Name three stressors that can be applied to an equilibrium system
1) Temperature
2) Concentration
3) Pressure/Volume
What does ICE stand for?
Initial, Change, Equilibrium
What is the Bronsted-Lowry definition of an acid and a base?
Acid: proton donor
Base proton acceptor
True or false: According to Le Chatelier's Principle, when a stressor is applied to a a system at equilibrium, the system will shift to oppose the change until a new equilibrium is established.
True
Write the Equilibrium Law expression for the following equation
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) ↔ Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq)
Kc = Zn2+(aq) / Cu2+(aq)
Consider the reaction for the decomposition of hydrogen iodine at 448°C. The initial concentration of HI(g) was 1.00x10-3 mol/L. Once an equilibrium was established, the concentration of HI(g) was measured to be 0.078x10-3 mol/L. Calculate the equilibrium constant (Kc)
2HI(g) < --> H2(g) + I2(g)
8.73
Identify the bases in the following chemical equation
HSO4- (aq) + HPO42- (aq) <--> H2PO4- (aq) + SO42- (aq)
HPO42-
SO42-
If the concentration of HF(g) increased, which direction would the equilibrium shift and would this produce more or less product?
CCl4(l) + 2HF(g) <--> CCl2F2(g) + 2HCl(g)
Equilibrium would shift right and more product would be produced
Draw the equilbrium expression for the following:
2H2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2H2O (l)
[H2]2[O2]
H2O (l) is a liquid and not part of this equilibrium expression.
In a 500 mL stainless steel reaction vessel at 900°C, carbon monoxide and water vapour react to produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Evidence indicates that this reaction establishes an equilibrium with only partial conversion of reactants to products. Initially, 2.00 mol of each reactant is placed in the vessel. The KC for this reaction is 4.20 at 900°C. What will be the concentration of each substance at equilibrium?
CO(g) + H2O(g) ↔ CO2 (g) + H2 (g)
CO(g) & H2O(g): 1.31mol/L
CO2(g) & H2(g): 2.69mol/L
Identify the conjugate acid base pairs from the following reaction
HCO3- (aq) + CN- (aq) < -- > CO32- (aq) + HCN (aq)
1. HCO3-(aq) & CO32-(aq)
2. CN-(aq) & HCN(aq)
If the pressure of this system increased, which direction would the equilibrium shift?
2SO2(g) + O2(g) <--> 2 SO3(g)
right
In the following system:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g)
0.249 mol/L of N2(g), 3.21 X 10-2 mol/L of H2(g) and 6.42 X 10-4 mol/L of NH3(g) are combined in a 1.00 L vessel at 375°C.
What is the Kc value for the reaction and are the products or reactants favored?
0.0500
Reactants are favored since 0.05 < 1
(Ignore the temperature.)
If a 100 mL sample of 0.344 mol/L unknown acid has a pH of 4.1 at 30 degrees, then the Ka is?
Ka = 1.8 x 10^-8
What will be the predominant reaction if nitric acid is mixed with potassium fluoride
H3O+(aq) + F-(aq) --> H2O(l) + HF(aq)
If the volume of this system decreased, which direction would the equilibrium shift?
H2(g) + Cl2(g) < -- > 2HCl(g)
The equilibrium would not shift
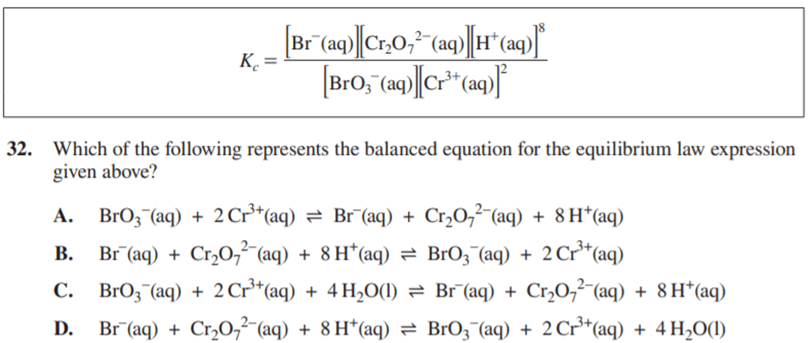
C
A student measures the pH of a 0.25 mol/L solution of carbonic acid to be 3.48. Calculate the Ka for carbonic acid from this evidence
Ka = 4.39x10^-7