What is the definition of psychology?

The scientific study of the mind and behavior
Explain what a case study is or give an example.
A descriptive research method where a researcher gathers detailed, qualitative, information about a single individual
Example: Studying the behavior and mind of a serial killer
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-write-a-psychology-case-study-2795722-final-f90b37ae2de34cc29b53e303fc0eef5d.png)
Give an example of naturalistic observation.
Descriptive research method used to systematically observe "real life" behavior in a naturalistic setting
Example: Studying chimpanzees in the wild
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-naturalistic-observation-2795391-5c2cfe704cedfd0001583331.png)
Who is the founder of psychology?

Willhelm Wundt
A descriptive research method used to obtain self-report data about people's experiences, attitudes, or feelings.
Survey

Fill in the blank:
In the scientific method, after making an observation about the world, you then form a __________.
BONUS: Correlation does not equal ___________.
Hypothesis/Testable Hypothesis
Hypothesis: Testable prediction about what will happen.
B: Correlation does not equal causation.
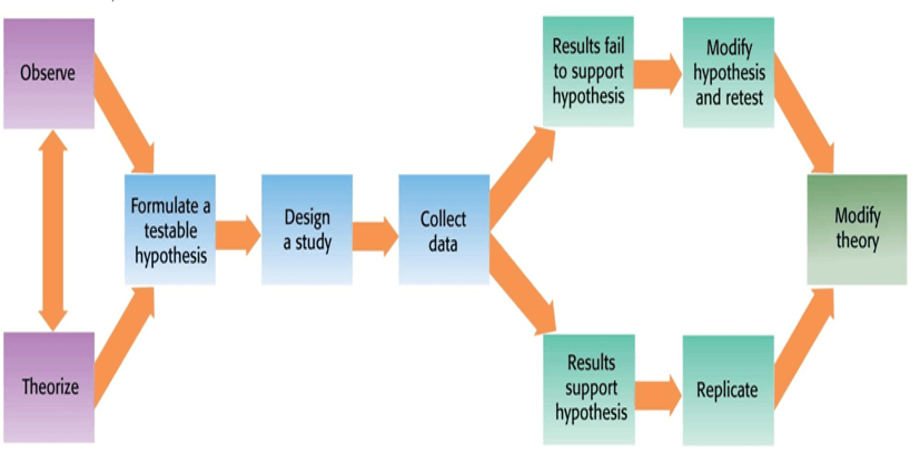
The idea that knowledge should be obtained through personal experience.
HINT: In the definition of science, "a unique, systematic, self-correcting _________ method of obtaining knowledge about the natural world.
Empirical
Give an example of
1. A strong correlation coefficient (CC)
2. A weak CC
3. A perfect CC
1. -.91
2. .21
3. 1.0 or -1.0

In a correlational study, when a variable the researcher had not considered is responsible for observed effects in both of the variables of interest.
BONUS:
True or False: Correlation equals causation
Third variable problem
False, correlation does not equal causation

What are the four goals of science?
HINT: The acronym is DCEP
Describe
Classify
Explain
Predict
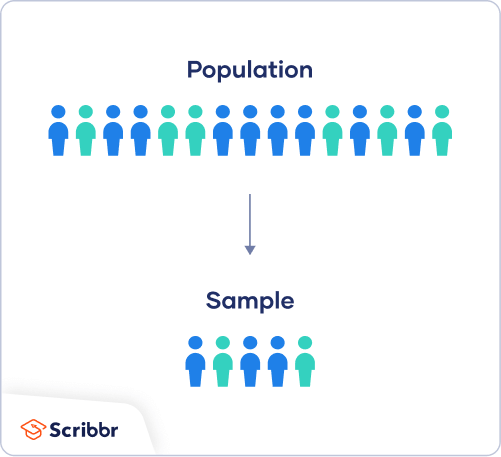
In a research experiment, what is a sample supposed to be representative of?
The population
What are the three aspects that make up a true experiment?
1. Random assignment to conditions
2. Use of control conditions (manipulation)
3. Control over confounding variables
What are the four distinct skills of critical thinking?
Name three of four to get credit.
HINT: Acronym is RAAR

Rational
Aware of biases
Always ready to revise previously held beliefs in light of new evidence
Reflects
Explain the term external validity, the main disadvantage of the experimental method.
The degree to which research results may generalize to the world outside the laboratory.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/internal-and-external-validity-4584479_final-a1cf2c26ce464856bb86fe5ceb99b17b.png)
A psychologist wants to study if caffeine affects the cognition of students. One group of students consumes 100mg of caffeine and the other group of students drinks water. The psychologist then observes how well they do on a concentration test.
In the experimental method, what is the independent variable (IV), dependent variable (DV), experimental group (EG), and control group (CG)?
IV: Caffeine
DV: How well they do on the concentration test
EG: Group of students consuming caffeine
CG: Group of students drinking water
________________________________________
IV = What is being manipulated, what I change
DV = What is being measured, what I observe
EG = Group that receives IV, group the experimenter is messing with
CG = Group that doesn't receive the IV, comparison/baseline group
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/control-and-experimental-group-differences-606113-FINAL1-5b7ad7d0c9e77c00574b71b5.png)