An American general who commanded the Southwest Pacific in World War II (1939-1945), oversaw the successful Allied occupation of postwar Japan and led United Nations forces in the Korean War.
Who is General Douglas MacArthur?
This term is the practice of making accusations of subversion or treason without proper regard for evidence. It also marks the time period of the second red scare.
What is McCarthyism?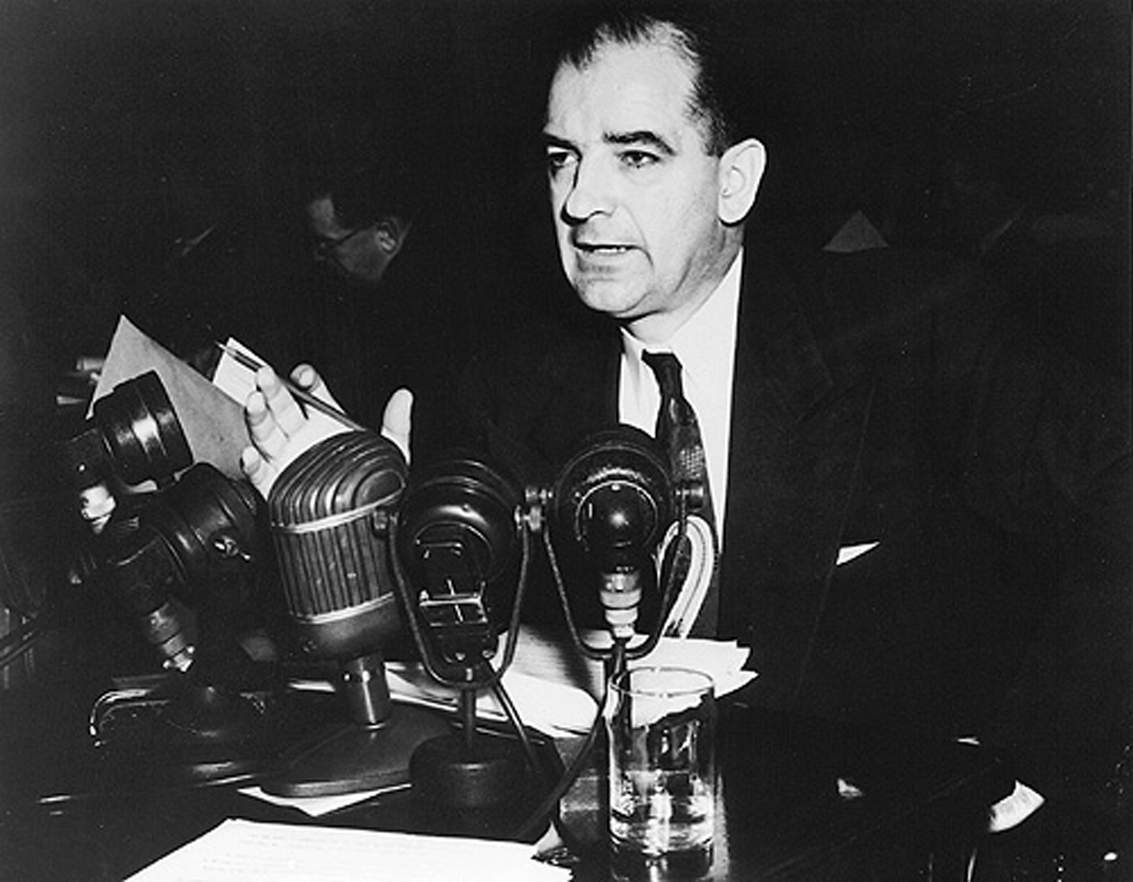
It was a direct and dangerous confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union. A pivotal moment during the Cold War as many feared the world was on the brink of nuclear war.
What is Cuban Missile Crisis?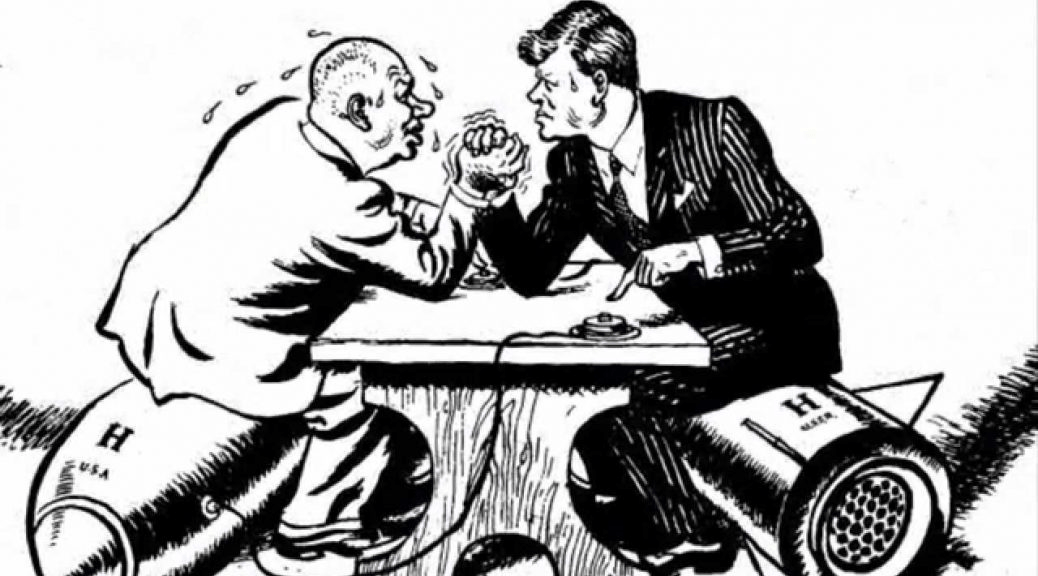
A very powerful and influential nation. The former allies during WW II, become rivals post WW II due to very different ideologies. This rivalry would decide future world status.
What is Superpowers?
China, the Soviet Union, the United States, and the United Kingdom form the basis for the United Nations at this conference.
What is the Dumbarton Oaks Conference?
It is best known as the Cold War policy of the United States and its allies to prevent the spread of communism abroad.
What is Containment?
Dictator and head of the Communist Party in Russia. He ruled by terror, and millions of his own citizens died during his brutal reign.
Who is Joseph Stalin?
Imaginary barrier separating Soviet-controlled countries and the free world. Winston Churchill coined the phrase.
What is the Iron Curtain?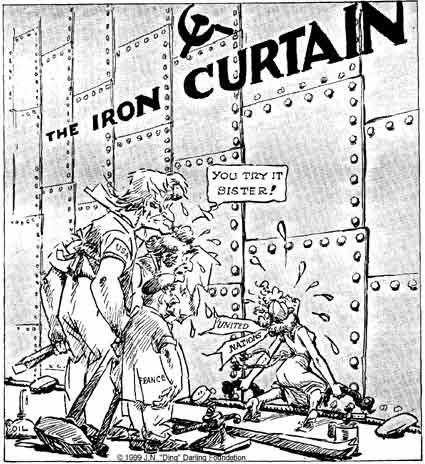
A military operation in the late 1940s that brought food and other needed goods into West Berlin by air. (“Operation VITTLES”)
What is the Berlin Airlift?
He was the commander of Allied forces during WW II and later became a two term President of the United States. He believed the future of national defense was nuclear.
Who is Dwight Eisenhower?
The creation of this German state was completed by merging France, Britain, and the U.S. occupation zones. The ideology was considered to be democratic.
What is West Germany?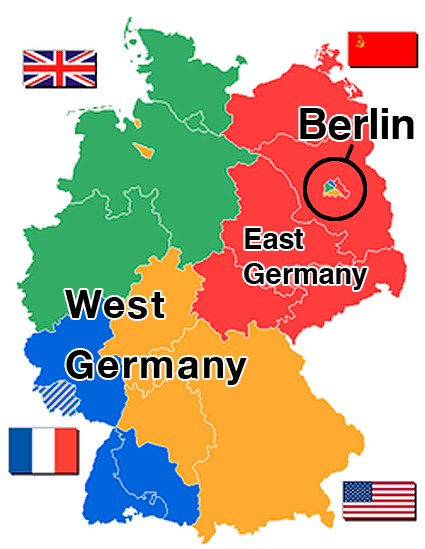
Economic support to help rebuild European economies after the end of World War II. Designed to improve European prosperity, and prevent the spread of Communism.
What is the Marshall Plan?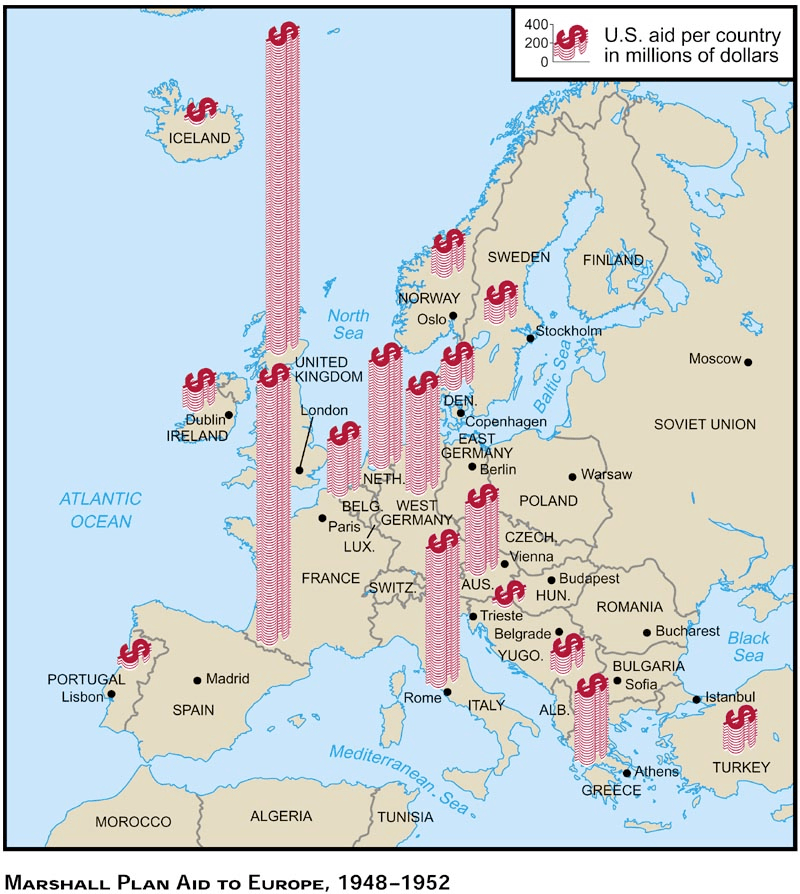
He established the first communist state in the Western Hemisphere after leading an overthrow of Fulgencio Batista in 1959. He ruled Cuba from 1959 - 2008 .
Who is Fidel Castro?
(Nuclear Arms Race) A rapid increase in the number of nuclear weapons. This is often seen as increasing the danger of nuclear warfare.
What is Nuclear Proliferation?
The Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies' railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control. The western powers countered and instituted an airlift.
What is the Berlin Blockade?
It was to keep Western “fascists” from entering East Germany and undermining the socialist state, but it also prevented mass defections. It remains one of the most powerful and enduring symbols of the Cold War.
What is the Berlin Wall?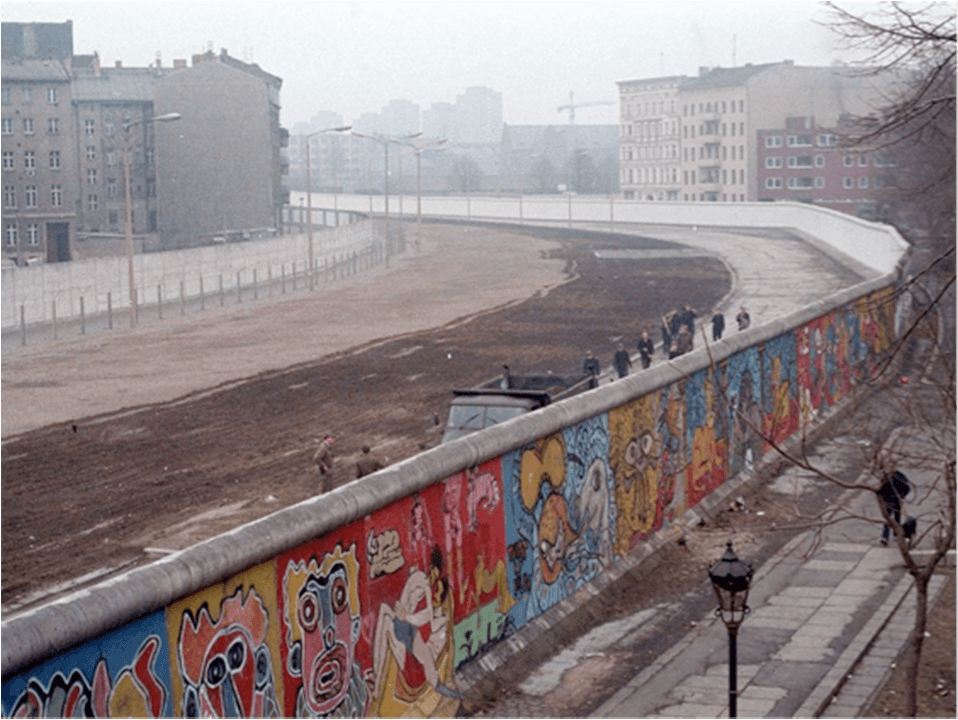
Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin met in February, 1945 in this city, in the Crimea, to plan the occupation of postwar Germany. The "Big Three" agreed that Germany should be divided into four separate occupation zones.
What is the Yalta Conference?
This Doctrine established the Middle East as a Cold War battlefield. The Middle East might be the site of World War III due to increased communist interest in the region. It was an extension of the containment policy.
What is the Eisenhower Doctrine?
He came close to war with the United States (Cuban Missile Crisis) and also clashed with China, which led to his being ousted by Leonid Brezhnev.
Who is Nikita Khrushchev?
Struggle in which the U.S. and Soviet Union became rivals but never fought directly in military conflict. A tension filled proxy-war. It lasted more than forty years.
What is the Cold War?
This invasion was the first military action of the Cold War. It was a war against the forces of international communism. (1950-1953)
What is the Korean War?
A village in the demilitarized zone between North and South Korea. It was here that the armistice ending the Korean War was signed.
What is Panmunjom?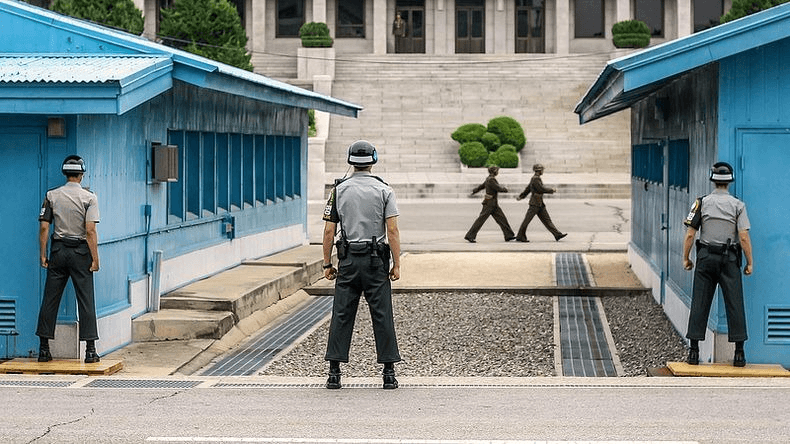
The capital of Berlin was in this part of the divided Germany. The territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces at the end of World War II. The economy was centrally planned and state-owned.
What is East Germany?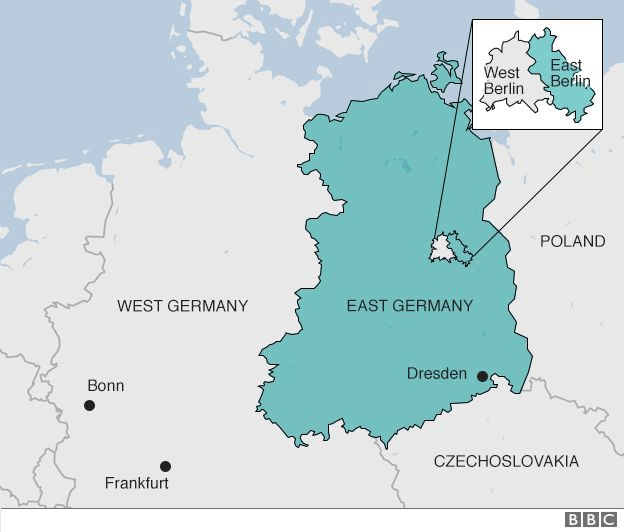
The Doctrine became the foundation of American foreign policy, and led, in 1949, to the formation of NATO, a military alliance that is still in effect.
What is the Truman Doctrine?
He was the youngest elected President of the U.S. He also led a renewed drive for Civil Rights. He spent the majority of his presidency managing relations with the Soviet Union.
Who is John F. Kennedy?
A treaty of mutual defense and military aid signed in Poland by communist states of Europe under Soviet influence. (1955)
This was actually used by the Soviet Union to justify its interference in the affairs of Eastern Europe. (It was the counter to NATO)
What is the Warsaw Pact?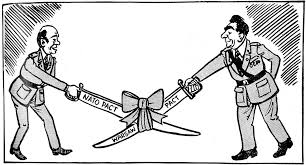
This failed attempt to oust Castro from Cuba cost the United States dearly. Castro used the attack by the “Yankee imperialists” to solidify his power in Cuba. Kennedy took the blame as he endorsed it.
What is the Bay of Pigs Invasion?
An organization sponsored by the US government that sends young people to work as volunteers in developing countries. A humanitarian effort that continues today.
What is the Peace Corps?
It was the last of the World War II meetings held by the “Big Three” heads of state. Stalin/Truman/Atlee
It was at this conference that Truman made the decision to drop the atomic bomb on Japan.
What is the Potsdam Conference?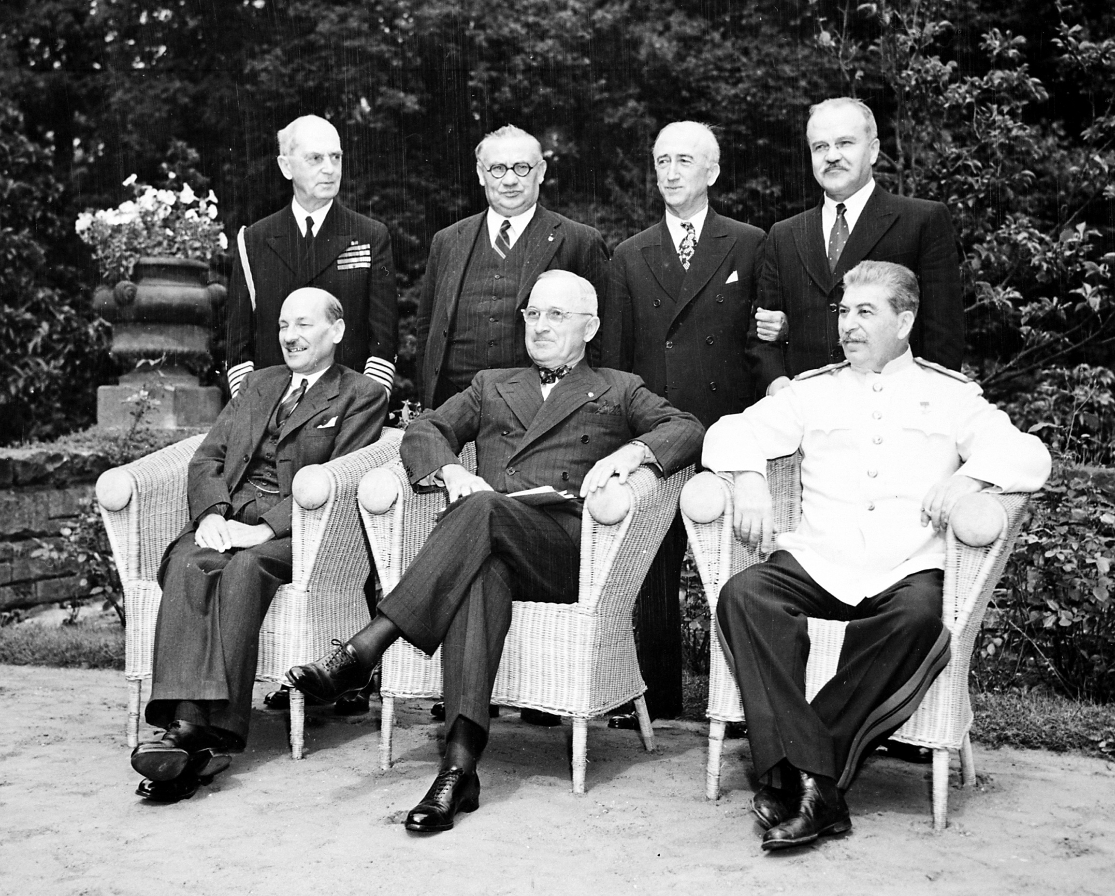
It was initiated by Kennedy in 1961 to establish economic cooperation between the U.S. and Latin America and to reduce the threat of communism moving closer to home.
What is the Alliance of Progress?