Acids are what? What do they produce?
Hydrogen ions/protons, electron acceptors
A 1.0L buffer solution is 0.10 M in HF and 0.050 M in NaF. Which action will destroy the buffer?
a) adding 0.050 mol of HCl
b) adding 0.050 mol of NaF
c) adding 0.050 mol of NaOH
Part 1: A 50 mL sample of 0.200M NaOH is titrated with 0.200M nitric acid. What are the moles of HNO3?
0.00600 mol HNO3
Which has a greater entropy?
1a) Solid CO2 or gaseous CO2
2a) N2 gas at 1 atm or N2 gas at 1.02*10^-2 atm
1a) Gaseous CO2
2a) gas at 1.02*10^-2 atm
Bases produce Hydroxide ion and are __
electron donors/Nucleophiles
This curve represents 
titration of a strong acid/strong base curve.
Part 2: A 50 mL sample of 0.200M NaOH is titrated with 0.200M nitric acid. What is the pH after adding 30 mL of HNO3?
12.70
Second Law of Thermodynamics
in any spontaneous process, there is always an increase in the entropy of the universe
Common Ion Effect: In which solution is BaSO4 most soluble?
a) In a solution that is 0.10 M in BaNO3
b) In a solution that is 0.10 M in Na2SO4
c) In a solution that is 0.10 M in NaNO3
A chemist needs a solution buffered at 4.30 pH and can choose from the following:
a) propanoic acid Ka=1.35*10^-5 [HA]/[A]=3.8
b) benzoic acid Ka=6.4*10^-5 [HA]/[A]=.78
c)hypochlorous acid Ka=3.5*10^-8 [HA]/[A]=1.4*10^3
Benzoic acid
Hydrogen Cyanide gas HCN is a powerful respiratory inhibitor with a Ka of 6.2*10^-10 when dissolved in water. If a 50 mL sample of 0.100 M HCN is titrated with 0.100M NaOH, calculate the pH of the solution at the halfway point.
9.21
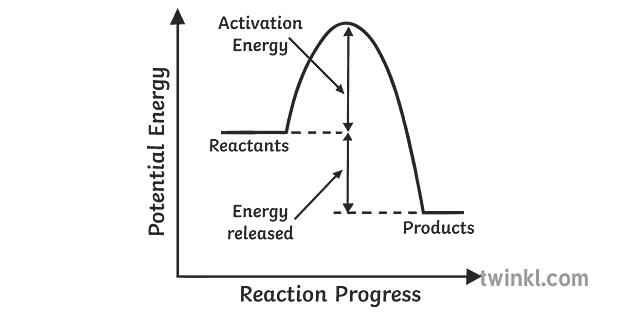
Exothermic- spontaneous(energy release)
Calculate the pH of a solution containing 0.75M lactic acid Ka=1.4*10^-4 and 0.25M sodium lactate.
3.38
A buffer solution contains 0.50 M Acetic Acid Ka=1.8*10^-5. Calculate pH when 0.0100 moles of solid NaOH is added to 1.0L of the buffered solution.
4.76
Hydrogen Cyanide gas HCN is a powerful respiratory inhibitor with a Ka of 6.2*10^-10 when dissolved in water. If a 50 mL sample of 0.100 M HCN is titrated with 0.100M NaOH, calculate the pH of the solution after 8.00 mL of 0.100 M NaOH has been added.
8.49
When delta S is zero...
System is at equilibrium, no tendency to occur
In a solution of H+ in a 1.0 M HF solution is 2.7*10^-2 M and the percent dissociation is 2.7%. Calculate [H] & percent dissociation of HF. Ka=7.2*10^-4 [NaF] is 1.0M.
[H]=7.2*10^-4 M and 0.072%
a) [HA]>[A]
b) [HA]<[A]
c) [HA]=[A]
10.96
Calculate delta G @25C for the synthesis of methanol, where carbon monoxide gas at 5 atm and hydrogen gas at 3 atm is converted to liquid methanol. delta G for H2=0kJ, methanol is -166kJ, and carbon monoxide is -137kJ
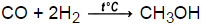
-38kJ/mol