A, T, C , G
What bonds with what?
A -- T
C--G
This joins nucleotides to synthesize a new complimentary strand of DNA.
What is DNA polymerase?
What are the three main types of RNA
tRNA, mRNA, rRNA (transfer, messenger, ribosomal)
Group of three nucleotide bases in mRNA that specify a particular amino acid to be incorporated onto a protein.
What is a Codon?
A group of genes that are regulated together.
What is an Operon?
A gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed
What is a point mutation
Which nitrogenous base is represented by the letters in DNA? (A,T,C,G)
A= Adenine
T= Thymine
C= Cytosine
G = Guanine
The tips of eukaryotic chromosomes that are associated with aging.
What are telomeres?
Which nitrogenous base is represented by the letters in RNA? (A,U,C,G)
A= Adenine
U= Uracil
C= Cytosine
G = Guanine
The process by which the sequence of bases of an mRNA is converted into the sequence of amino acids of a protein.
What is Translation?
A group of homeotic genes clustered together that determine the head-to-tail identity of body parts in animals.
HOX genes
A mutation that shifts the “reading frame” of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
What is a frameshift mutation?
What holds the 2 strands of DNA together?
Hydrogen Bonds
 What is represented by the letter d?
What is represented by the letter d?
Replication Fork
The process of copying a base sequence from DNA to RNA is know as what?
Transcription
What would be the anticodons for the below mRNA sequence?
AUG, GUU, AAC
UAC, CAA, UUG
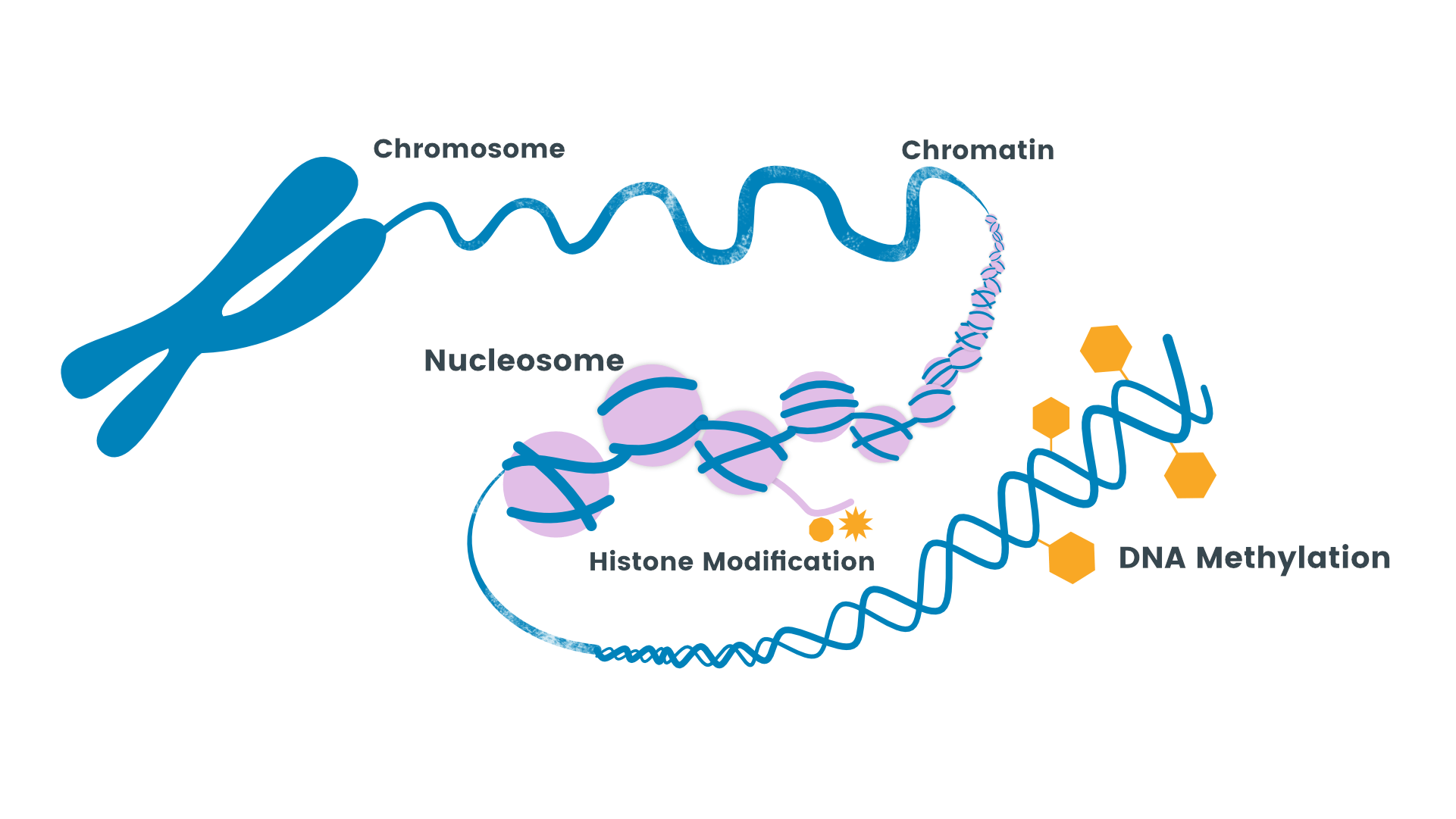 What is depicted in the image above?
What is depicted in the image above?
Epigenetics
Tobacco smoke, certain pesticides, UV light, and X-Rays are examples of these.
What are Mutagens?
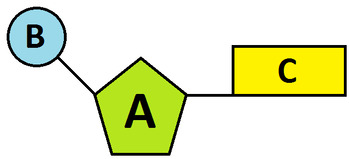
What part of a DNA nucleotide is represented by each letter?
A = 5 Carbon Sugar (Deoxyribose)
B= Phosphate Group
C = Nitrogenous Base
How does DNA replication differ between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes- starts from a single points and proceeds in two directions until entire chromosome is copied
Eukaryotes- Starts at dozens or hundreds of points on the DNA molecule. Then proceeds in both direction until each chromosome is copied.
What would the complimentary RNA strand for the DNA sequence below be?
AATCGT
UUAGCA

What amino acid would the codons CAA and AGC code for?
CAA - Glutamine
AGC - Serine
Explain the environmental conditions necessary for E. coli Lac genes to be turned on. (Think Lac Operon)
Lactose must be present and Glucose must be absent
This condition is generally lethal in animals, but could be considered beneficial for plants, being associated with larger and stronger plants.
What is polyploidy?