The use of the senses to process information about the external environment
-Ex: Someone sees a dog jump and someone who loves dogs may think they’re being playful.
While someone who’s scared of dogs may think it’s being aggressive or about to attack them.

What is Perception?
- Perception can be defined as the process by which an individual selects, organizes, and interprets information to create a meaningful picture of their environment.
-Process begins with environmental stimuli, which are then attended to, processed by the senses, and organized and interpreted by the brain.
-Based on prior experiences and memory, allowing us to recognize and respond to stimuli.
The tendency to expose yourself to information that reinforces, rather than contradicts, your beliefs or opinions.
Example: Explains why you hide a video from someone who had opinions that you don't agree with or want to be exposed to

What is Selective Exposure?
This phenomenon is prevalent in various contexts, including media consumption, political attitudes, and personal decision-making. The core idea behind selective exposure is that people actively choose to expose themselves to information that aligns with their pre-existing views.
Making a hasty generalization about a group based on a judgment about an individual from that group.
Example: The idea that "All lesbians are masculine" or that "All elderly people don't know how to use technology.

What is Stereotyping?
- It's meant to help you interpret your surroundings
- It becomes an issue when you refuse to see others beyond what you believed to be true about all people in that group
Perception of what makes an individual unique with regard to various personality characteristics, interests, and values.
Example: Someone might define themselves as "introverted," "creative," or "a problem-solver"
 What is Personal Identity?
What is Personal Identity?
Perception in which your mind selects, organizes, and interprets that which you sense.
-Example: In sports like basketball, actively tracking the ball, anticipating player movements, and positioning yourself to make a play

What is active perception?
- It's not just about passively receiving information; it's about using our actions to gather data and construct our understanding of the environment
The tendency, when you expose yourself to information and ideas, to focus on certain cues and ignore others.
-Example: In an elevator, you may pay attention to the conversation between strangers rather than the elevator music
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-selective-attention-2795022_final-5b6348f0c9e77c0050ba4710.png)
What is Selective Attention?
-Mental filter that helps to prioritize information for processing, enabling concentration on what is most relevant
-Crucial because the brain has a limited capacity to process all sensory input
An unfavorable predisposition about an individual because of that person’s membership in a stereotyped group.
Example: Women might not be hired for particular jobs because of prejudice, people might be rejected from housing because of religious beliefs, people might fear others because of their race or ethnicity.
What is Prejudice?
The process in which the self develops through the messages and feedback received from others.
Example: Someone might develop their sense of style based on how their peers react to their clothing choices. Positive reactions can reinforce their fashion choices, while negative reactions can lead them to reconsider their style
 What is Symbolic Interactionism?
What is Symbolic Interactionism?
Your uniquely constructed meaning attributed to sensed stimuli
-Example: One person might find the same weather pleasant while another finds it too hot
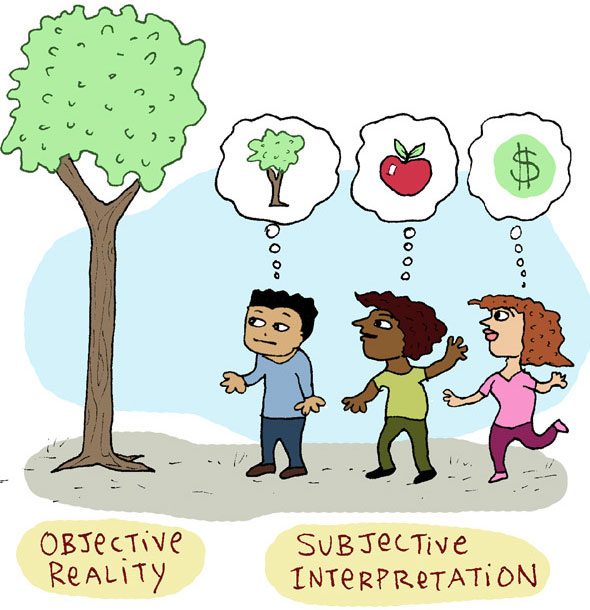
What is Subjective Perception?
- Personal Experiences, Emotions and Feelings, Beliefs and Values, Biases, and Sensory Input can affect subjective perception.
-Two people can experience the same event but perceive it differently due to their individual backgrounds, expectations, and emotional states.
The tendency to see, hear, and believe only what you want to see, hear, and believe.
Example: If someone believes a friend is upset with them, they might selectively perceive the friend's neutral or even positive actions as signs of continued anger
 What is Selective Perception?
What is Selective Perception?
One may ignore or shift focus away from stimuli that are irrelevant or negatively impact an individual, sometimes even altering the perception of these stimuli to make them more acceptable
This occurs when we positively evaluate our own groups and negatively evaluate other groups.
Example: Those dedicated to one sports team may believe theirs is superior to another team.

What is Differentiation?
This is our emotional, psychological, and social well-being that affects how we think, feel, and act.
Example: Past trauma can significantly impact communication, causing individuals to be easily triggered, have difficulty trusting others, or struggle with expressing their needs and feelings
 What is Mental Health?
What is Mental Health?
Relates to how you feel about and express your gender.
-Identity Factors: You’re not identical to anyone else. People differ from each other in terms of biological sex assigned at birth, gender height, body type, senses, abilities, and ethnicity, to name a few factors that make up an individual’s identity.
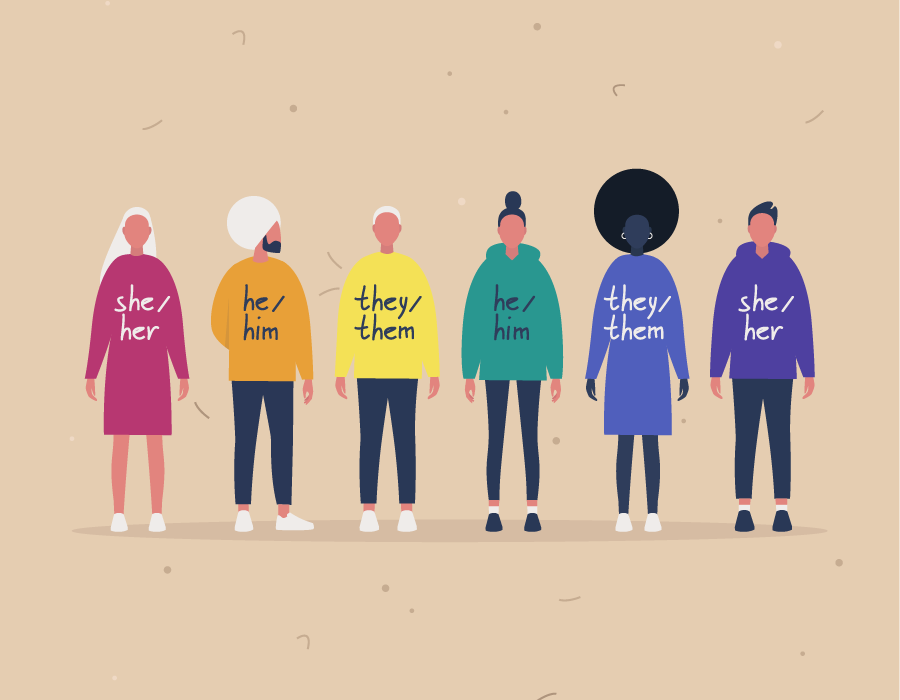

What is gender identity?
-Societal norms and expectations often influence how gender is understood and expressed
-Deeply personal experience, distinct from biological sex assigned at birth, and how a person outwardly expresses their gender
The tendency to better remember the things that reinforce your beliefs than those that oppose them.
-Ex: If someone has a strong belief about a friend's character (for example that they are always reliable), they might selectively retain memories that support this belief, even if the friend has been unreliable in some instances. They might rationalize or downplay the negative experiences to maintain their positive perception
 What is Selective Retention?
What is Selective Retention?
-Involves interpreting information in a way that favors existing beliefs, while selective attention focuses on paying attention to information that aligns with personal interests
-Selective retention then determines which of this filtered information is stored in memory
This is when we base our perceptions on someone due to their appearance and nonverbal cues in as little as three seconds.
Example: If others appear to be of a professional or social level comparable to our own, we may admire them and see them as a valuable contact.
What is First Impressions?
- First impressions can be formed in as little as three seconds
This is when you share personal details in order to present an idealized self.
Example: In a job interview, candidates may emphasize their accomplishments, skills, and positive personality traits while minimizing any potential weaknesses or gaps in their experience to present themselves as ideal for the position.
 What is Impression Management?
What is Impression Management?
The idea that your past experiences lead you to see the world in a way that is difficult to change; your initial perceptions persist.

What is Perceptual Constancy?
-A bad experience in a given situation may cause you to avoid that situation in the future
-Experiences affect how you respond to professors, police, and politicians
The grouping of stimuli into meaningful units or wholes.
Ex: A to-do list
 What is Organizing?
What is Organizing?
-Abundance of stimuli that we encounter every day can be overwhelming.
-Our brain helps process information in ways that organize what your senses tell you about your surroundings.
To reduce perceptual errors, this is used as process of describing, interpreting, and verifying that helps us understand another person and his or her message more accurately.
Example: A coworker interrupts you several times during a meeting. First you describe the behavior to them. Next, you share your feelings. Then, you offer alternate interpretations. And finally, you ask if your interpretations are correct or allow them the opportunity to offer a different reasoning

These are kind of tests like the Myer-Briggs type indicator (MBTI) and Enneagram Tests
What is Personality tests?
