What are the 3 parts of the cell theory?
1. All living things are made of cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function for living things
3. Cells come from pre-existing cells
What is the job of the Nucleus
to control the activities of the cell, store and transmit DNA and signals
This organelle is responsible for making Proteins
Ribosomes
What is E pointing to?
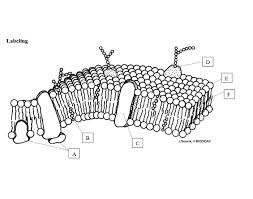
phosphate head
Sperm cells
All specialized cells start as this. They are a unique type of cell, because, while they're immature cells without any specialization, they can follow a developmental "blueprint" to develop into the thousands of unique cell types found throughout your body.
Stem Cells
Which scientist was the first two observe living organisms under the microscope and called them Animalcules
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
To build ribosomes
cell membrane
What is F pointing to?
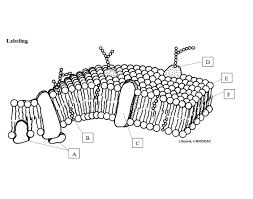
Fatty acid tails
Type of animal specialized cell that are thin, long and branched; they also send signals and messages throughout the body
Nerve Cells
What is the function of Phloem?
Who is the scientist that first saw cells?
Robert Hooke
What is the job of the cell wall? *be specific*
Surrounds a plant cell and supports its structure
provides extra structure and support to the plant cells
This organelle is responsible for the clean up of unwanted material in the cells and even dispose of dead or ‘broken cells’
Lysosomes
What is B pointing to?
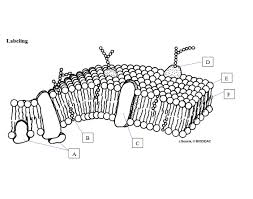
Cholesterol
A specialized cell that is small, biconcave, and carries the oxygen around the body attached to hemoglobin
Red Blood cells
What is the function of Xylem?
To transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. This travels on way- up the plant
What did Mathias Schielden and Theodor Schwann contribute to the cell theory? (Be specific)
Mathias stated that all plants are made of cells
Theodor stated that all animals are made of cells
The two parts of a plant cell that an animal cell does not have.
cell wall and chloroplast?
This organelle Contains chlorophyll - makes food for plants using energy from the sun.
chloroplasts
What is C point to? *a type of protein*
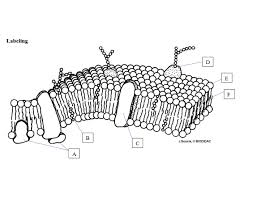
Integral Protein
Specialized cells that make movement possible. These cylindrical cells are made up of banded fibers that allow for contraction.
Muscle cells
What is the function of Root Hair Cells?
To absorb and store water and minerals from the soil
Who stated that all cells come from pre-existing cells?
Rudolf Virchow
What is the job of the Golgi Body
It modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the ER for storage in the cell or release outside the cell
Name any 2 structures that both animal and plant cells have
What is a vacuole, cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, ribosomes, Golgi body, ER
What is D pointing to?
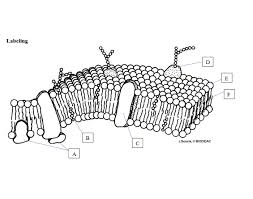
Glycoprotein
An animal specialized cell that works to keep the human body free of infection. These cells find and destroy microbes within the human body, responding to and treating infection.
White blood cells
To make energy and perform photosynthesis. It does this by having lots of chloroplast