
The stage of mitosis pictured
What is anaphase?
The stage of mitosis pictured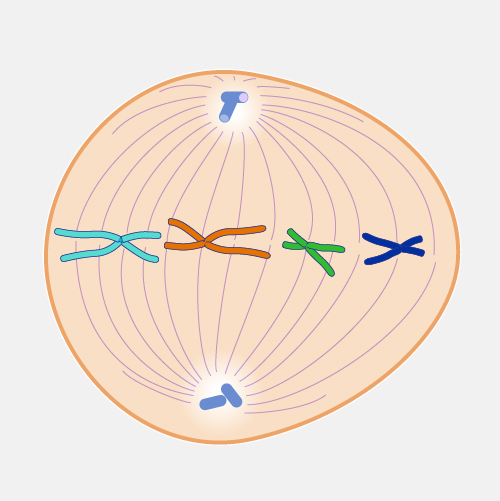
What is metaphase?
The phase in which the DNA is replicated
What is S phase?
The number of chromosomes in a human cell.
What is 46?
The unrestrained, uncontrolled growth of cells
What is cancer?
The stage of mitosis pictured
What is prophase?
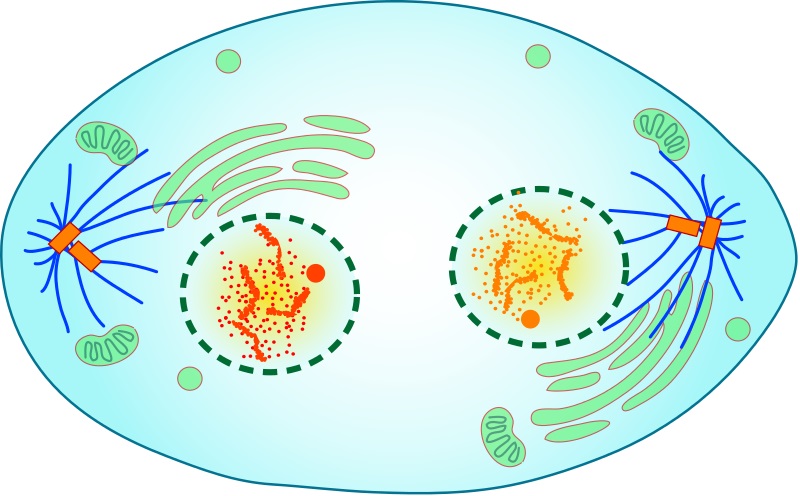
The stage of mitosis pictured
What is telophase?
The longest stage of interphase
What is G1?
The way in which bacteria divide, where reproduction is clonal.
What is binary fission?
Genes that control cell division. Both alleles of these genes must be mutated in order to have a nonfunctional gene.
What are tumor suppressor genes?
The 3rd phase of mitosis
The stage of mitosis where the golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and nuclear envelope reform.
What is telophase?
The stage before DNA has been replicated in interphase
What is G1?
Chromatin that is not expressed and is tightly wound
What is heterochromatin?
Normal cellular genes that stimulate normal cell growth. Mutation in one allele is enough for loss of function of the gene, which can cause uncontrolled division.
What are protooncogenes?
What is the kinetochore?
The name of the structures that are pulled apart in mitosis
Sister chromatids
The stage in which the centrioles are replicated (in animal cells)
What are histones?
The gene associated with retinoblastoma if it is mutated.
What is the Rb gene?
The stage in mitosis where chromosomes attach to microtubules, each chromosome is oriented such that the kinetochores of sister chromatids are attached to microtubules, and chromosomes move to the equator of the cell (but aren't quite there yet)
What is prometaphase?
The structure in a cell where the spindle fibers reach out from
What is a centriole?
The protein that holds the 2 identical DNA molecules (sister chromatids) together after S phase.
What is cohesin?
The name of the structure resulting from nucleosomes being wrapped into higher order coils
What are solenoids?
A specific tumor suppressor gene that plays a key role in the G1 checkpoint and monitors the integrity of DNA. This gene is absent or damaged in many cancerous cells.
What is p53?
