This is the definition of...

ABILITY
How many Skilled Performance Characteristics are there?
6
Name the three Skills Continua
Basic and Complex
Fine and Gross
Open and Closed
Name the 4 Stages of the Information Processing Model.
1. Input
2. Decision-Making
3. Output
4. Feedback
Identify the 3 Stages of Learning.
1. Cognitive
2. Associative
3. Autonomous
Identify the Four Different Types of Feedback
-Intrinsic
-Extrinsic
-Knowledge of Performance
-Knowledge of Results
Identify and describe the 4 different types of guidance
Verbal - In the form of words
Visual - In the form of images, video or demonstration
Mechanical - The use of physical supports/tools such as harnesses
Manual - ‘Hands on’ guidance
This is the definition of...

SKILL
Aesthetically Pleasing - a display that looks good to the eye of who?
The Spectator, Judge, or Coach.
1. More difficult skills that require a higher level of coordination and concentration are known as...
2. Simple skills that do not require a high level of coordination and concentration are known as...
1. Complex Skills
2. Basic Skills
Explain the difference between Short-Term and Long-Term Memory
1. Short-Term Memory stores small amounts of info while Long-Term Memory can store vast amounts of info
2. Short-Term Memory holds info for a short time while Long-Term Memory holds info for a longer period of time
Identify this Stage of Learning
This Stage of Learning is also known as the practice stage. You continue repeating and practicing skills and techniques so that they improve.
Associative Stage
TRUE or FALSE - Intrinsic Feedback is good for performers in the Cognitive Stage of Learning (Beginners)? JUSTIFY YOUR ANSWER
FALSE - They don't have the skills or knowledge to understand they performance and need support from a coach
Which type of Guidance is represented in this photo?
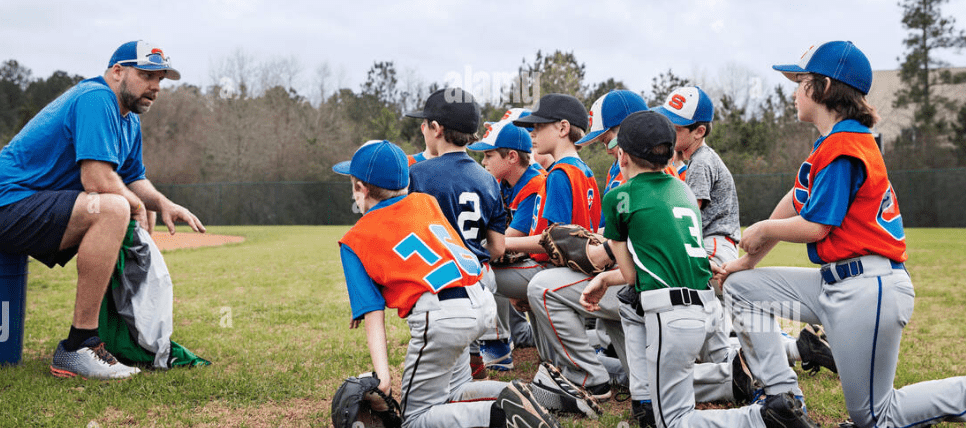

Verbal Guidance
Explain how the factor - Age and Maturity affect skill level?


Using movements that are quick, smooth and flowing, without hesitation or stumbling defines which characteristic of a skilled performance?
Fluent
1. Skills that are not affected by the environment or the performers within it are known as...
2. Skills that are affected by the environment are known as...
1. Closed Skills
2. Open Skills
Explain the concept of Single-Channel Hypothesis.
When receiving many stimuli from the environment, the brain can only deal with one thing AT A TIME/AT ONE TIME. Until one stimulus has been dealt with, another cannot be acted upon.
Identify the Stages of Learning Describe below
A

B

C

A - Associative Stage
B - Cognitive Stage
C - Autonomous Stage
Give 2 Reasons - why feedback is important when learning or developing a skill?
Identifies strengths so they can be built on
Identifies weaknesses to work on
Stops mistakes being repeated
See if extra training or practice is needed
Set goals or targets for improvement
Motivates performer/develops self-esteem
Allows comparison to the ideal performance
TRUE or FALSE - Visual Guidance is most effective at the Autonomous Stage of Learning.
FALSE - Visual Guidance is most effective at the Cognitive Stage of Learning.
Explain how the factor - Arousal Conditions affect skill level.
1. Under Arousal/Overarousal results in a lack of focus which results in low skills levels
2. A performer who prefers low arousal activities (calm) may perform well w/ fine motor skills (archery)
3. A performer who prefers high arousal activities may perform well w/ gross motor skills (football/boxing)
These are examples of which characteristic of a skilled performance?
Example 1 - Badminton players are focused on winning each point and use tactics, select shots that help them achieve this.
Example 2 - The football player follows the coaches game plan (ie - kicking the ball across the pitch when a player is unmarked)
-Goal Directed - Focusing performing on a specific target and being determined to achieve that target. All actions in sport should be directed towards a goal.
1. Skills that require large muscle groups, powerful movements, and use the while body are known as...
2. Precise, small movement that require small groups of muscles, like the fingers, and high levels of accuracy and technique
1. Gross Skills
2. Fine Skills
When receiving a tennis serve, using your eyes to see the speed of the ball, direction of the ball, and position of your opponents is an example of which of the 4 Stages of Information Processing Model.
Input
These examples describe which Stage of Learning?
-Needs lots of guidance from a coach
-Learning a new skill
-Beginner who is trying to understand the demands of the skill
-Consciously thinks about what to do
Cognitive Stage
Which two types of feedback are most suited towards performers in the Autonomous Stage of Learning?
1. Intrinsic
2. Knowledge of Performance
Autonomous performers are able to judge how well they performed and can work out their mistake by themselves
What are two advantages of Visual Guidance?
-Performers can form a mental picture of correct performance
-Demonstrations can be repeated if necessary
-Slow-motion video can be used to focus on specific sub-routines of a skill
-Useful in all stages of learning
Identify & Describe the 8 Key Factors that can affect the variation of skill level in a performer.
1. Age & Maturity
2. Arousal Conditions
3. Facilities
4. Environment
5. Teaching & Coaching
6. Anxiety
7. Motivation
8. Culture
Identify and Define the 6 characteristics of a Skilled Performance


Give an example of each of the following and justify each:
-Open Skill
-Closed Skill
-Basic Skill
-Complex Skill
-Gross
-Fine
Many Possible Answers
Identify and Describe each of the 4 Stages of the Information Processing Model.
1. Input - information is received via the senses. The performer must ‘select’ the most important information to focus on
2. Decision-Making - The information is analysed and a decision is made. If the situation has been experienced many times before, the performer will have information in their long-term memory.
3. Output - The decision is made and acted upon. The brain sends information to the muscles. The muscles contract creating movement and the skill is performed
4. Feedback - Information is received about the outcome (‘how successful was I?’). This knowledge will be initially stored in short-term memory, but will be moved to the LTM if the skill is practiced many times. This will help the performer to improve their decision making next time.
Name 3 Characteristics of a performer is the Autonomous Stage of Learning.
-Makes few mistakes and can identify what went wrong
-Able to perform the skill without conscious thought
-Able to analyze own performance/uses intrinsic feedback
-Able to use verbal feedback and understand technical language
-Links skills smoothly w/ flair, control and accuracy
-Consistent successful outcome
-Able to Adapt to different situations
Which two types of feedback are most suited towards performers in the Cognitive Stage of Learning?
1. Extrinsic
2. Knowledge of Results
Cognitive performers have not developed a feel for the skill/their performance and need lots of guidance from a coach
The following are disadvantages of which type of Guidance?
-Learners can come to depend on support from coach/equipment
-Can give learners an unrealistic feeling of the motion (e.g. when they do not support their full body-weight in gymnastics)
-Learners may resist having manual/mechanical guidance taken away
Manual/Mechanical Guidance