What is the name of the following Amino Acid? What pH is this drawn at?
Lysine
Lysine does not exist like this at any pH.
What is pH?
-log[H]
Name an Intermolecular Force.
Dipole-Dipole
Pi Stacking
Pi-Cation
H-Bonding
Van Der Waals
What does the H and S stand for in Gibb's Free energy equation.
Name a Purification method that utilizes protein size to separate a sample.
Size Exclusion Chromatography.
Which two amino acids contain either a guanidino or imidazole group?
Arginine
Histidine
If 0.01 M of KOH is dissolved into DI Water, what would you expect the pH to be?
Higher than 7.
What Intermolecular Forces are at play in the following image?
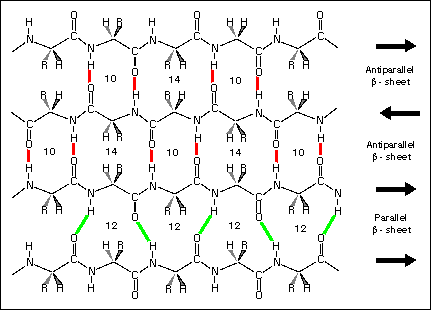
H-Bonding
Dipole-Dipole
Van Der Waals
What is ΔG? How can it describe "spontaneity" of chemical reactions.
Change in free energy. When it is negative, the describe reaction is spontaneous.
Would this compound be used as substrate for a cation exchange or anion exchange column?

Anion exchange column.
At pH 7, most amino acids are extremely soluble. What is the name of this charged form. Why does it contribute solubility?
If the pH is significantly lower than the pKa, is the weak acid likely protonated or deprotonated.
If the pH is lower than the pKa, the weak acid is likely protonated.
Water and Oil separate spontaneously. Which intermolecular forces are involved in both layers?
H-Bonding in Water.
Van der Waals in oil.
Since most proteins exist in water, what component of Gibb's Free Energy Equation increases as a protein folds. What do we call this "effect."
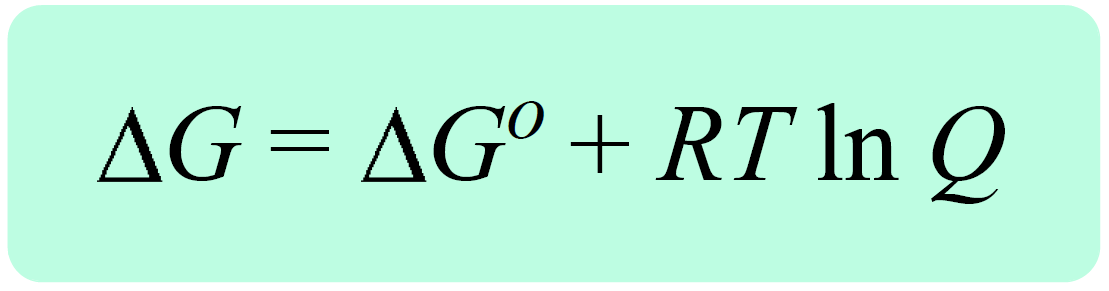
Enthalpy and Entropy. Entropy by way of freeing water molecules from extremely structured cages around hydrophobic components. Enthalpy by favorable IMF interactions. Hydrophobic effect.
A method to separate proteins based on size, utilizing a detergent like sodium dodecyl sulfate.
SDS PAGE
Does amino acid K, R, or E have the lowest isoelectric point?
Because E has a carboxylic acid for its R group (pka ~ 4), which lowers its isoelectric point.
How can you determine ratio of acid and conjugate base given pH and pKa. What happens when pH = pka?
Using Henderson Hasselbalch Equation, it is possible to solve for ratio of acid and conjugate base.
pH = pKₐ + log([A⁻]/[HA])
What structural characteristics contribute to H-bonding or dipole-dipole interactions?
Hydrogen bonded to electronegative atom. Carbon double bonded to oxygen.
Which side of the arrow shows a more disordered system? Explain.
The bottom. Less water molecules are forming highly structured cages around lipids, therefore there is more entropy.
Protein A is larger and does not get stuck in the gel particles, compared to B which gets stuck and travels slower through the system.
What are the amino acid residues of the following peptide? Is it drawn correctly for pH 7?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tetrapeptide-5bd89c07c9e77c0052095570.jpg)
V-G-S-A
No, C and N terminus should be either deprotonated or protonated.
How does a buffer resist pH change. What makes a buffer useful (or useless) at a specific pH?
A buffer resists pH change by taking or giving hydrogen ions from other acids or bases in solution, as it exists in equilibrium with its weak acid/base forms at a specific pH, which correlates with its pka.
pH far from pka makes for a poor buffer.
Name two Amino Acids capable of forming ionic interactions with one another.
Glutamate, Aspartate can form salt bridges with Lysine or Arginine.
Proteins are thermodynamically unstable, with high free energy released when they are hydrolyzed, yet you and I do not spontaneously fall apart. Why is this?
High activation of energy of hydrolysis of peptide bond.
Protein A has a pI of 4, and Protein B has a pI of 9. Which protein elutes first from a cation exchange column at pH 7? Explain.
Protein B has a higher pI, meaning it will exist in a predominantly positively charged state at pH 7, compared to Protein A. Higher pI also suggests more positively charged residues like lysine, compared to lower pI suggesting more negatively charged residues.