The name of the concept/action represented in this diagram.
What is diffusion?
Has a pH of less than 7.
What are acids?
The purpose of a bond.
What is to hold atoms together to form stable compounds and molecules?
Do molecular biologists work closely together with other scientists, such as chemical biologists?
What is yes/true?
The name of the concept/action represented in this diagram.
What is osmosis?
The use of phenolphthalein.
What is an acid-base indicator?
The type of bond polyatomic ions use.
What are Ionic bonds?
The functional difference between RNA and DNA.
Does DNA form chromosomes, whereas RNA are proteins that "read" and "translate" the sequence of DNA?
The name of this type of diagram.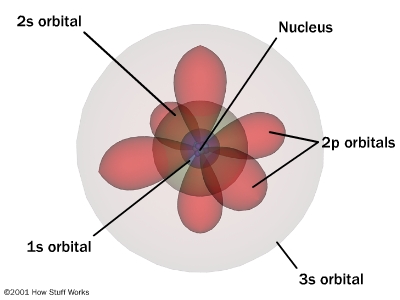
Another name for bases that are soluble in water.
What are alkalis.
The primary way oppositely charged ions interact with each other.
What is attract
This is Molecular Biology (definition/explanation).
What is the branch of biology that deals with the structure, function, and manipulation of nucleic acids and proteins?
The name of the topic where this type of diagram is found.
What is organic chemistry?
OH is a common component of these substances.
What are bases?
The most common type of bond.
What are Covalent Bonds?
This kind of bond is very important to the formation of many molecules in living organisms, such as DNA and other proteins.
The definition/explanation of a restriction enzyme.
What is an enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence?
What this (image) discovered.
What is the nucleus?
What is their composition? Organic acids have a carbon backbone; mineral acids do not.
The "sea of electrons" is a part of this bond. 
What is a metallic bond?
The definition/explanation of DNA sequencing.
The process of determining the sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA. (The process of determining a sequence of DNA.)