The following reaction occurs via a two step mechanism.
What is the intermediate?
A + 2B -> C
1. A + B -> D (slow)
2. D + B -> C (fast)
D is the intermediate
Write the expression for the equilibrium constant of the following reaction:
Cu(s) + H+(aq) + NO3- <-> Cu2+(aq) + NO(g) + H2O (l)
Draw the pH curve for a weak base titrated with a strong acid
Find ΔS°rxn for the combustion of methane to carbon dioxide and liquid water
ΔS°rxn= -242.5 J/K
Balance the following redox reaction in an acidic solution.
H2S(g) + NO3−(aq) ⟶ S8(s) + NO(g)
24H2S(g) + 16NO3−(aq) + 16H+(aq) → 3S8(s) + 16NO(g) + 32H2O(l)
Which of the possible rate laws for the reaction
A + B ⟶ C + D
is first-order overall?
(a) rate=𝑘[A][B]
(b) rate=𝑘([A][B])/[C]
(c) rate=𝑘 [A]2/([C]+[D])
(d) rate=𝑘[A]2
b
At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant 𝐾𝑐 for the reaction
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g)
equals 1.0 × 104. What is the equilibrium constant of the reaction
1/2N2(g) + 3/2H2(g) ⇄ NH3(g)
at the same temperature?
1.0 x 102
Given carbonic acid (H2CO3), write down the reactions where the amphiprotic anion acts as an acid and where it acts as a base
Acid-
HCO3–(aq) + H2O(l) ⇄ CO32–(aq) + H3O+(aq)
Base-
HCO3–(aq) + H2O(l) ⇄ H2CO3(aq) + OH–(aq)
At what point is ΔG equal to ΔG°?
When Q = 1
ΔG = ΔG° + RTlnQ
Balance the following redox reaction in a basic solution.
SO32−(aq) + Cl2(g) ⟶ SO42−(aq) + Cl−(aq)
SO32−(aq) + 2OH−(aq) + Cl2(g) → SO42−(aq) + 2Cl−(aq) + H2O(l)
In the Michaelis-Menten rate law for an enzymatic reaction
rate= k2[E]0[S]/[S] + ((k-1+k2)/k1)
what are the units of the rate constants?
(a) (𝑘1):L mol−1s−1 (𝑘−1):s−1 (𝑘2): s−1
(b) (𝑘1):L mol−1s−1 (𝑘−1):mol L−1s−1 (𝑘2): mol L−1s−1
(c) (𝑘1):s−1 (𝑘−1):mol L−1s−1 (𝑘2): mol L−1s−1
(d) (𝑘1):s−1 (𝑘−1):L mol−1s−1 (𝑘2): L mol−1s−1
(a) (𝑘1):L mol−1s−1 (𝑘−1):s−1 (𝑘2): s−1
When an acid is added to a solution of potassium chromate K2CrO4 (which is yellow), an orange potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) is
made:
2CrO42–(aq) + 2H+(aq) ⇄ Cr2O72–(aq) + H2O(l)
At a temperature where the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 𝐾𝑐 =1.4×105, an initial solution is prepared containing 0.024 M CrO42–(aq),
0.0077 M Cr2O72–(aq), and 4.0×10−4 M H+(aq).
(a) Find the reaction quotient 𝑄𝑐 at the start of this reaction.
(b) In what direction will the reaction proceed? Justify your answer.
Qc= 8.4 x 107
The reaction will proceed in reverse because Qc > Kc
Find the buffer component ratio for a solution of Na3PO4/Na2HPO4 with a pH of a) 12.25 and b) 12.45
Ka1= 7.2 x 10-3 , Ka2=6.3×10−8 , Ka3= 4.2×10−13
a) ratio = 0.758
b) ratio = 1.2
Find ΔG° for this reaction using enthalpy and entropy values.
H2(g) + I2(s) ⟶ 2HI(g)
ΔG°= 2.4 kJ
Consider the following voltaic cell:
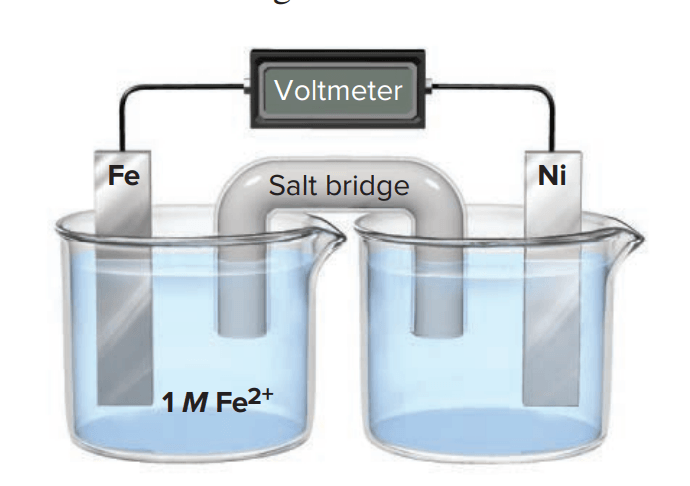
(a) In which direction do electrons flow in the external circuit?
(b) In which half-cell does oxidation occur?
(c) In which half-cell do electrons enter the cell?
(d) What is the purpose of the salt bridge?
a) from the iron half cell to the nickel half cell (anode to cathode)
b) oxidation occurs in anode, so iron half cell
c) reduction occurs in cathode, so nickel half cell
d) allows for flow of electrons between half cells
A first-order reaction A ⟶ B has a rate constant
𝑘 =2.34×10−3 s−1. At the start, the reaction mixture contains compound A at a concentration [A]0 =0.174 M. It does not contain any B.
Find the half-life of this reaction.
Find the concentration of A after 8 minutes.
Half-life= 296 s
[A]= 0.0566 M
The equilibrium constant of a certain chemical reaction equals 15.0 at 298 K. The enthalpy change in this reaction is Δ𝐻0rxn = ―37.7 kJ/mol.
At what temperature will the equilibrium constant be equal to 1.00?
T2= 363 K
Hydrocyanic acid HCN is a strong poison, but its acidic properties are very weak (𝐾𝑎 = 6.2 × 10―10). Find the pH value for a 0.200 M solution of hydrocyanic acid.
pH= 4.95
Calculate ΔG° for this reaction using ΔG°f values:
2Mg(s) + O2(g) ⟶ 2MgO(s)
ΔG° =-1138.0 kJ
Balance this redox reaction and calculate E0cell
AgCl(s) + NO(g) ⟶ Ag(s) + Cl−(aq) + NO3−(aq)
Is the reaction spontaneous?
3AgCl(s) + NO(g) + 2H2O(l) → 3Ag(s) + 3Cl– (aq) + NO3– (aq) + 4H+ (aq)
E0cell = E0cat – E0an = 0.22 V – (0.96 V) = –0.74 V
The reaction is non-spontaneous.
The rate constant of a reaction doubles when the temperature is increased from 10°C to 20°C. Find the activation energy of this reaction.
Ea= 47.8 kJ/mol
Nitrogen gas (N2) reacts with hydrogen gas (H2) to form ammonia gas (NH3). 1.00 atm of nitrogen gas is mixed with 2.00 atm of hydrogen gas in a closed container. After the equilibrium is reached, the total pressure is 1.78 atm. Calculate the partial pressure of hydrogen gas at equilibrium and the value of 𝐾𝑝 for this reaction.
PH2= 0.17 atm
Kp= 777
Find the pH during the titration of 20.00 mL of 0.1000 M butanoic acid, CH3CH2CH2COOH (Ka = 1.54×10−5), with 0.1000 M NaOH solution after the following additions of titrant:
(a) 0 mL
(b) 15.00 mL
(c) 20.00 mL
(d) 25.00 mL
a) pH=2.91
b) pH=5.29
c) pH=8.76
d) pH=12.05
At what temperature will the combustion of methane to carbon dioxide and liquid water be spontaneous?
T= 3671 K
Given the following half reactions, write the balanced equation for the spontaneous reaction.
Al3+(aq) + 3e− ⟶ Al(s) E° = −1.66 V
N2O4(g) + 2e− ⟶ 2NO2−(aq) E° = 0.867 V
Calculate E0cell and write the line notation for the cell.
Ox: 2{Al(s) → Al3+(aq) + 3e– } E° = –1.66 V Red: 3{N2O4(g) + 2e– → 2NO2– (aq)} E° = +0.867 V
3N2O4(g) + 2Al(s) → 6NO2– (aq) + 2Al3+(aq)
E0cell = 0.867 V – (–1.66 V) = 2.53 V