Name the 4 types of noise and if they are frequency dependent!
Thermal Noise-- Independent, fluctuations in current or voltage due to random motions of elections in a wire
Shot Noise-- Independent, random variations in discrete events (electrons crossing a junction)
Flicker Noise-- Legit = 1/f thus dependent, slower long term drift in an instrument
Environmental Noise-- Dependent, instrument pick up on EMF signals from surrounding electronics
What is happening in this UV-vis calibration curve?

STRAY LIGHT!!!!!!!!
Name an advantage of atomic emission over absorption
1. Lower chemical interference
2. Simultaneously measure multiple elements
3. Detection of elements not easily atomized
4. Large dynamic range
Name 3 mass analyzers!
Examples: Quadrupole, Ion trap, TOF, orbitrap, FT-ICR, Double Focusing
Which side of the CV is oxidation?

(US Conventions)
Bottom!!!!!!!!!!!!
In RPLC, would more polar or less polar compound elute faster?
What is the difference between sensitivity and analytical sensitivity?
Sensitivity = slope of linear calibration plot
Analytical S = account for changes that may increase both signal and noise
What is the difference between a tungsten lamp and a halogen-tungsten lamp? What advantage does halogen have over pure tungsten?
1. Addition of halogen gas to tungsten filament lab
2. Allow for redeposition of tungsten onto the filament resulting in higher output power, longer life, and higher temperature
Name three factors that contribute to band broadening and overall band width in atomic spectroscopy.
100 bonus points for definitions!
Uncertainty Effect: atomic transitions have a defined lifetime, thus there is uncertainty in frequency
Doppler Effect: wavelength compression and extension based on if the molecule is moving towards or away from the detector-- random motion- always moving away or towards
Pressure Broadening: Gas phase collisions transfer energy, broadening observed wavelength
You have a tandem mass spec that is made up of three quadrupoles. You want a 2D MS spectra where you can see both precursor and fragment ions of this precursor, what is the purpose of each quad?
Quad 1: SELECT -- Selection of parent ion/ions of interest
Quad 2: COLLISION -- acts as a collision cell to fragment ion/ions of interest
Quad 3: SCAN -- scans all fragments that come from the collision cell
If you increase the temperature of a solution and you are detecting for fluorescence, what would happen to the quantum yield, why?
Decrease quantum yield because increasing temp increases collisions and intensity of collisions resulting in increasing the rate of external conversion.
For a GC-FID detector, why do only small organic chemicals work?
Analytes with C-H bonds generate ions in the flame which are then collected
Name the three 'types' of information you can get from an instrument, give an example of each.
Analog -- measured magnitude/intensity of the signal i.e. cassette tapes, temperature measurements
Time-Domain -- information recorded in the time course of fluctuations i.e. frequency, pulse width, period
Digital -- discrete values across a specific range
i.e. computers!! like legit everything now days
As temperature increases what happens to the emission spectrum in a tungsten lamp?
1. The intensity increases
2. Blue shift -- i.e. maximum wavelength decreases
Why does the addition of ethanol or a similar alcohol into an aqueous sample increase absorption values in atomic absorption?
Ethanol desolvates easier than water-- lower boiling point
Get a piece of paper and draw the ESI diagram, be able to explain each portion!
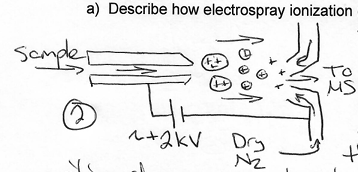

What room, day, time is your final?
1:30 PM to 3:30 PM, Monday, May 12. The exam will
be held in our regular classroom (512B Bruininks Hall)
In size exclusion chromatography, in what order to molecules elute given the following masses?
A. 46737 amu
B. 75860 amu
C. 2745 amu
The larger they are the sooner they elute: B -> A -> C
Define LOD, LOQ, and Dynamic Range
LOD: limit of detection 3*σblank
LOQ: limit of quantification 10*σblank
Dynamic Range: From the LOQ to the end of signal, the range at which the analyte is quantifiable
Name 3 unique properties of a laser.
1. Narrow output lines at specific wavelengths
2. Uniform direction
3. Same phase
What type of error does a lock in amplifier correct for?
Slow drift over long term measurements, can also reduce flicker noise and flame variations.
Name 5 ionization types and rank them from hardest to softest!
ICP < EI < CI < ESI = MALDI
What is Red/Stokes Shift in fluorescence spec and what is it attributed to?
luminescence photons occur at longer wavelengths/lower energies than the photons that are absorbed due to excitation.
Attributed to vibrational relaxation where excess vibrational energy is lost prior to emission.
Three peaks are eluting in 50:50 MeOH:H2O with a flow speed of 2.00 mL/min too close together. How can we fix this?
Slow it down or change the mobile phase to increase the water concentration.
What is the purpose of an internal standard?
A student is using a traditional 1 cm cuvette but is having issues measuring their sample. The absorbance is consistently under 0.1 AU, but for their old instrument they need an absorbance of at least 0.5 to accurately quantify their sample. They cannot reliably concentrate their sample and only have 10 mL. They have 5 different cuvettes, the 5 mm, 10 mm, 20 mm, 50 mm, and 100 mm. What should they do?
They only need to amplify their signal by a factor of 5 so they should choose the 50 mm cuvette, as the 100 mm would waste sample!
Explain this diagram with the context of flame atomic absorbance:
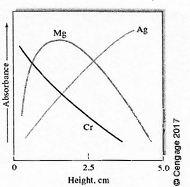
The longer atoms stay in the flame (and thus the higher they are on the flame) the more their absorbance increases, unless they oxidize. Silver is the hardest to oxidize which is why it increases in absorbance the higher it gets in the flame, where as Chromium easily oxidizes.
Given the two statements, fill in the blanks:
In quadrupole mass analyzers, ___ ions respond much more to the DC voltage. The two positive electrodes destabilize ions with a m/z ___ a certain threshold, while the negative electrodes destabilize ions __ a certain threshold.
In a time-of-flight mass analyzer, ion with a(n) ___ m/z travel faster and thus reach the detector first. To correct for variations in kinetic energies a(n) ___ is used.
1. Larger
2. Below
3. Above
4. smaller
5. reflectron
Explain TLC
Thin Layer Chromatography
More soluble compounds in the mobile phase will travel further up the TLC plate.
What does increasing the temperature of the GC column do?
Shifts equilibrium from the liquid (stationary) to the gas (mobile) that results in a quicker elution
Given the three graphs below could you perform a linear least-squares regression:
A) 
B) 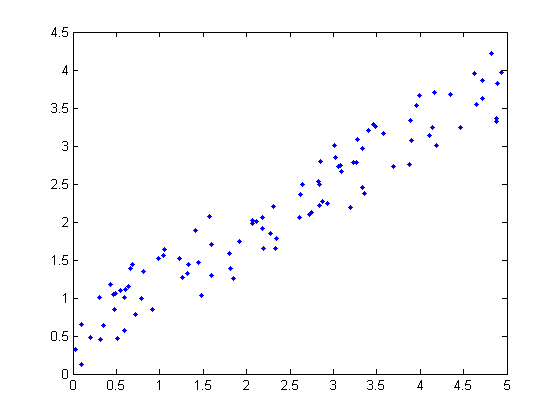
C)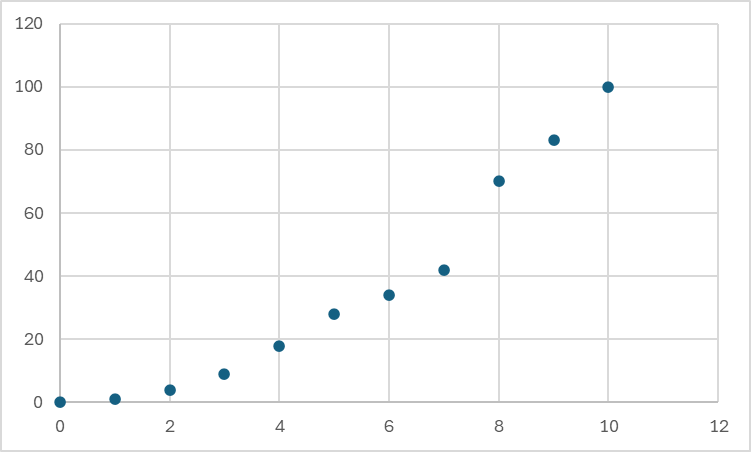
Only B can use linear least-squares. Why? There are 4 assumptions that must be true:
1. Trend is linear
2. Error is Gaussian
3. Error primarily in the y direction
4. Error in all points is equal
Describe how a photomultiplier tube works.
If 1 photon is introduced and there are 9 total dynodes, assuming no electron loss, what is the total number of electrons emitted?
1. photon hits photocathode
2. electron is then emitted
3. strikes dynode, release 4-6 more electrons
4. repeats through a series (typically 9)
5. current recorded at anode
262,000 - 10,100,000
Label the Diagram, naming parts 1-7:
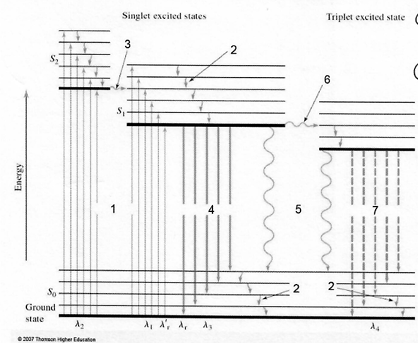
1. Absorption
2. Vibrational Relaxation
3. Internal Conversion
4. Fluorescence
5. Internal/External Conversion
6. Intersystem Crossing
7. Phosphorescence
Name the three primary parts of an FT-ICR.
1. Transmitter Plates
2. Receiver Plates
3. Big magnet
Name the three electrodes that make up a 3 electrode cell?
1. Working
2. Reference
3. Counter
Label A, B and C term on the curve and define what each term means:
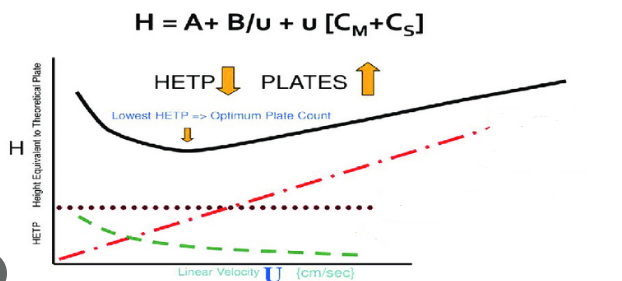
Red Dot-Dash: C term-- mobile and stationary mass transfer
Dotted Line: A term-- multipaths term--particle size and packing
Green Dash: B term -- Axial diffusion or longitudinal diffusion