These are the levels of organization in ecology.
(At what levels do ecologists study the relationships between living and non-living systems?)
Individual, Species, Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biosphere
Define metabolism.
Breaking down and rearranging molecules needed for growth and development.
This is HOMEOSTASIS.
A balance between the all the levels of organization in the body.
The definition of a stimulus. Give one example.
Something that provokes a response.
A loud sound, hunger pains, movement, etc.
The definition of growth.
An increase in the size of an organism or part of the organism.
Bacteria, archaea, & eukaryota
What are the three domains of organisms?
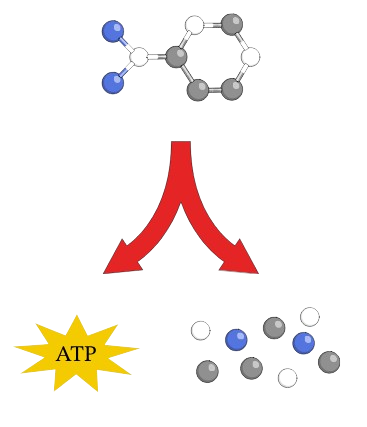
Write or draw what occurs during anabolism.
Changing small molecules into larger molecules.
List at least three systems of our body that need to be monitored and maintained.
Temperature, Weight, Sleep, Thirst (others may be given not listed)
These cells in the eyes detect colors of light.
What are cones?
These are the five factors affect growth.
Nutrition, genetics, contamination, environmental conditions, hormones
These characteristics are used to place living organisms in a phylogenetic tree.
What are physiology and genetics.
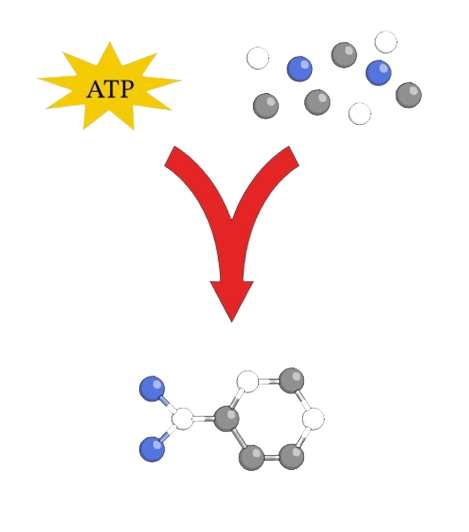
Write or draw the process of catabolism.
Breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones and energy (ATP).
These are the steps of a feedback loop.
Stimulus, Receptor, Control Unit, Effector
Name the four different receptors in living organisms.
Photoreceptors, Thermoreceptors, Chemoreceptors, Mechanoreceptors
These four factors affect development.
Genetics, Environment, Nutrition, Gender
These are the five kingdoms of classification.
Monera, Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals
This is why plants have a second metabolism.
To adapt to their environment.
Give two behavioral strategies that are used to combat changes in temperature.
Seeking shade, Huddling, Movement, Spraying self with water
This is the definition of adaptation. Give one example.
A process by which an organism becomes more fitted to its environment.
Ex. Color change of fur for the seasons.
These are the two ways an animal or plant can reproduce.
Sexually or asexually
These show the progression of evolutionary development.
What is a cladogram?
A state of slowed metabolism that allows a living thing to go through long periods of inactivity.
What is torpor?
Name one animal that is classified as an ectotherm.
Any amphibian or reptile.
This is how is evolution different than adaptation.
Adaptation can be reversable, evolution is not reversable and changes the complexity of an organism.
These are the three categories of asexual reproduction.
Fragmentation, Division, and Budding