The atomic number of Iodine
What is 53?
The atomic number of air
What is 7.6
The differential absorption between various tissues of the body
What is subject contrast?
This is directly proportional to the patient dose, as well as the potential of scatter on the image
The atomic number of Barium
What is 56?
The atomic number of soft tissue
What is 7.4?
This is essential to the visibility of detail in any image
What is contrast?
Penetration is the _______ of attenuation
What is the opposite?
The atomic number of a tissue must be expressed as
What is an average?
Soft tissue density is equal to
What is water?
If a part increases 4cm thickness, the x-ray penetration through to the receptor plate will be
What is 1/2?
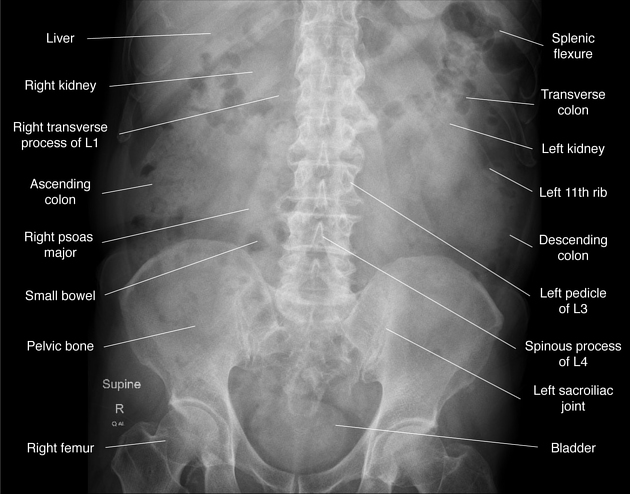 Does this image have increased or decreased subject contrast
Does this image have increased or decreased subject contrast
What is decreased?
Smaller differences in atomic number results in ________ differences in absorption of the x-ray beam
What is Larger?
Soft tissue will absorb nearly ____more x-rays than the lungs
What is 1000?
How does bone appear on an x-ray image
What is White?
Photoelectric produces the _______ on the image
What is the "whites" or lighter areas?
The average atomic number is ______ in the attenuation of x-rays
What is Exponential?
If tissue density decreases, the space between atoms will
What is increase?
How does fat appear on an X-ray image in comparison to soft tissue?
What is dark?
Compton scatter lays down a "blanket: of _____ at the image receptor
What is fog?