True or False. Prokaryotic cells have both cilia and flagella
False. Prokaryotic cells only have flagella. Their flagella are not the same as those of eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic flagella are composed of the protein flagellin and have rotating device embedded in the plasma membrane structure to rotate it.
True or False. Mitochondria are only found in eukaryotic animal cells.
False. In ALL eukaryotic cells
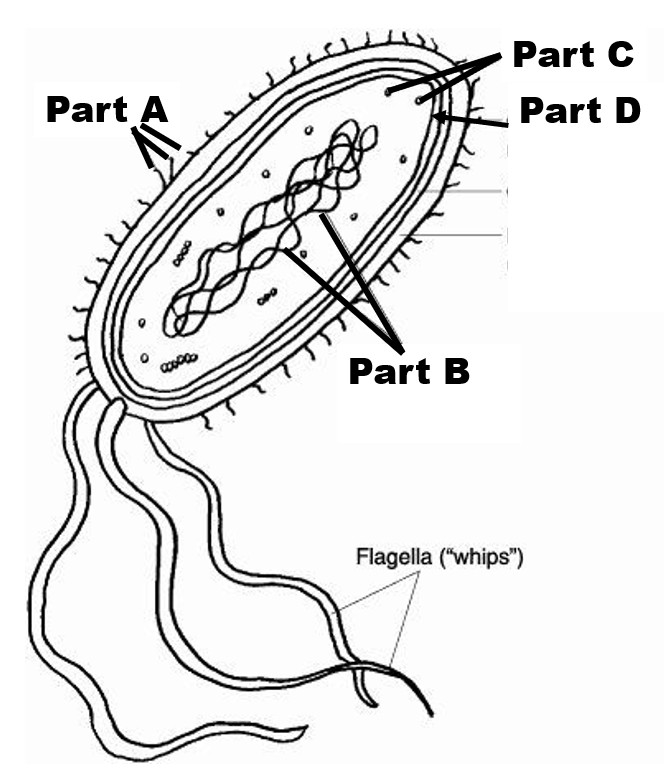
Identify Part A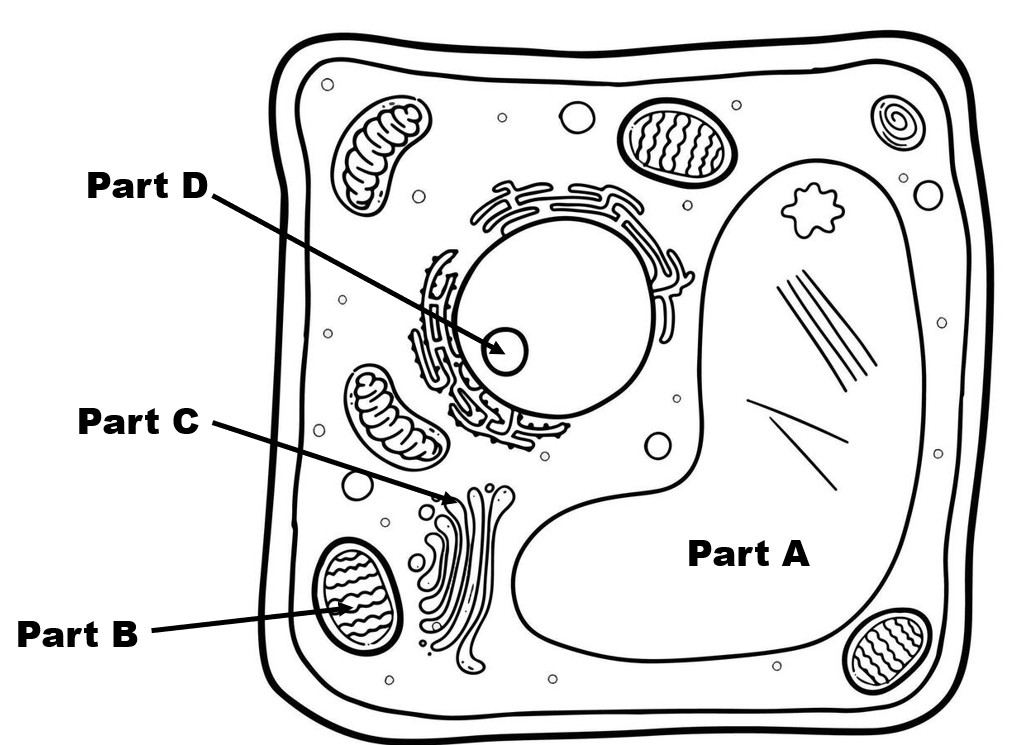
large central vacuole
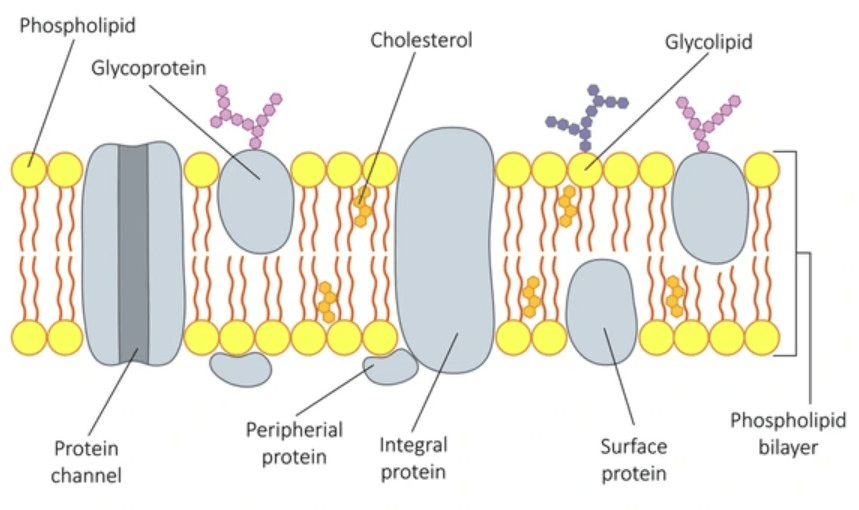
What is the purpose of glycolipids and glycoproteins?
Cell identification
What molecule do you need to carry out active transport?
ATP adenosine triphosphate (energy molecule)
Moving from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration through a protein
Facilitated diffusion
What is the name of the protein that water uses to moves through the plasma membrane?
Aquaporin
What is the function of the capsule, on the outside of a prokaryotic cells?
prevent drying out (desiccation) and an additional defense for viruses and cells that want to destroy it (i.e. white blood cells/lymphocytes of immune system).
Unique to animal cells. This vesical full of hydrolytic enzymes is formed by the Golgi apparatus
lysosomes
Identify Part B
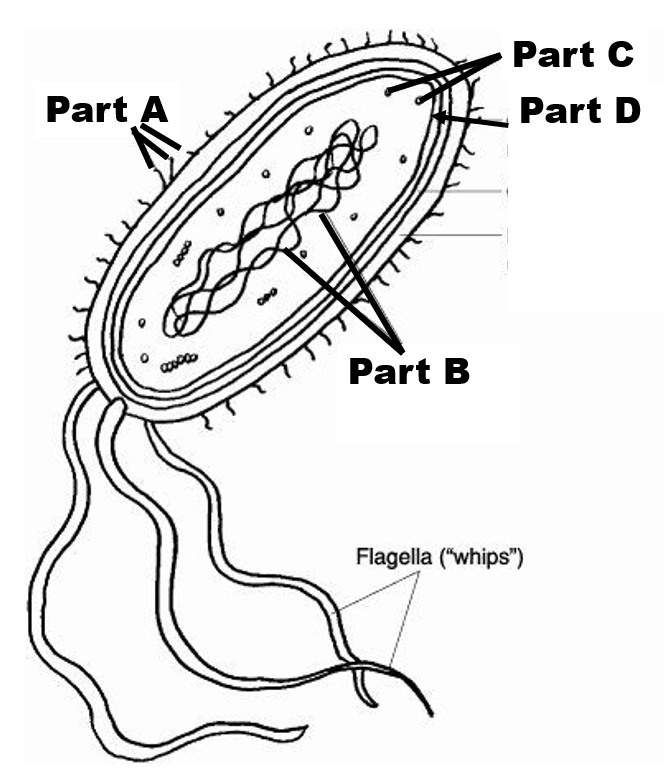
Circular genome the DNA of the prokaryotic cell
In the fluid bi-layer, phospholipids rarely move in this direction.
flip flop (aka. top layer to bottom layer)
This type of transport involves receptors to take in a vesical
Active transport-bulk transport (endocytosis)
What is this specific type of transport? Tell me 3 things that would move this way through the plasma membrane?
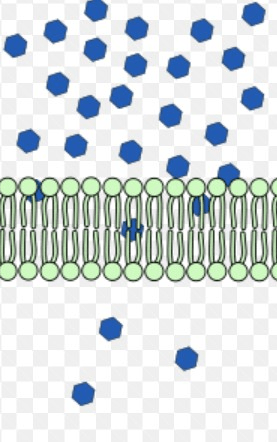
Passive transport simple diffusion. Gas (oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen), ethanol, lipids, water, small nonpolar substances.
What would you call the solution inside of the beaker? and Where will the water move?

hypertonic solution inside of the beaker. Will move from bag to the beaker (hypotonic to hypertonic)
Where is the genetic material (DNA) found in this cell type and in what format?
Cytoplasm of the cell and circular genome
Proteins like actin and tubulin are made by ribosomes to make microfilaments and microtubules, both components within the cell. Where are the ribosomes that assemble actin and tubulin located?
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Identify #1
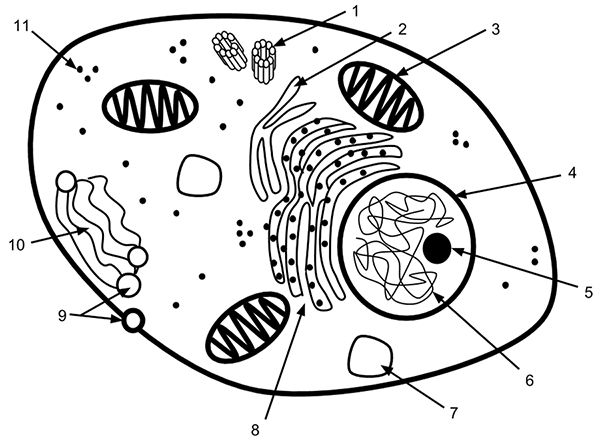
Centrioles (microtubles)
Longer fatty acid tails __________ plasma membrane fluidity.
decrease
Transport that moves substrates from high areas of concentration to low areas of concentration without expending energy
All types of passive transport
Name 3 molecules (i.e. substances) that will be moved via facilitated diffusion.
glucose, amino acids, large molecules, polar molecules, water
An ocean sunfish (Mola mola) is __________ to the _________ water it is in.
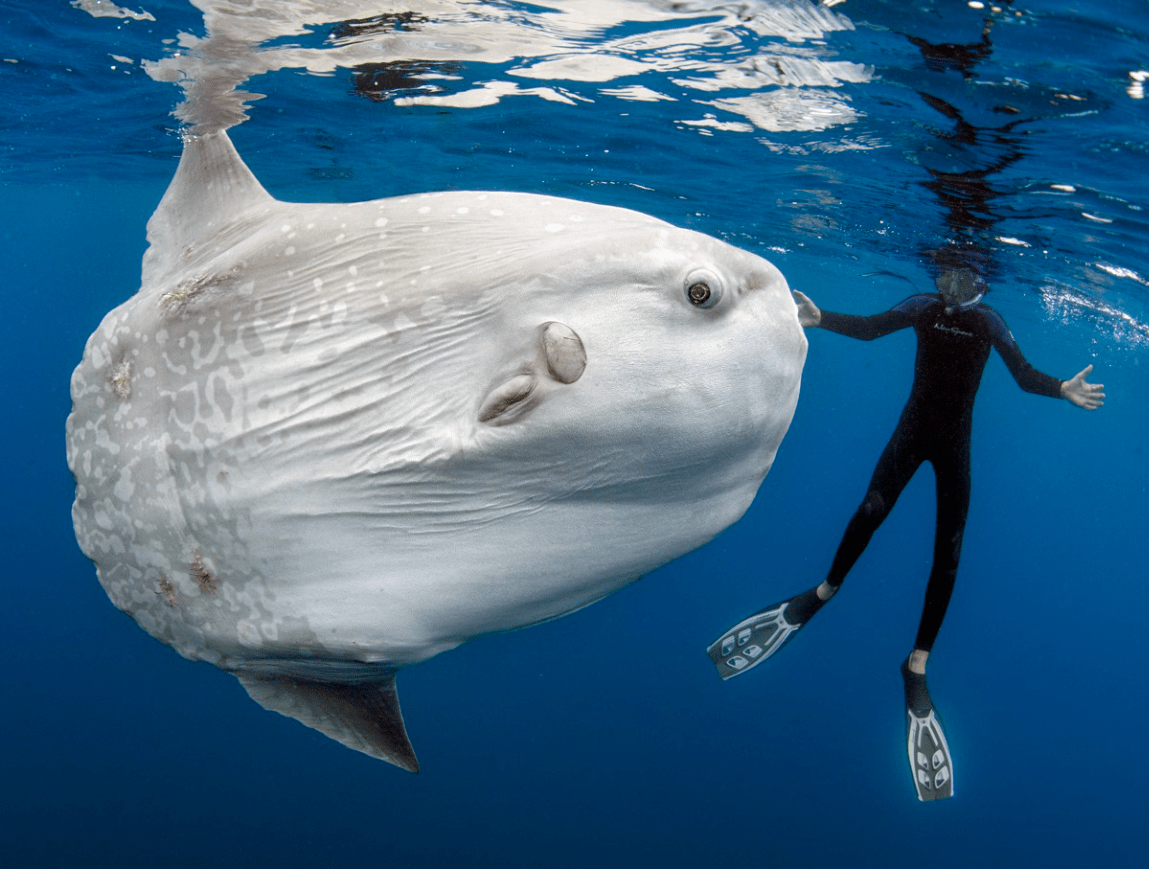

the fish is hypotonic to its hypertonic ecosystem (ocean/saltwater)
This prokaryotic cell structure will be made of peptidoglycan.
Cell wall
Liver and muscle cells would all have more of this organelle that detoxifies, stores calcium and hydrolyzes glycogen
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
Identify Part D
Plasma mebrane
Adding _________ to increase the fluidity of the membrane during cold temperatures is one thing a animal cell can do that a plant cell can't.
cholestrol
This type of transport uses a protein to move substances through
BOTH passive and active transport
The secretion of proteins and neurotransmitters from a cell.
Exocytosis (Active transport)
A celery stalk is placed in a glass of seawater. How will the water move and what will happen to the plant cell?
The seawater is hypertonic to the plant cells (hypotonic) so water will passively leave the plant cell for the glass where water is low. The plant cell will crenate or plasmolysis
Draw the phospholipid bilayer correctly. Be sure to include carbohydrate, lipid, and protein structures with it.
This part/structure can be found in the cytoplasm, mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum and chloroplasts.
ribosomes
Identify # 8
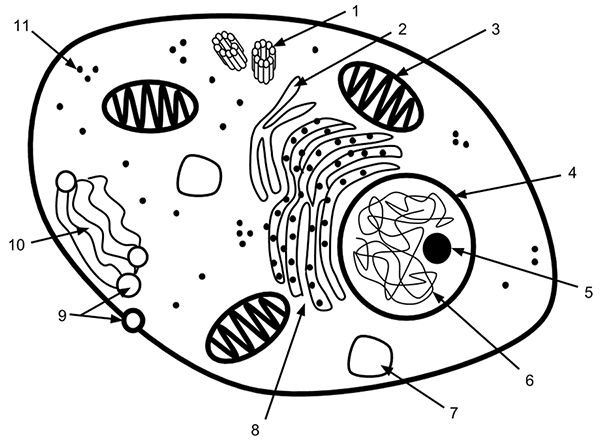
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
What will warmer temperatures and excess cholesterol do to the fluidity of the plasma membrane?
make it more fluid
Movement of water through an aquaporin
passive transport-facilitated diffusion
What specific type of transport is represented in this image?
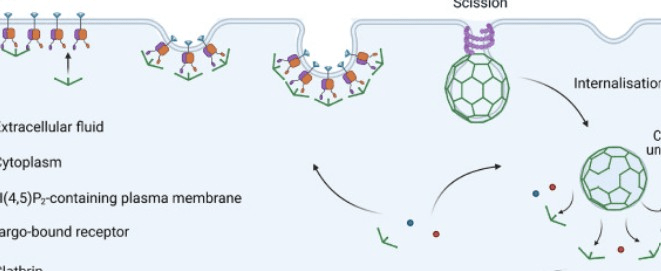
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
What direction will the sucrose move?
What direction will the water move?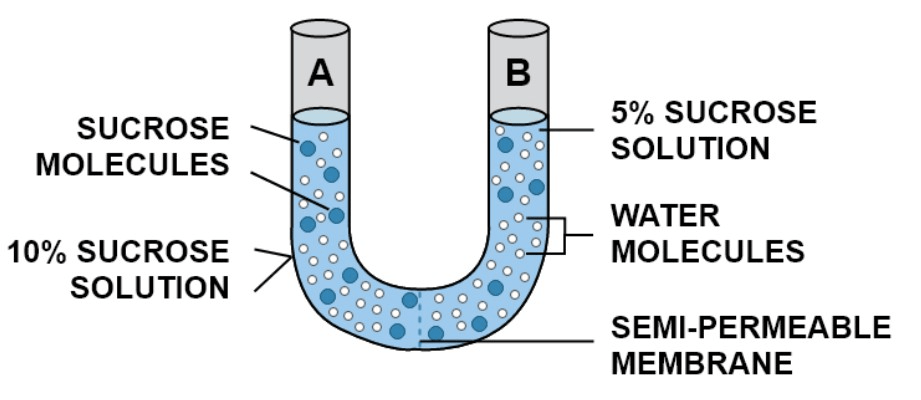
Sucrose will move from side A to B
Water will move from side B to A
What 2 important complex metabolic reactions take place on the infolds of the prokaryotic plasma membrane?
aerobic cellular respiration (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus species, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Escherichia coli) and photosynthesis (ex. cyanobacteria)
Name 3 eukaryotic cell parts that are a result of (linked with) endosymbiotic theory?
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts (only in plant and algal cells)
Golgi apparatus
Rough and smooth ER
Identify Part D
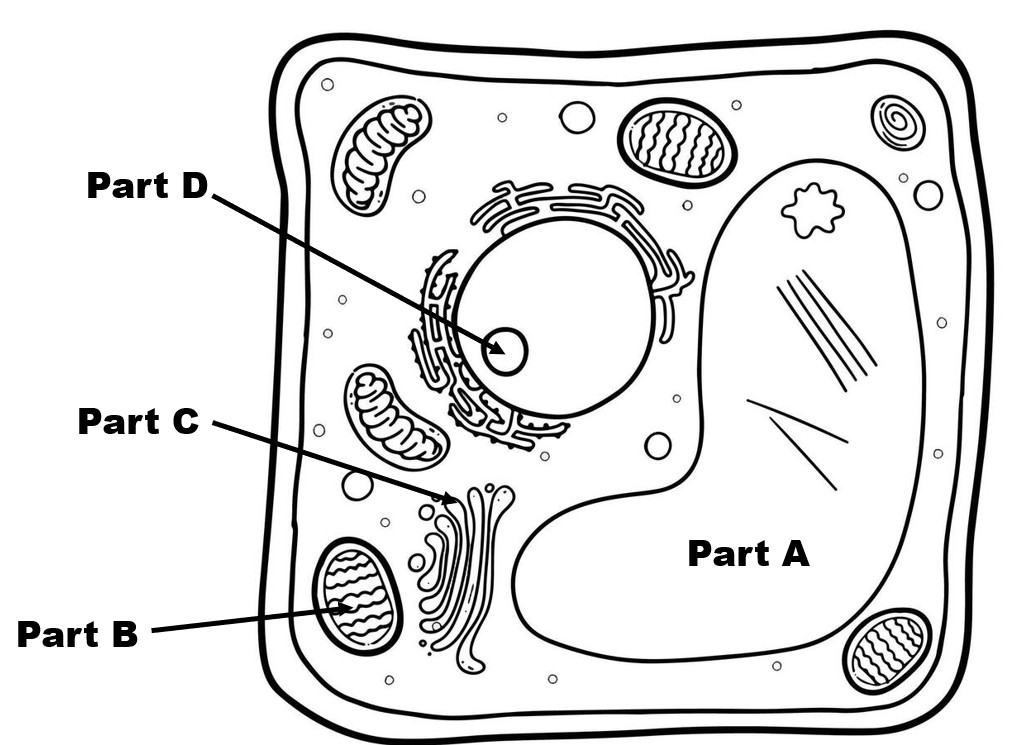
nucleolus (cloud of ribosomal subunits inside the nucleus)
When temperatures are increasing and plants need to acclimatize. Explain 2 things that can be done to decrease the fluidity of their plasma membranes?
lengthen fatty acid tails and increase the # of saturated fats in the fatty acid tails.
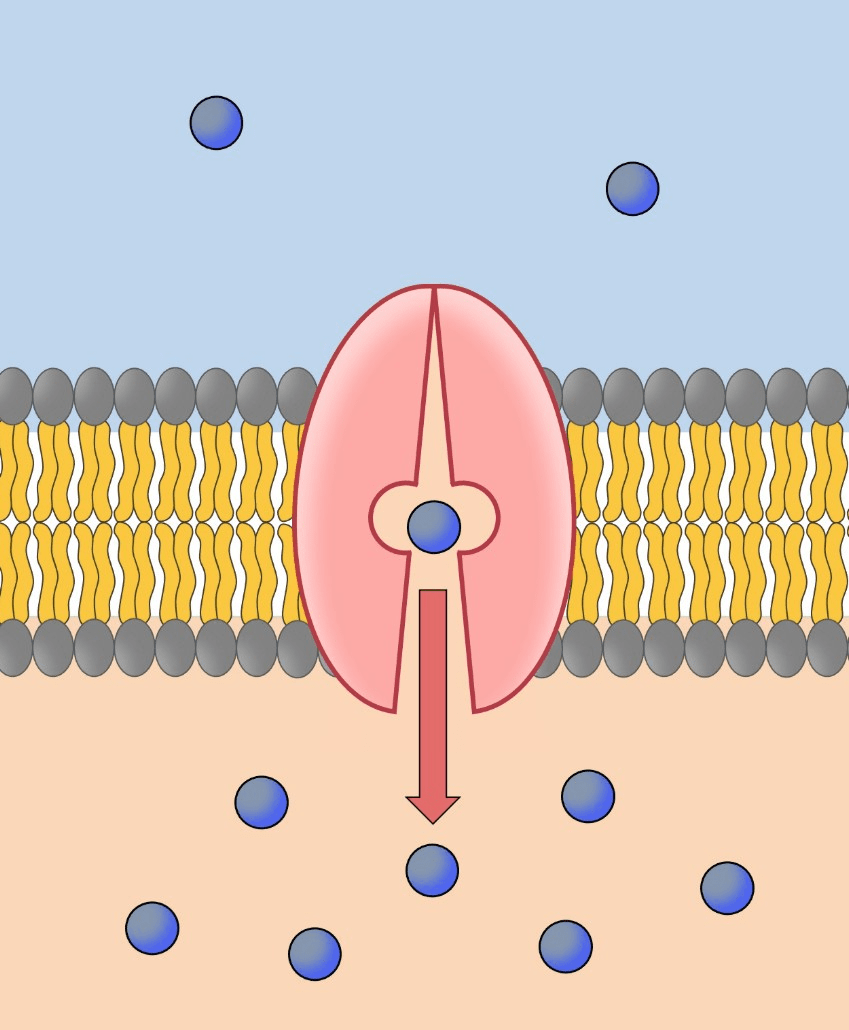
Active transport
Identify the specific type of transport. And include an example.
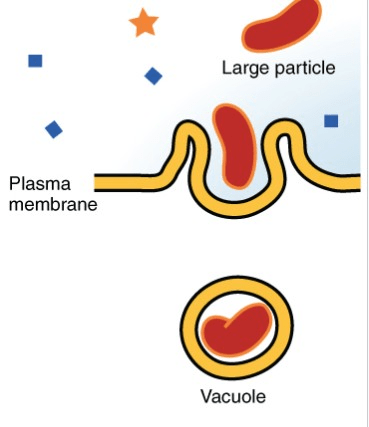
Phagocytosis (endocytosis/bulk active transport)
Ex. Ameboa eating a bacterium. White blood cells getting rid of a bacterium.
A freshwater paramecium or amoeba is placed in a a distilled water solution. What will happen to the organism?
What organelle might the paramecium have to control this situation?
The organism is hypertonic to the distilled water solution (hypotonic) so water will passively enter the animal cell and thus burst or lyse the paramecium cell.
Typically contractile vacuoles will help the paramecium activity pump out the water to keep from bursting (at least for some time).