possible cost.
Point C
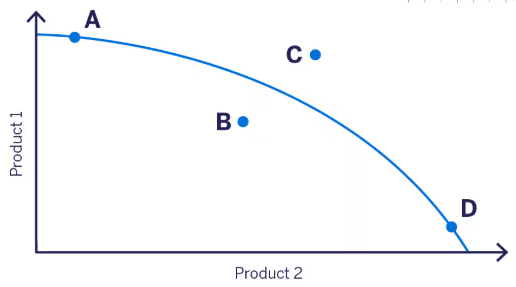
What is an unattainable level of production?
The subfield of economics which considers how and why individual actors (households, firms) make economic decisions.
What is Microeconomics?
The study of how human's (individual and socially) make decisions allocating scarce resource among unlimited wants.
What is Economics?
The process used to produce goods or services, depending on the skill of workers and quality of equipment.
What is technology?
When people or countries focus on their comparative advantage in order to benefit the most from trade.
What is specialization?
The reason a trade is mutually beneficial for both parties involved.
What is comparative advantage?
The type of analysis economists use when discussing/researching the economy.
What is positive analysis?
The three traditional economic resources.
What are Land, Labor and Capital?
The difference between a firm's revenue and it's costs - including its opportunity costs.
What is economic profit?
The idea that through voluntary exchange and pursuing comparative advantage, the free market can help make everyone better off "as if guided by a(n) ________."
What is the Invisible Hand of the Market?
The observation that which implies that the PPF is curved outward.
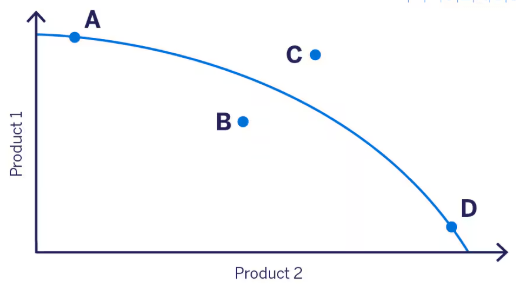
What is the law of increasing marginal opportunity costs (or diminishing marginal returns)?
When people's private property is protected, they are more likely to take responsibility for it and use it efficiently.
What is an economic incentive?