tissue
What are the three basic plant organs and explain a function of each of them
roots:
Stems:
Leaves:
Name a system and its main components.
Ex. Digestive System: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, etc.
Is Professor Mokrzan an endotherm or ectotherm and why?
Endotherm, humans are less dependent on the external environmental temperatures.
What is a biome
all communities within a specific environmental region
Name and explain an example of a differentiated plant cell.
Parenchyma: large central vacuoles, thin flexible primary cell walls, no secondary walls, relatively undifferentiated at maturity
Collenchyma: grouped in strands, have thicker uneven cell walls, lack secondary walls, remain alive at maturity
Sclerenchyma: Thick secondary cell wall, large amounts of lignin, mature cells are dead
Name a few differences between primary and secondary growth...
- Primary growth has apical meristems
- lateral meristems are in the secondary growth
- primary growth is growing in length
- secondary growth is grows in width and thickness - secondary growth has vascular cambium and cork cambium
Give an example(s) of negative and positive feedback.
Negative feedback: the regulation of blood sugar and temperature, etc.
Positive feedback: baby drinking milk
What are the four types of heat exchange?
Convection, conduction, radiation, and evaporation
What is immigration and emigration?
Immigration- in, births
Emigration- out, deaths
Which of the following arise, directly or indirectly, from meristematic activity?
secondary xylem, leaves, dermal tissue, all of the above
all of the above
Joke: What did one leaf say to the upset leaf?
Hint: It has something to do with the epidermal pores formed by pairs of guard cells, which allows for gaseous exchange and are major avenues for water loss.
What's STOMATA with you??
What properties do all types of epithelia share?
All types of epithelia consist of cells that line a surface, are tightly packed, are situated on top of a basal lamina, and form an active protective interface with the external environment.
Basal lamina- the basal surface is attached to a basal lamina, a dense mat of ECM that separates the epithelium from the underlining tissue
Define thermoregulation and give an example of an endotherm and ectotherm.
Thermoregulation- how an animal maintains its internal temperature within a tolerable range
Endotherm- animals generate heat by the internal source of metabolism; can maintain a stable body temperature in the face of large fluctuations in the environmental temperature; ex. polar bears, penguins, prairie dogs
Ectotherm- animals gain heat from external sources; may regulate temperature by behavioral means; ex. fish, reptiles, invertebrates
Clumped, uniform, and random.
How do the root system and shoot system work together with xylem and phloem?
The root system is the below the soil with the roots, and the shoot system is above the soil with the stems and leaves.
The root system is in charge of the xylem with bringing water from the roots up to the stem and leaves. The shoot system is in charge of the phloem with food production (photosynthesis) and reproduction.
What are the types of tissues (3 of them)?
1. The dermal tissue is the plant's outer protective covering and acts as the first line of defense against physical damage.
2. The vascular tissue facilitates the transport of materials through the plant and provides support (xylem and phloem).
3. The ground tissue is between the dermal and vascular tissue. It includes the pith and the cortex.
What are some life challenges in plants and animals?
Nutritional mode, growth and regulation, environmental response, transport, reproduction, absorption, and gas exchange.
What are the four types of tissues and tell us one thing about each
Epithelial- exterior surface of organ
Connective- Forms structure of organs. elastic and collagenous fiber for binding
Nervous- Receives and processes stimuli.
Muscle- responsible for voluntary movement
Name 2 terrestrial and aquatic biomes
desert, chaparral, temperate grassland, tropical forest, savanna, temperate broadleaf forest, northern coniferous forest, tundra
wetlands and estuaries, lakes, streams and rives, intertidal zones, coral reefs, oceanic pelagic zone, marine benthic zone
Name and illustrate three differences between a monocot and a eudicot.
Monocot: one cotyledon, veins usually parallel, vascular tissue scattered, many roots, pollen grain with one opening, floral organs in multiples of 3
Eudicots: Two cotyledons, veins usually netlike, vascular tissue is arranged in a ring, a main root or taproot, pollen grain with 3 or more openings, floral organs usually in multiples of 4 or 5.
Name as many evolutionary leaf adaptations as you can.
Rhizomes, Stolons, Tubers, Tendrils, Spines, Storage Leaves, Reproductive Leaves
What is the difference between endocrine and nervous system?
Nervous system- fast response, sense and respond to stimuli, deliberate movement with coordination.
Endocrine system- slower response, long term, coordination of digestion, hormone made by the glands and released into the bloodstream.
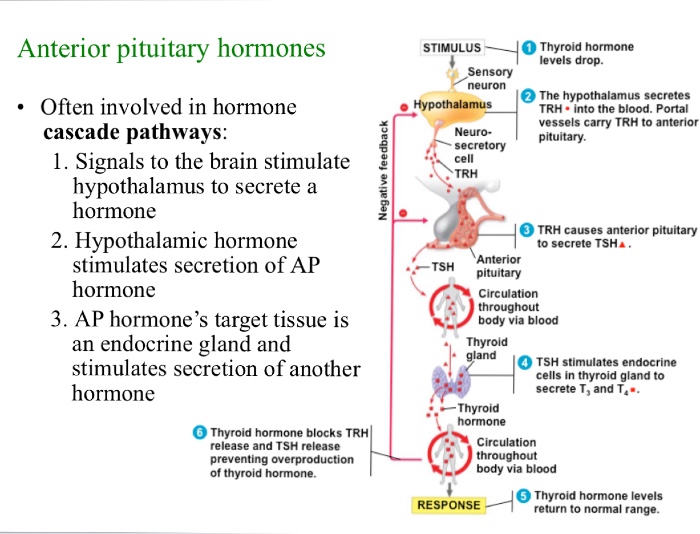
Explain hormone cascade pathway
What shape does the exponential growth show on a graph?
J shaped