what type of organisms would you view under a light microscope
living organisms
what is the function of the mitochondria?
to produce the energy for the cell (ATP)
which cells have cell walls?
plant cells and prokaryotes
what is the unified cell theory?
theory that states one or more cells make up human beings
what's the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes

what are advantages and disadvantages of light and electron microscopes?
light advantages: cheap and easy to use, Lightweight and Small
electron advantages: larger magnification
light disadvantage: can only see living organism, can see cells if stained but that will kill them off, Limitations on magnification
electron disadvantage: expensive, size, maintenance
what are the function of lysosomes?
digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses
what are the types of cell junctions and explain them
Plasmodesmata: allow for the transport of ions, water, and other substances
Gap junctions: allow for the transport of ions, water, and other substances
Tight junctions: cells are held tightly against each other making for a tight seal
Desmosomes: act like spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells. attaches cells to make tissues which then form organs
describe the function of flagella and cilia
Cilia and flagella move liquid past the surface of the cell. flagella allows them to swim.
What's difference between animal and plant cell
what is magnification?
The action or process enlarging something visually
what is the function of the nucleus?
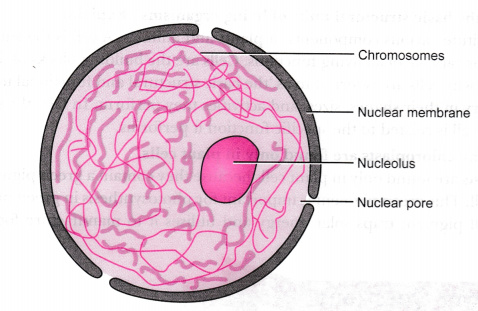
regulating all activity such as cellular metabolism and growth in addition to storing and maintaining the cell's DNA for transcription and replication.
describe the function of the cell wall in plants
functions include: Support, withstand pressure, regulate growth, regulate diffusion, communication, protection & storage
Explain function of extra cellular matrix
cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation
2 examples of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
prokaryote: E. coli & strep
Eukaryote: Humans & yeast
what is resolving power
the ability to separate or distinguish small or closely adjacent images.
what is the function of the golgi apparatus
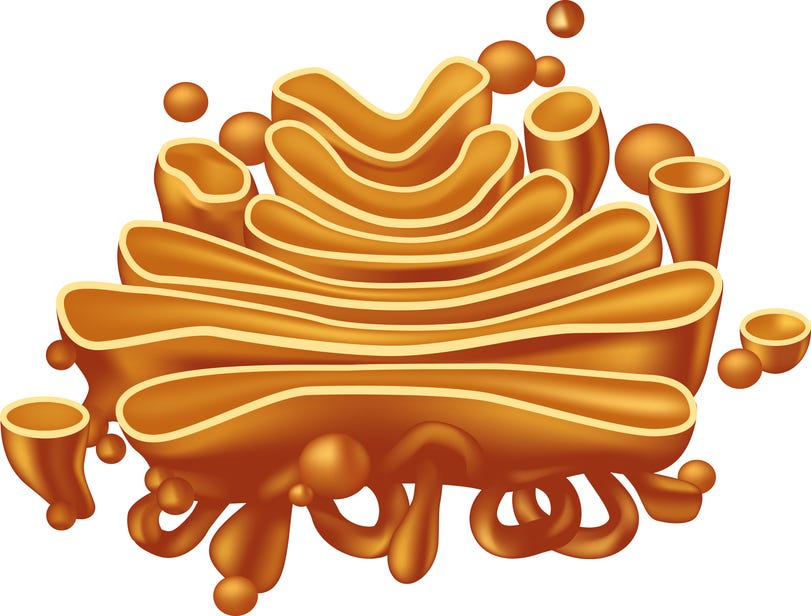

modifying, sorting and packaging of proteins for secretion, transport of lipids around the cell and the creation of lysosomes.
what is the cytoskeleton, what does it do and what is it made of
cytoskeleton provides support in a cell and keeps organelles in place inside the cell.
its made of intermediate filaments, microfilaments, and microtubules
explain surface area to volume ratio in a cell
surface area to the volume ratio gets smaller as the cell gets larger.
if the cell grows beyond a certain limit, not enough material will be able to cross the membrane fast enough to accommodate the increased cellular volume.
what is the structure of a prokaryote?
peptidoglycan cell wall, flagella, pili, capsule
how does an electron & light microscope work?
a beam of electrons hit the surface of the object and bounce off it. A detector registers these scattered electrons and turns them into a picture
Light from a mirror is reflected up through the specimen. The image produced by the objective lens is then magnified again by the eyepiece lens
what are the functions of rough and smooth ER
The smooth ER also regulates and releases calcium ions and processes toxins.
The rough ER works with the ribosomes to continue protein assembly
what are some components of the plasma membrane and what is its job
plasma membrane is responsible for regulating the materials that enter and exit the cell. it is made of a phospholipid bilayer.
it also is made of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and cholesterol
describe the function and parts of the endomembrane system.
endomembrane system is a series of compartments that work together to package, label, and ship proteins and molecules.
it includes: Endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear Envelope, Golgi apparatus, Vacuoles, Vesicles, Lysosomes, Plasma membrane
what does prokaryotic DNA look like (is it linear?)
it is circular