In what year did Hooke name cells?
A. 1492
B. 1665
C. 1765
D. 1776
B. 1665
Which of the following is NOT a fundamental chromophore group?
A. C=C
B. N=O
C. C=S
D. S=O
D. S=O
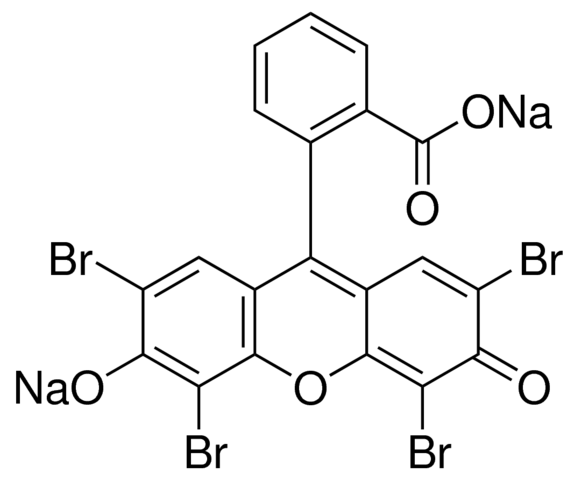
Which molecule is depicted above in sodium salt form?
A. phloxine B
B. eosin Y
C. hematoxylin
D. hematein
B. eosin Y
A. impure water
B. xylene
C. alcohol
D. This is normal.
B. xylene
For which fixative will the Feulgen reaction not work properly?
A. formalin
B. Zenker
C. Helly
D. Bouin
D. Bouin
Who declared, "cells are organisms, and entire animals and plants are aggregates of these organisms arranged according to definite laws"?
A. Hooke
B. Schleiden
C. Schwann
D. van Leeuwenhoek
C. Schwann
Given an IEP of pH 6, tissue in a pH 5 solution will be:
A. basophilic
B. acidophilic
C. metallophilic
D. amphoteric
B. acidophilic
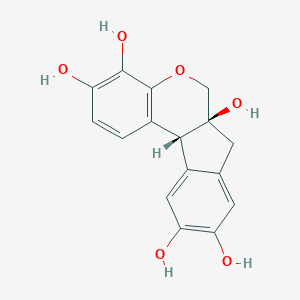 Which molecule is depicted above?
Which molecule is depicted above?
A. hematin
B. hematein
C. hematoxylin
D. hemalum
C. hematoxylin
Uneven H&E staining with varying small, concentrated patches and diffuse areas is likely due to:
A. improper pH
B. water in the infiltrating paraffin
C. too short of a time in each stain
D. too long in the differentiation step
B. water in the infiltrating paraffin
Differential staining of the Methyl Green-Pyronin Y stain is due to:
A. differing charges on DNA and RNA
B. polymerization differences between DNA and RNA
C. differing backbone sugar structures between DNA and RNA
D. a change of pH between two staining steps
B. polymerization differences between DNA and RNA
When was the first reported use of hematoxylin for microtechnique?
A. 1810s
B. 1820s
C. 1830s
D. 1840s
D. 1840s
Which list has correctly categorized dyes?
A. basic: crystal violet, safranin
acid: orange G, picric acid
amphoteric: hematein, lithium carminate
B. basic: crystal violet, orange G
acid: lithium carminate, picric acid
amphoteric:hematein, safranin
C. basic: crystal violet, safranin
acid: hematein, picric acid
amphoteric: orange G, lithium carminate
D. basic: hematein, orange G
acid: crystal violet, picric acid
amphoteric: safranin, lithium carminate
A. basic: crystal violet, safranin
acid: orange G, picric acid
amphoteric: hematein, lithium carminate
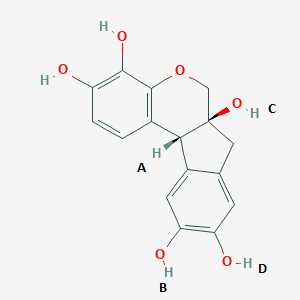 In the above image, which hydrogens are removed in the oxidation process known as ripening?
In the above image, which hydrogens are removed in the oxidation process known as ripening?
A. A and B
B. C and D
C. A and D
D. B and C
C. A and D
Considering the three methods given for restoring tissue basophilia, which of the following is not used in any of these methods:
A. lithium carbonate
B. sodium bicarbonate
C. periodic acid
D. glacial acetic acid
D. glacial acetic acid
Which of the following is not used in the reagent preparation steps of the Methyl Green-Pyronin Y stain?
A. glacial acetic acid
B. sodium acetate trihydrate
C. chloroform
D. lithium carbonate
D. lithium carbonate
When did Romanowsky first use his namesake stain?
A. 1691
B. 1791
C. 1891
D. 1991
C. 1891
Which fixative will reduce hematoxylin binding but increase eosin binding?
A. glutaraldehyde
B. picric acid
C. osmium tetroxide
D. potassium dichromate
D. They resist decolorization by acid.
D. potassium dichromate
(It takes up the COOH and OH binding sites)
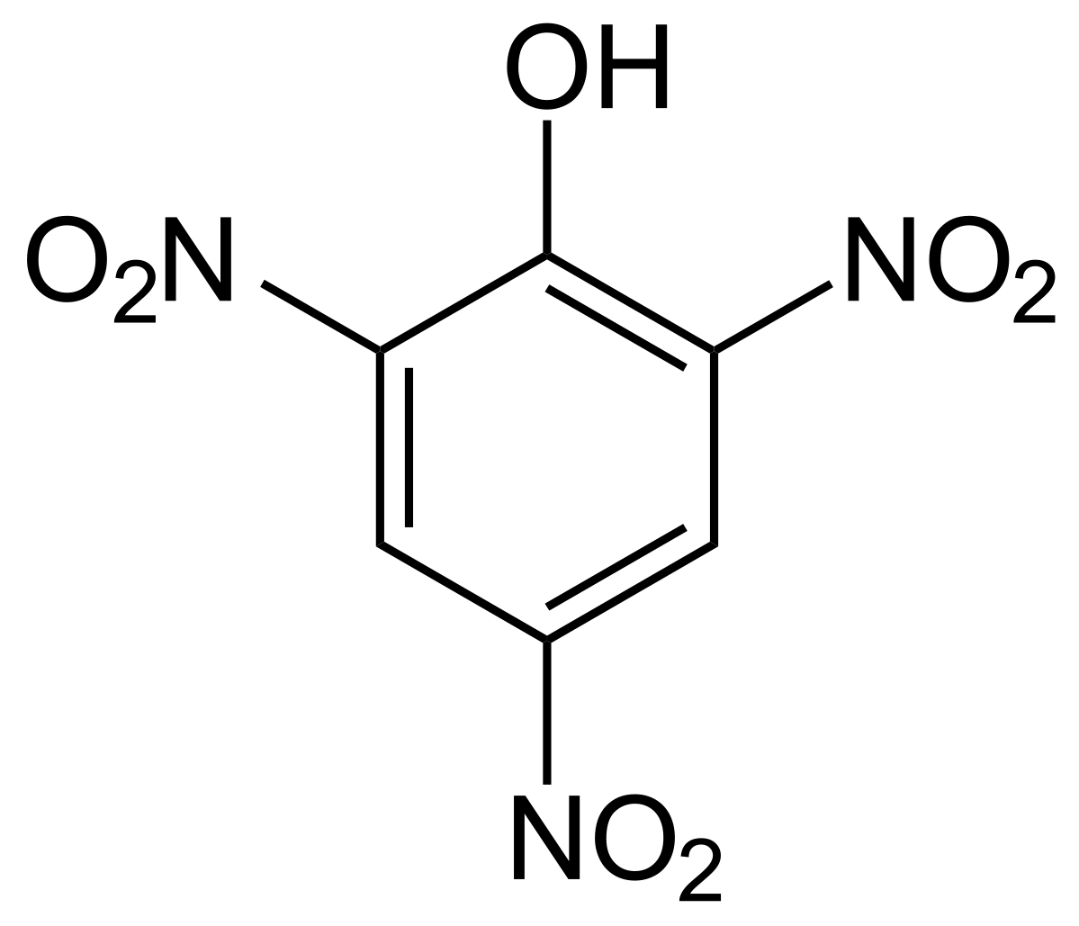 Classify the above molecule.
Classify the above molecule.
A. chromophore
B. chromogen
C. auxochrome
D. dye
D. dye
Upon completion of an H&E stain, you notice that the nuclei are red / red-brown. Why?
A. The eosin was too concentrated.
B. The hematoxylin was too oxidized.
C. The section was not dehydrated well before staining.
D. The section spent too long in the dehydrants.
B. The hematoxylin was too oxidized.
DNA hydrolysis and the removal of purine bases in the Feulgen reaction leaves which group available for binding by Schiff reagent?
(Bonus: Which are the purine bases?)
A. carboxyl
B. hydroxyl
C. phosphate
D. aldehyde
D. aldehyde
(Adenine and guanine.)
When and where did scientific cultivation of Hematoxylon campechianum begin?
A. 1715, Jamaica
B. 1765, El Salvador
C. 1815, Guatamala
D. 1865, Honduras
A. 1715, Jamaica
Why are iron hematoxylins preferred for special stains?
A. They provide a more vibrant stain.
B. They are less toxic.
C. They do not need to be ripened.
D. They resist decolorization by acid.
D. They resist decolorization by acid.
(Acids are common in special stains, but iron hematoxylins differentiate with excess mordant instead.)
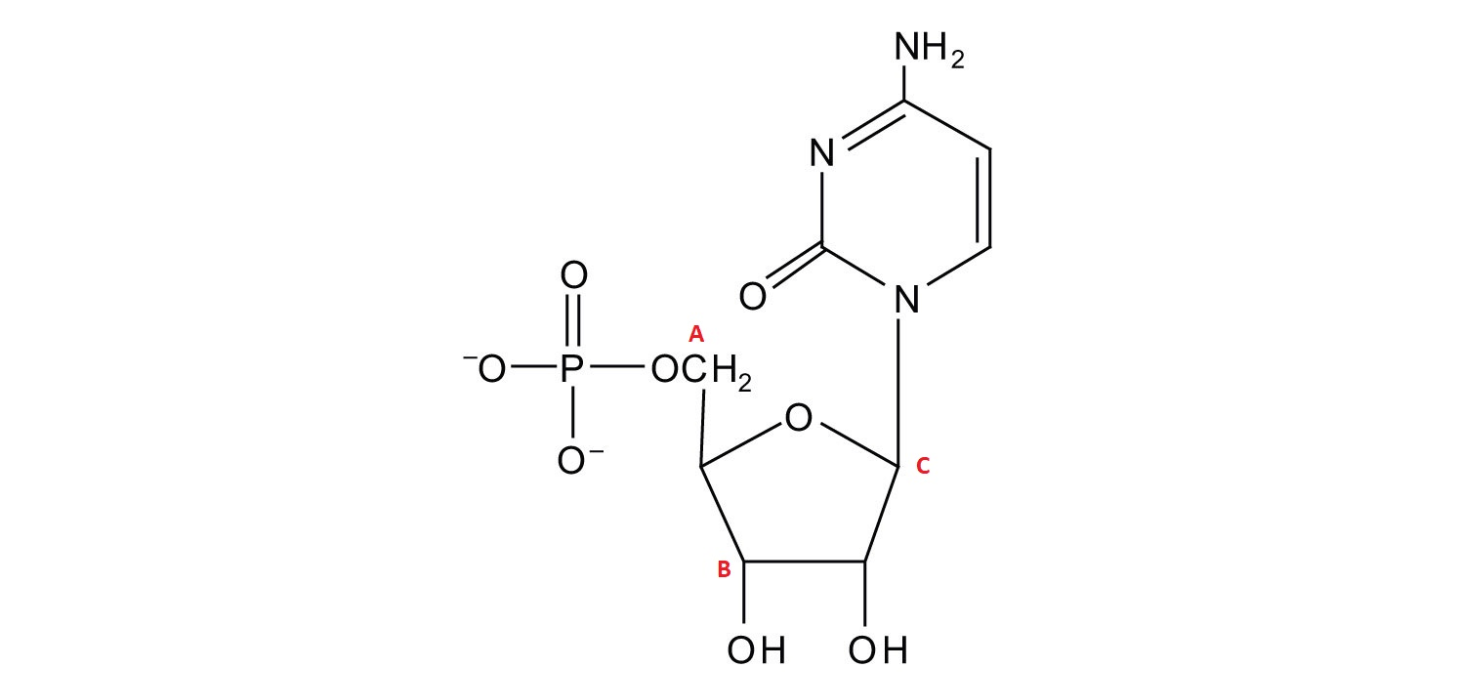
Given the molecular structure of a thymine segment of DNA above, if performing a Feulgen reaction which of the marked carbons would be the site of an aldehyde formation for Schiff reagent binding.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. None
D. None.
(Bonus: Why?)
Though you do not know the history of a sample prior to sectioning and H&E staining, which of the following could you infer is the most likely cause for the pale nuclei the completed section exhibits?
(Bonus: Why?)
A. The section spent too long in eosin.
B. A decalcifying solution was used
C. The section was allowed to dry before mounting.
D. The section was fixed with a Zenker solution.
D. The section was fixed with a Zenker solution.
(The acidity of the Zenker solution disrupts tissue's basophilia and thus inhibits binding of hematein.)
You wish to perform a Giemsa stain on tissue fixed with Zenker solution. Care must be taken to do which of the following:
A. work under a vented hood
B. maintain a pH below 6
C. remove mercury pigment
D. double the staining time of formalin-fixed tissue
C. remove mercury pigment
(Bonus:How?)