What is the name of the two round openings located in the lower portion of the pelvis?
What is the obturator foramen.
Why and how many degrees do you rotate the lower limbs inward for an AP pelvis?
What is to place the femoral necks parallel to the IR and what is 15 to 20 degrees internally.
What is the name of the bony structure on the pelvis that cannot be palpated (because it is inside the body)?
What is the ischial spine.
Where is the CR for an AP pelvis?
Where is midway between the ASIS and symphysis pubis?
Name the position that best demonstrates signs of developmental dysplasia of the hip.
What is AP bilateral modified Cleaves method?
Name the bones that fuse to form the acetabulum.
What are the ischium, pubis, and ilium.
In an AP bilateral modified Cleaves method, what is the ideal amount of abduction recommended to minimize foreshortening of the femoral necks?
What is 20 to 30 degrees?
When using the hip localization method, what two bony landmarks are palpated?
What are the ASIS and the symphysis pubis.
In an AP Axial Taylor Method "Outlet," what is the degree of angulation of the CR for a male patient?
What is 20 to 35 degrees cephalad.
What is the name of the projection to rule out a subtle fracture of the lower pelvic ring?
What is the bilateral Judet method.
This pelvis has a narrow, deep, less flared pelvis. The pelvic inlet is heart-shaped. One term associated with this pelvis is "android." Is this a male or female pelvis?
What is a male pelvis?
You are told to perform a posterior axial oblique projection for the acetabulum (Teufel method). How many degrees do you rotate the body?
What is 35 to 40 degrees.
When using the hip localization method, how can the femoral head be found?
What is palpate 1 1/2 inches distal to the midpoint of the imaginary line between the two bony landmarks?
What is the CR angle for the AP axial inlet projection?
What is 40 degrees caudad.
A patient enters the ED having sustained a trauma to the pelvis. The left hip hurts. What image is taken first to rule out fracture or dislocation?
What is an AP Pelvis.
Which of the following letters is associated with the femoral head?
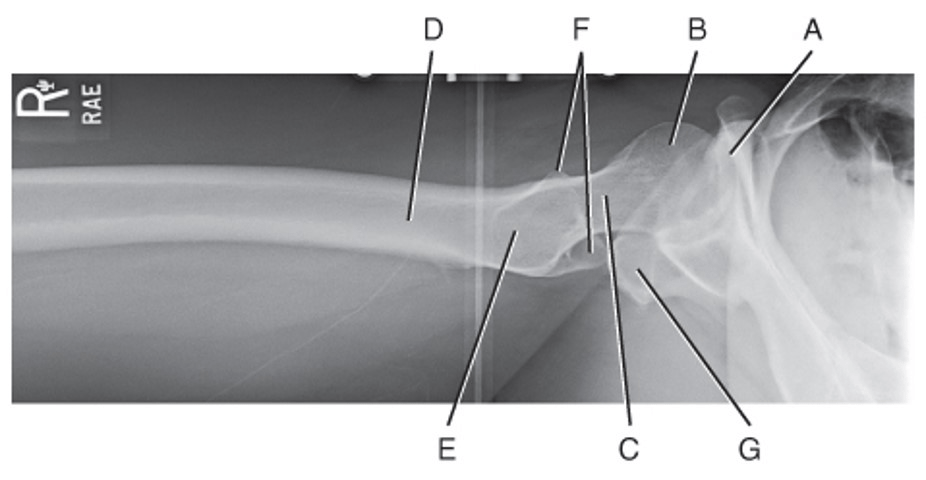
What is B?
In a posterior axial oblique projection for the acetabulum (Teufel method), what is the CR angle?
What is 12 degrees cephalad.
The AP image of the hip does not show the entire hip prosthesis; however, the complete hip prosthesis is visible in the lateral image. What do you do?
What is repeat the AP image?
You are performing a Clements-Nakayama modified axiolateral projection of the hip. From horizontal, what is the required CR angle?
What is 15 to 20 degrees from horizontal.
What is the name of the condition that produces the radiographic sign referred to as a bamboo spine?
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis.
The SI joints are classified as _______ joints with _______ movement type.
What is synovial and irregular gliding.
What is the name of the method that tilts the IR 15 degrees from the vertical plane?
What is the Clements-Nakayama Method.
To determine the position of the femoral head and femoral neck, you must palpate the symphysis pubis. Since we no longer palpate the symphysis pubis, what structures are at the same level as the symphysis pubis?
What are the greater trochanters.
In an AP Axial Taylor Method "Outlet," what is the degree of angulation for a female patient?
What is 30 to 45 degrees cephalad.
What is the name of the pathologic condition often associated with males older than age 45?
What is Chondrosarcoma.