Electron pair is shared in
What is a covalent bond
This type of hybrid orbital geometry has four-sides, or four faces – maximum distance between electrons requires 3D structure with 109.5° between each outer atom
What is tetrahedral
What is an electron
These molecules have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of the bonded atoms.
What are constitutional isomers
Keto-enol transformation.
Electrons are represented by dots and bonds are represented by dashes
What is a Lewis dot diagram
Three outer atoms are separated by 120 degrees
What is trigonal planar
An acid reacts with water to produce
what are anions and a Hydronium ion or H3O+
This molecule is an example of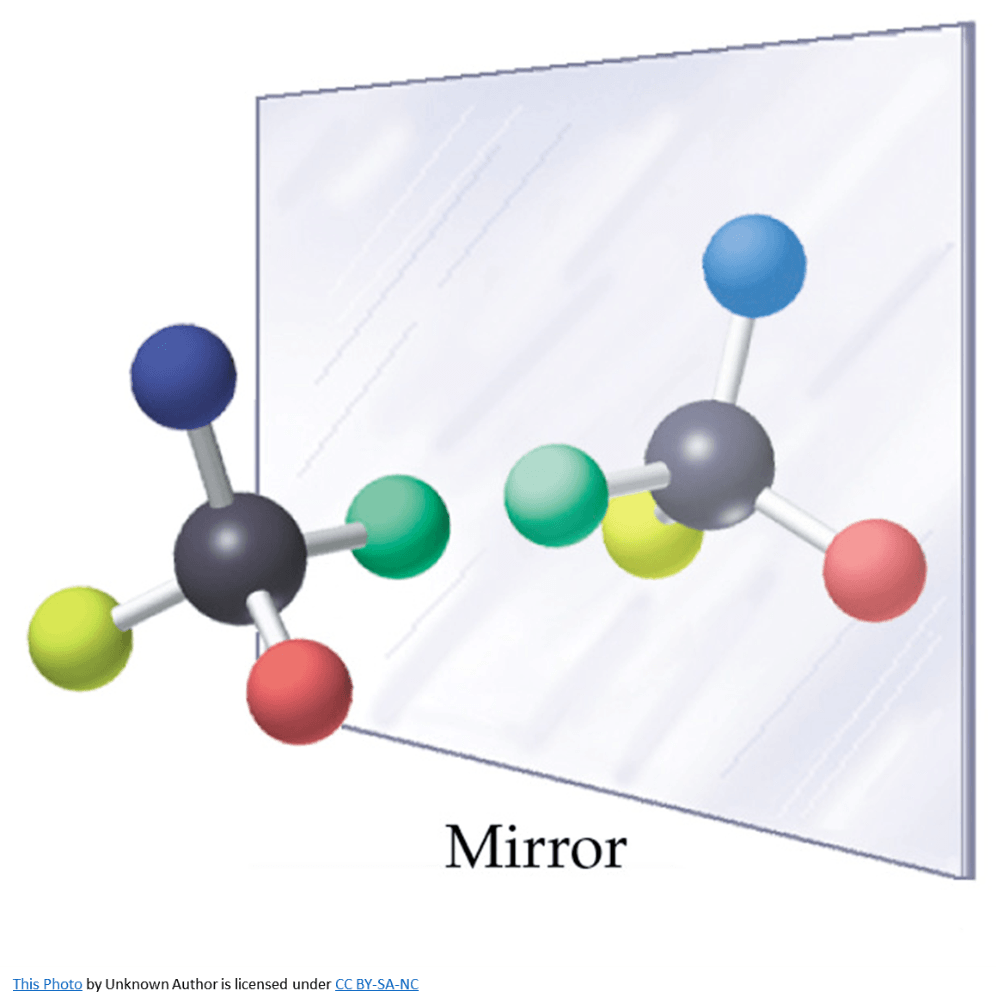
What is an optical isomer or an enantiomer
This is a measure of how readily a species with a lone pair may attack an electron deficient atom.
What is nucleophilicity.
These outermost shell electrons are not shared in a bond
What are lone pairs
In Carbon dioxide, the three lone pair of electrons force the molecule to be:
What is linear
pKa is a fancy way of saying
What is -Log Ka
This isomer has the same chemical formula but has a different spatial arrangement
What is a stereoisomer
These nucleophilic substitution reactions are faster.
What are SN2 reactions
Lowest energy orbitals are filled first according to this Principle
What is Aufbau Principle.
Water has a special chemical properties. One reason is the presence of lone pair of electrons on the central oxygen atom forcing it to bend further from 109.50
What is 104.50
This constant is measure of a molecules ability to give up a H+
What is a dissociation constant
The two optical isomers have identical physical properties such as melting point, solubility and density. They differ in this property.
What is rotating the plane of polarized light to either right or left.
Elimination reactions almost always produce this class of compounds
What are alkenes
The bonds with head on overlap of two atomic orbitals along a line between two nuclei (single bonds) are the strongest form of covalent bond.
What are Sigma bonds.
VSEPR theory is a shortened form of this phrase
What is Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Acetic acid is very soluble in water, almost all of the acetic acid in solution exists in the form of neutral molecules (less than 1% dissociates). This is a hallmark of a strong acid.
What is false.
Stereoisomers are catalogued into two different categories.
What are Cis-Trans and geometric isomers or Z and E isomers
During this type of reaction, the base removes a proton from beta Carbon containing the least number of substituents.
What are elimination reactions.
Bonds with sideways p orbitals and are weaker than the sigma bonds.
What are pi bonds
True or false:
Each atom in a molecule will achieve a geometry that minimizes the repulsion between core electrons of the element.
What is false.
Acids differ in the number of protons they can donate. How many protons can CH3CH2 C (COOH)2 can donate?
What are two.
A mixture of optical isomers does not rotate the plane of polarized light. This mixture is called.
What is a racemic mixture
10 and 20 halides undergo this type of elimination reaction and this type of substitution reaction.
What are E1 and Sn2 reactions.
The region of space around two or more atoms inside which e- are likely to be found .
What are molecular orbitals
A Trigonal Bi-Pyramid geometry is used for distributing these many pairs of valence electrons.
What is five.
Challenger: pH = - log [H3O+].
If you have an acid which produces 0.002 Moles of H3O+ ions/L, what is the pH?
What is 2.70
In a C-compound containing an oxygen when the Alpha proton is donated to the O, and the double bond forming pair of electrons moves over an Enol forms.
What is Keto -enol transformation.
In an asymmetric haloalkene, a process that favors bond formation at a particular atom over other possible atoms.
What is regioselectivity