The cell's protein synthesis machinery, composed of rRNA and protein
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ribosome_lrg_sm_subunits-23b46a3be6354c4eacb550b25fa3c69d.jpg) What is a ribosome?
What is a ribosome?
Found in eukaryotic cells. Carry out oxidative metabolism and have their own DNA. Transforms energy in food nutrients into cellular fuel (ATP).
 What is the mitochondria?
What is the mitochondria?
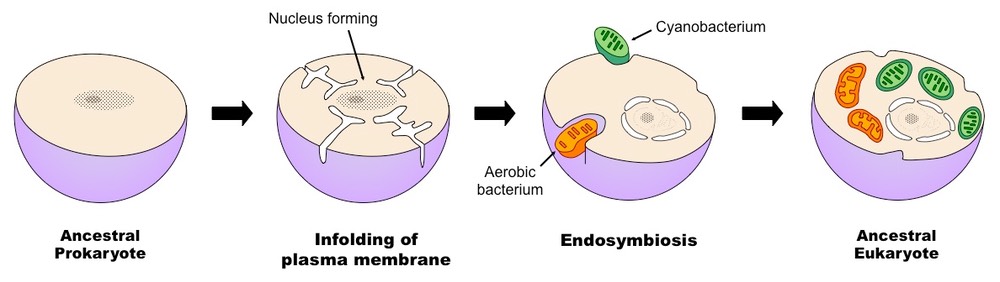
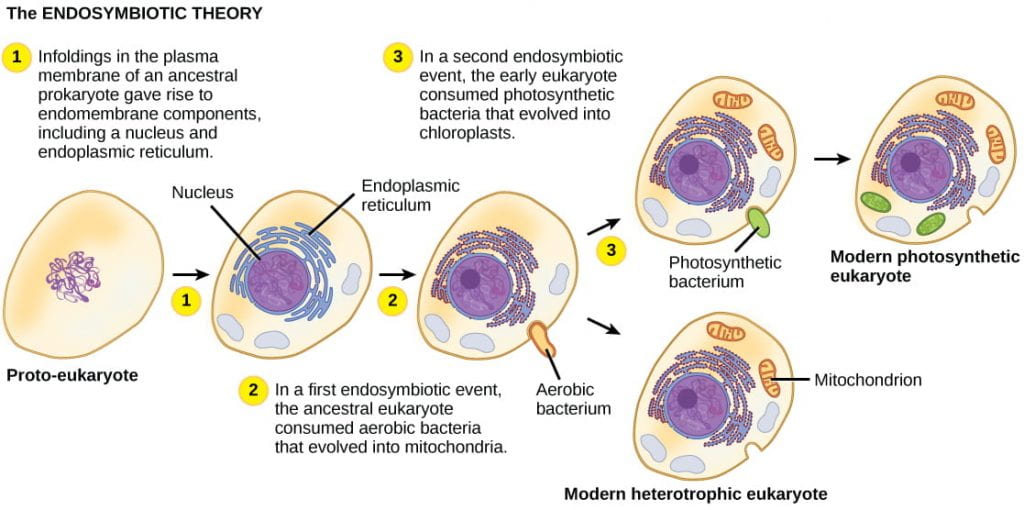
Proposes that some of today's eukaryotic organelles (chloroplast and mitochondria) evolved by a symbiosis between two cells that were each free-living.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
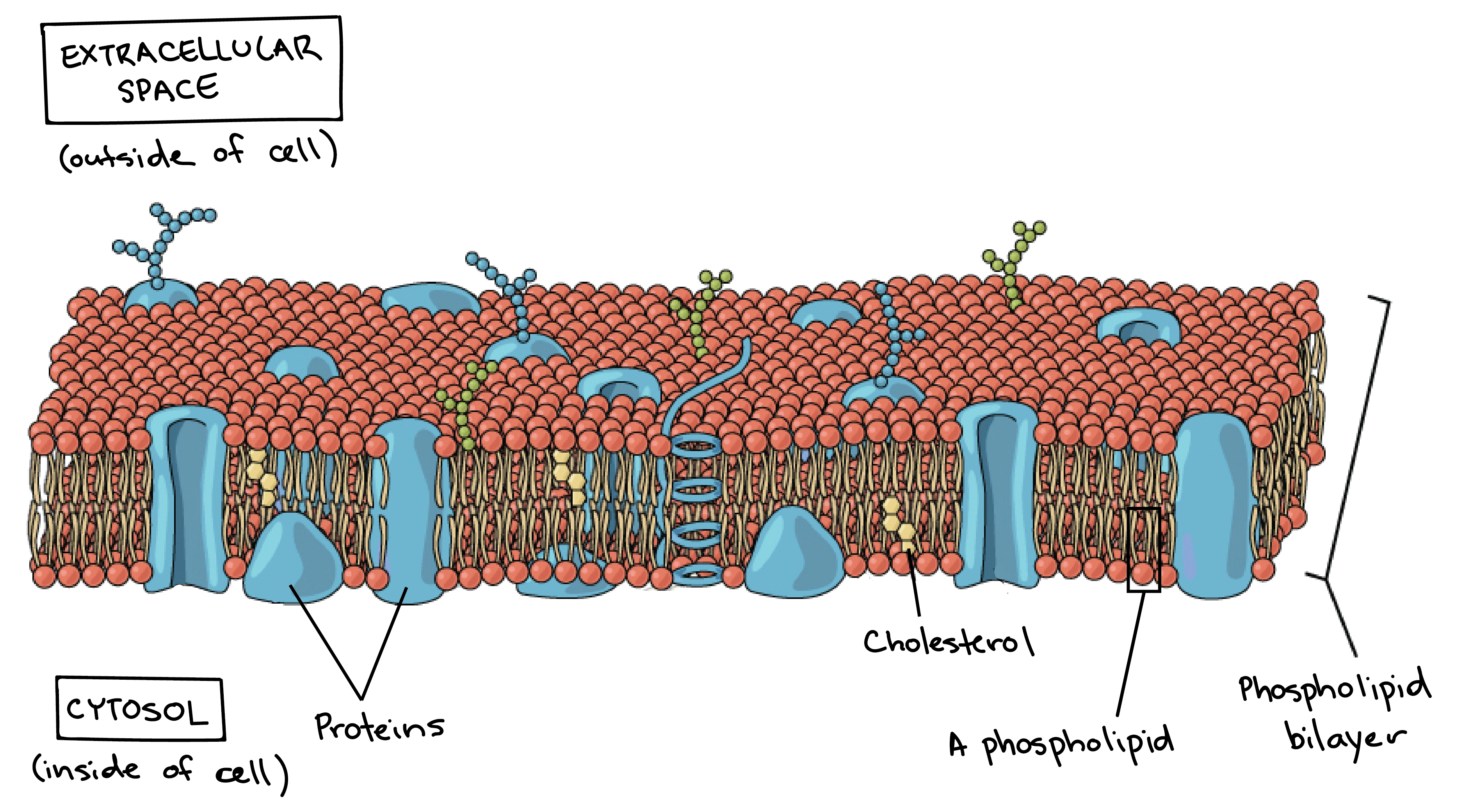
The components of the plasma membrane
What are phospholipids, membrane proteins, and sterols?
Has membrane bound organelles/compartmentalization.
What is a eukaryote?

The organelle involved in the packaging and distribution of molecules. Vesicles transport these molecules to their destination.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The organelle involved in photosynthesis, found in plant cells.
What is a chloroplast?

What is cell theory?
What is cholesterol?
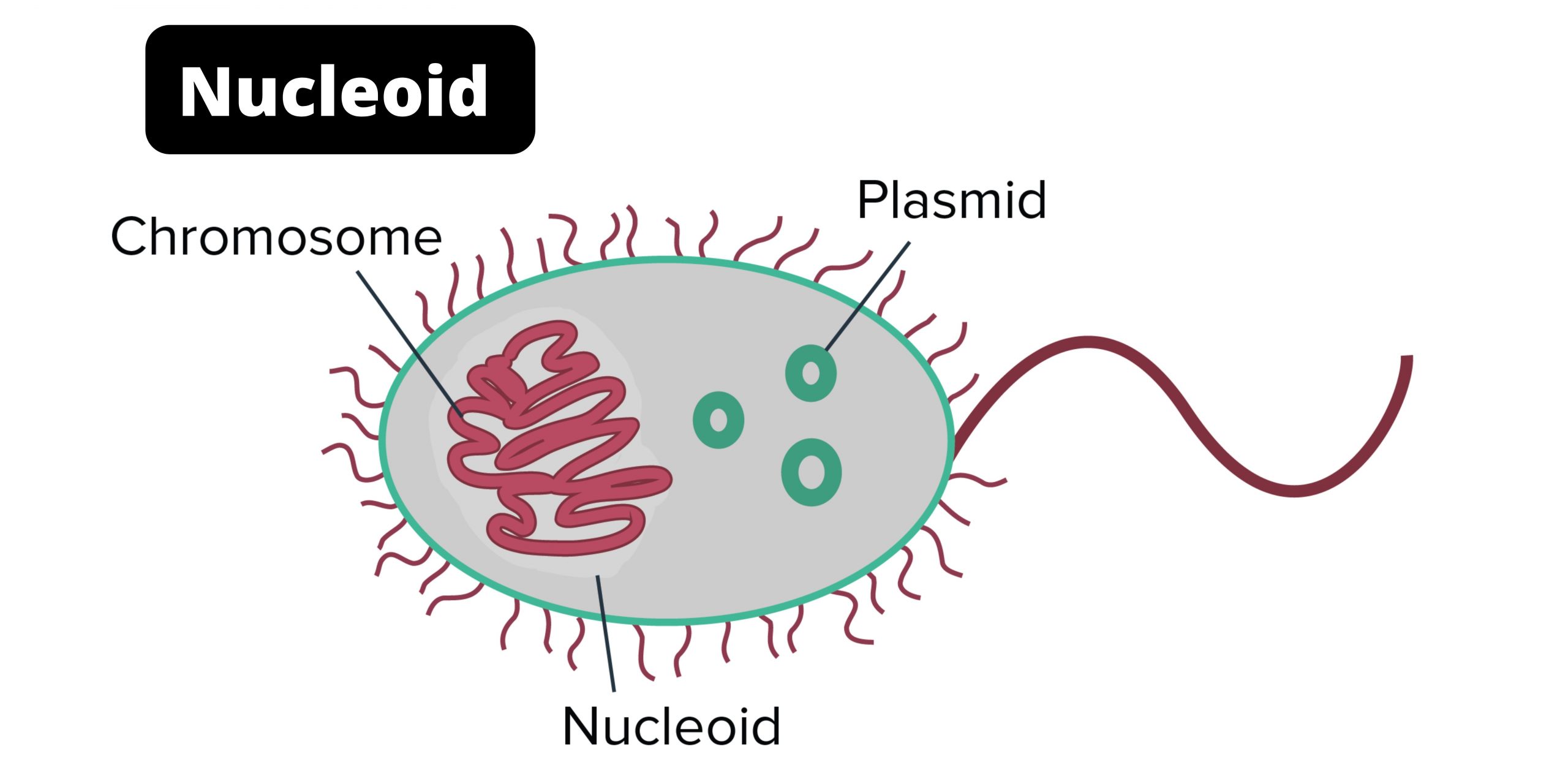
Possess DNA located in the nucleoid.
What is a prokaryote?
Organelle that can be used for storage, contraction, and storage of water. Various functions are dependent on cell type.
What is a vacuole?

This organelle has bound ribosomes attached to it. It is involved in the synthesis of proteins to be secreted, sent to lysosomes, or the plasma membrane.
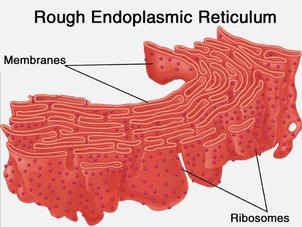 What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
Discovered cells
Who is Robert Hooke?
The result of a plant cell being put into a hypertonic solution
What is plasmolysis

Possess ribosomes.
What is prokaryotes AND eukaryotes?
The site of rRNA synthesis
 What is the nucleolus?
What is the nucleolus?
What is a microbody?
The "organelle" that was first engulfed in endosymbiotic theory.
What is the mitochondria?
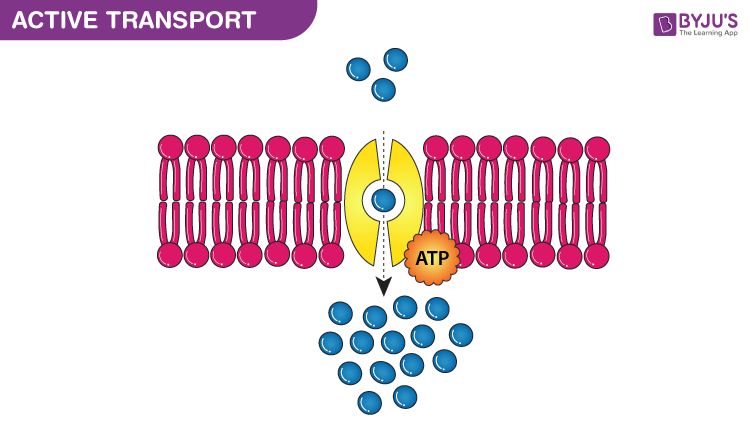
Moves substances up their concentration gradient using energy, usually in the form of ATP
What is active transport?
Has a single, circular chromosome.
What is a prokaryote?
The organelle with a variety of functions, such as synthesis (lipids, etc), storing of calcium, and detoxification
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?

The organelle that contains enzymes involved in the oxidation of fatty acids. H2O2 is catalyzed by catalase here.
What is a peroxisome?
Does not fit the requirement of being a living organism, because it is not composed of cells.
What is a virus?

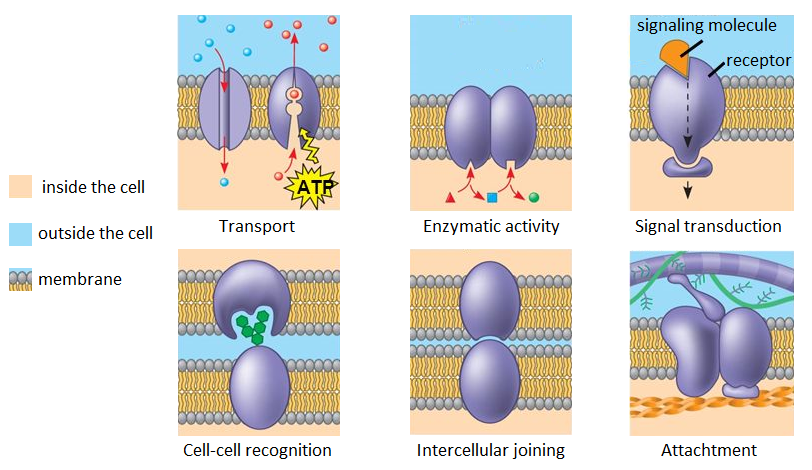
The six major functions of membrane proteins.
What is transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell-cell recognition, intracellular joining, and attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix?
Possess a cell wall that contains peptidoglycan (murein) or a variation of peptidoglycan.
What is a prokaryote?

