This is the hardest structure of the body.
What is enamel?
This is an example of what abnormality of enamel

Hypocalcified enamel
Pulp stones negatively impact the health of the pulp and must be removed
False
During this stage, the inner enamel epithelial cells become taller and are known as preameloblasts
What is the bell stage?
Examples are primary, secondary & reparative
What is dentin?
The black lines in this picture represent
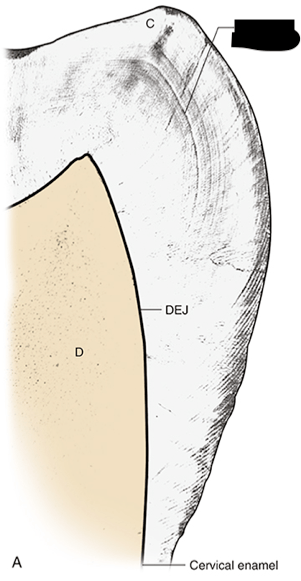
What is the Striae of Retzius?
Sclerotic dentin and Transparent dentin are the same thing
True
Ameloblasts lay down a matrix and deposit hydroxyapatite crystals in this stage
What is mineralization?
Microscopically, this type of pulp stone resembles an onion cut in cross-section.
What is a false stone?
Dentinal tubules that are empty because of the death of the odontoblasts that originally occupied them
What are dead tracts?
It is impossible to determine the type of trauma a tooth has endured based on a radiograph
False! It is possible.
In this stage, the hydroxyapatite crystals grow until they are tightly packed together.
What is maturation?
This is formed in response to trauma.
What is reparative dentin?
Small, circular, calcified areas found in the pulp
What are pulp stones?
Reparative dentin is formed in response to one of these three types of trauma: occlusal, chemical, or emotional
False! Occlusal, chemical or mechanical
As the ameloblast moves away from the DEJ, it begins to compress the two layers in the middle. What are the two layers?
Stratum intermedium and the stellate reticulum
What is pulp?
Areas of poorly calcified dentin that become entrapped during the process of calcification, found next to the DEJ in the crown and the DCJ in the root
What is Interglobular Dentin?
Attachment epithelium is found at the base of the gingival sulcus
True
As the pulp ages, ________ replace damaged cells
odontoblasts