The process of inhaling and exhaling air by the lungs is called....?
Breathing
What is the name of the system in the body that helps us to breath?
Respiratory system
State one respiratory disease
Asthma/ Bronchitis/ Emhysema/ Lung Cancer/
State the muscle located between the ribs that are crucial for breathing and stabilizing the chest
Intercostal muscle
In theory, percentage of oxygen is higher/lower in inhaled air?
higher
State the respiratory structure of a fish
Gills
State the name of celss surrounding stomatal pores.
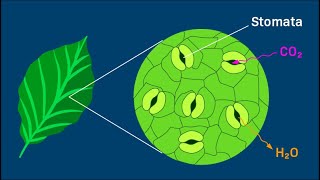
Guard cells
Most plants carry out process of gaseous exchange with their surroundings through their leaves, _________________ and ___________________
stems, roots

What disease is this?
Emphysema
dark red-coloured compound in red blood cells
haemoglobin
Air enters or leaves trachea of a grasshopper through a breathing pores called ______________________

Spiracles
State two respiratory structure of a frog
lungs and moist outer skin
A person who does not smoke but inhales cigarette smoke is known as

Passive smoker
Disease X is an inflammation of the bronchus caused by tar and irritants in cigarette smoke. The symptoms include shortness of breath and insomnia.
What is disease X?
Bronchitis
Trachea in grasshopper is divided into fine branches known as ____________________ ?
Tracheoles
This is the direction of air in breathing mechanism.
Nostrils > Nasal cavity > Pharynx > Larynx > Trachea > X > Bronchiole > Alveolus
What is X?
Bronchus
During inhalation, what happens to diaphragm?
contracts and moves downwards
Complete the sentence
Osmosis is the process of movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration of water molecules to a _______________________________________________________________________
region of low concentration of water molecules
Carbon monoxide + haemoglobin -> Y
What is Y?
carboxyhaemoglobin
Brown-coloured gas with a pungent smell that irritates air passage.
Nitrogen dioxide
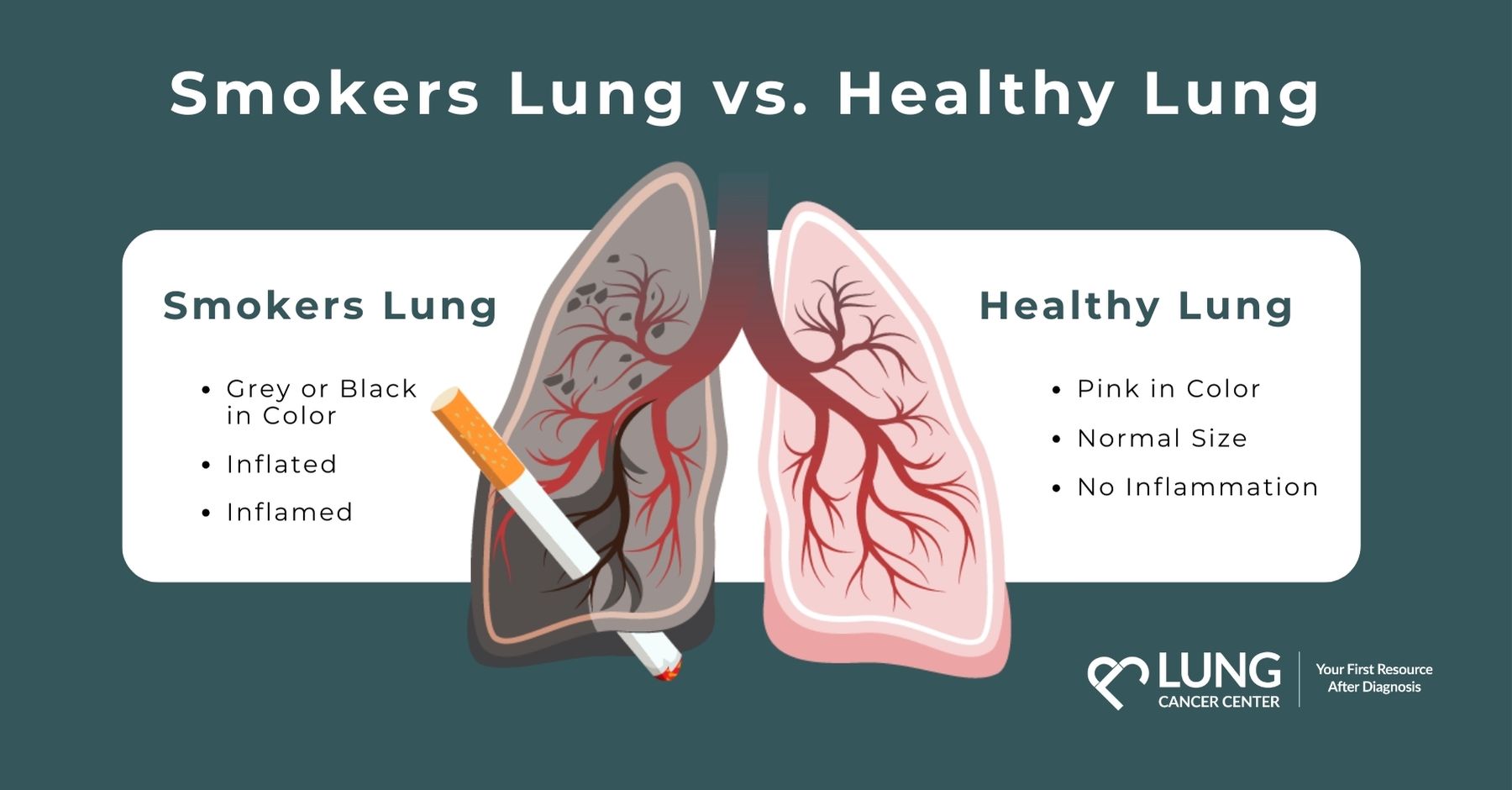
Explain specifically the bad effects of cigarette tar to human respiration system.
Cigarette tar in inhaled air sticks to and kills cells in the air passage such as thorax pharynx, epiglottis, larynx, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli. It also increases the production of mucus and phlegm in the lungs.
I irritate the air passage causing cough, bronchitis and lung cancer. I am colourless and normally produced by combustion of coals. Who am I?

Sulphur dioxide
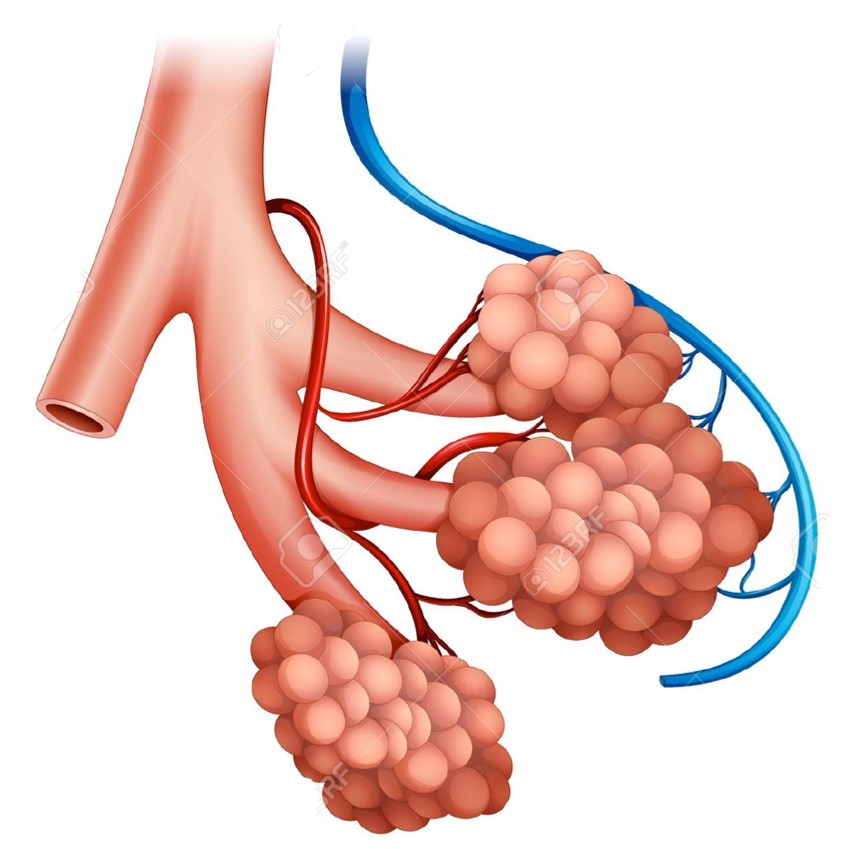
State two adaptations of the alveolar structure to increase the efficiency and maximise the exchange of gases in the human body.
1. Thickness of the walls of alveolus and blood capillaries
2. Moist wall of alveolus
3. Surface area of alveolus
4. Network of capillaries covering the alveolus
Write a chemical equation to describe cellular respiration
Glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water + energy
State the full name of the abbreviation API.
Air Pollutant Index