This element is the backbone of most organic molecules because it has four valence electrons that it can share in its outer shell.
What is Carbon?
Carbohydrates main fuction is this
What is short-term energy storage?
This is the main function of Lipids.
What is long-term energy storage.
These are the monomers of protiens.
What are amino acids?
What is your parents?
Why type of lipid is seen below?
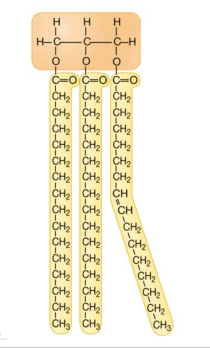
What is a triglyceride?
This reactions builds polymers by building monomers.
What is dehydration reaction.
This polysaccharide is a major component of cells walls and cannot be digested by humans.
What is cellulose?
What are Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen?
What are R groups/side chains?
The monomers of DNA include these nucleotides (4)
What are Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine?
What is the relationship with water for the two parts of this macromolecule?
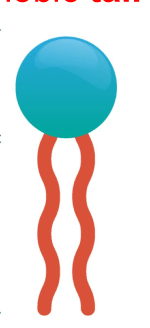
What is hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tale?
Excluding Methyl groups, this property describes the other five functional groups that make up macromolecules
What is polar/hydrophilic/soluble in water.
This polysaccharide forms the exoskeleton of arthropods.
What is chitin?
These monomers make up lipids hydrophobic.
What are fatty acids and glycerol
These elements make up proteins (6).
What are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur?
The monomers of Nucleic Acids are made of these three parts.
What are the 5-carbon sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogen containing base?
Because of this structure, the phospholipid bilayer of cell walls are called this.
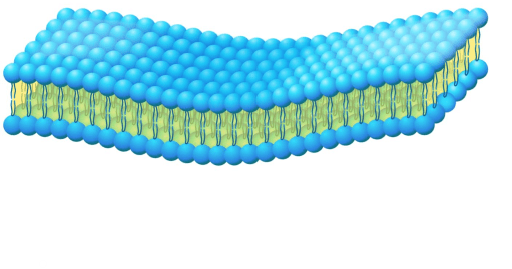
What is selective permeable?
This process breaks polymers into smaller monomers.
What is Hydrolysis?
When stored in the body of plants, glucose becomes this polysaccharide.
What is starch?
The monomers of fats are joined via this bond.
What is an ester linkage?
These are degenerative brain diseases present in human that are caused by misfolded proteins.
What is Alzheimer's and Parkinson's?
This is the difference between Deoxyribose and Ribose sugars.
What is one less oxygen?
What level of protein structure is this and how is its shape determined?
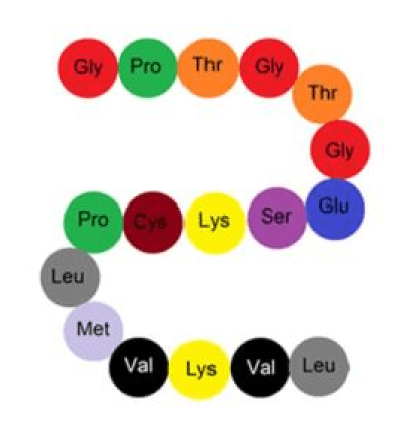
What is Primary Structure and by genes?
This type of bond is created between monomers during a dehydration reaction.
What is covalent bond?
When stored in the body of animals, glucose become this polysaccharide.
What is glycogen?
This fatty acid has no double bonds in its hydrocarbon chain linking the maximum hydrogen and carbon atoms.
What is saturated fatty acids?
This covalent bond link the carboxyl group on one amino acid to the amino group of another animo acid.
What is a peptide bond?
Where on the monomers do the bonds between nucleotides occur (what part)?
What are the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another nucleotide.
What is the name and shape of this polymer?
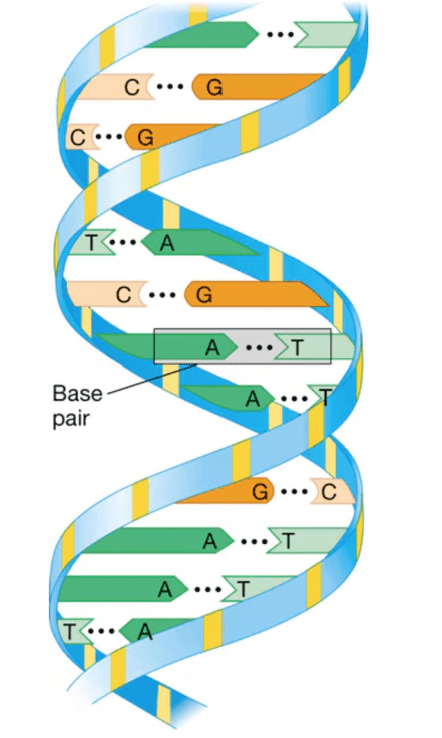
What is DNA and double helix?
These have the same molecular formula but different structures.
What are Isomers?
The molecules of monosaccharides are always in multiples of this molecular fomula.
What is CH2O
This is a molecules that is composed of carbon and hydrogen and is a major component of fats.
What are hydrocarbons?
These processes (3) can lead to the denaturization of protein's structure.
What is changes in pH, changes in salt concentration, and high temperatures?
Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil are this type of Nitrogenous base.
What is Pyrimidines (one ring with 4 carbon and 2 nitrogen)?
What type of fatty acids is below and why does it have that name?
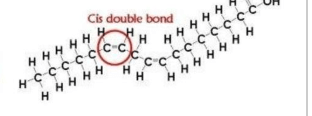
What is a unsaturated fatty acid and because there is a double bond?