Manual published by the America Psychiatric Association (APA) used to diagnose psychological disorders
DSM-5
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
"Bible of psychiatry"
Explain anxiety
1. Unpleasant feeling of tension
2. Physiological arousal (heart rate)
3. Apprehension or worry in anticipation of a threat
- Anxiety is future-oriented, not present-oriented like fear.
Describe Schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia is a group of related psychotic conditions characterized by severally distorted perception and experience of reality, disorganized thought and speech, and inappropriate emotions and emotional responses.
- Key symptoms are the two positive symptoms of hallucinations and delusions
True or False:
The point of behavior therapy is to teach a client how to substitute adaptive patterns of behavior (good) for maladaptive patterns (bad).
True!
Mood stabilizers are used to treat bipolar disorder. Which common mood stabilizer is unique among drugs used to treat disorders because it is a naturally occurring body salt? It can also come with serious side effects as well.
(300 Points instead of 100)
Lithium

Explain Psychotherapy (first page of the chapter)

Unique, modern, healing relationship between a client and a paid therapist. The relationship is temporary and focused entirely on the needs and problems of the client. Each meeting between a therapist and client is time-limited, confidential, and conducted in a structured setting.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/types-of-psychotherapists-5188864-DD-V4-0b63a7e5d34e47a4942a02180e5f832a.jpg)
According to the DSM view, for something to be a psychological disorder, it must have two conditions. What are those two?

1. Dysfunction --> Breakdown in mental functioning
2. Distress --> Upset
Explain depression
Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, grief, guilt, and low feelings of self-worth.
What are the two key positive symptoms of schizophrenia?
1. Hallucinations
2. Delusions

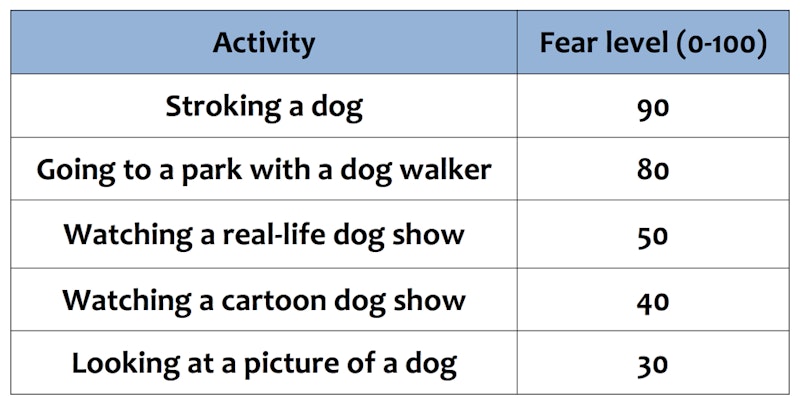
Explain systematic desensitization or flooding
1. Controlled, incremental exposure to phobic stimuli (anxiety hierarchy) while simultaneously practicing relaxation techniques that are incompatible with anxiety
2. Non-incremental, total immersion in anxiety-producing phobic stimuli for a prolonged period

Two parts:
1. True or False: Anxiety is treated with anxiolytics (angk·see·uh·li·tuhks)
2. The most common anxiolytic drug to treat anxiety is SSRI's
1. True!
2. False! It is benzodiazepines, i.e. Xanax. SSRIs are antidepressants, which are used to treat depression.
To treat depression, what type of medications are used?
SSRIs, a type of antidepressant drug
True or False:
In the United States the main goal is to institutionalize people in mental institutions/wards, instead of trying therapy of medications.
False!
The United States has a policy of Deinstitutionalization (pg. 621)

What psychological disorder used to be considered an anxiety disorder and is characterized by obsessions and compulsions?
OCD
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-different-types-of-ocd-2510663_color3-5b3f8fda46e0fb00370d01bf.png)
True or False:
In schizophrenia, positive symptoms we add something (hallucinations, delusions) and negative symptoms we remove something (depression). They do not mean "good" or "bad."
True!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-symptoms-of-schizophrenia-2953120-e15ca22957ec44ff8969cf9b8ac24568.jpg)
True or false:
Behavior therapy consists of exposure and cognitive therapy.
False.
Behavior therapy consists of exposure and operant therapies.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exposure-therapy-definition-techniques-and-efficacy-5190514_final1-d55b6157d7de44ffabb7615fb2e75ecf.png)
True or False:
The goal of an effective treatment in Psychotherapy is to not just achieve statistical significance, but to achieve efficacy. Where the outcome of the treatment is large enough that it would be effective in the real world outside the laboratory.
False!
It is to achieve clinical significance.
- Efficacy only shows how statistically superior a treatment is to a placebo in a clinical trial
- An effective treatment shows it has significance in the "real world" to clinicians, hospitals, clinics, etc.

What medication is used to treat schizophrenia?

Antipsychotics
- Reduces the severity of positive symptoms
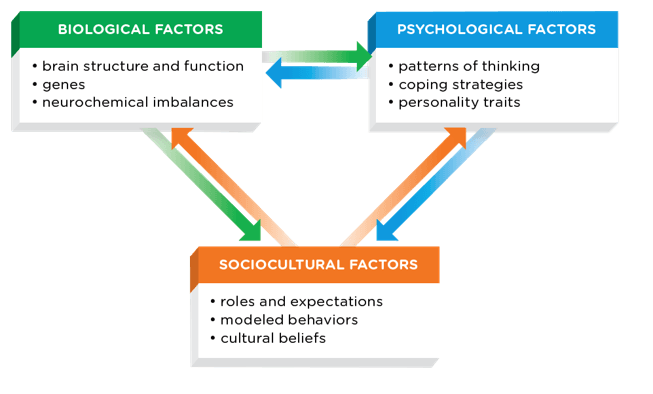
There are three factors/causes of psychological disorders
1.
2. Psychological
3.
1. Biological
2. Psychological
3. Sociocultural
- Depression is not simply a chemical imbalance
What two mood disorders make up bipolar disorder?
1. Depression
2. Mania
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/379962-bipolar-disorder-symptoms-and-diagnosis-5b1150af3418c60037552e47.png)
Describe delusions of grandeur or delusions of persecution.
1. The belief that one is a person of importance and accomplishment, such as a U.S. present or even a holy person such as Jesus Christ or Buddha
2. The idea that people are to do one harm
What are a few techniques of classical psychoanalysis?

1. Dream Work --> where patients' dreams are interpreted by an analyst
2. Free Association --> allow unconscious material to be expressed without censorship from the patient's conscious mind
3. Transference --> belief that patients in therapy may transfer their feelings about important people in their lives (even themselves) onto the therapist
Who founded client-centered therapy? A humanistic form of therapy where the goal is to promote personal growth in the client in a nondirective manner by treating the client with empathy and unconditional positive regard?
Carl Rogers
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CarlRogers-5c78400d46e0fb00011bf28e.jpg)
Explain the Myth of Mental Illness by Thomas Szasz

Mental "illnesses" do not exist and are social judgments about people's unusual behavior. He denounced the medical model of mental illness, which views psychological disorders the same as physical illnesses.
Explain Mania.
Highly energized mood state characterized by exaggerated feelings of elation, unrealistically high self-esteem, racing thoughts, reduced need for sleep, and ceaseless energy.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-recognize-a-manic-or-hypomanic-episode-380316-5c4548cdc9e77c000161b239.png)
Describe either borderline or paranoid personality disorder.
2. Sufferers have an unstable sense of self and often engage in self-injuring behavior
What is the goal of classical psychoanalysis?
Also, are we analyzing the unconscious or conscious?
To obtain insight — awareness of what is unconscious

Who is the pioneer of cognitive therapy and then went on to develop rational-emotive behavior therapy (REBT)?
Albert Ellis
- Believed that humans can be taught to control their feelings by controlling their thoughts
- REBT is directive — the therapist's job is to forcefully dispute the client's illogical and unrealistic beliefs.

