What is the difference between intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are between molecules
Intramolecular forces are within molecules
What is the pressure at boiling point?
760 torr
What is the Molarity of 17 g NaCl (58.44 g/mol) in 5 L of solution?
0.0582 M
What happens to boiling point if I increase the pressure?
It increases, think boiling point elevation
C=kP
The concentration of H2 gas in water is 2.45 M. Henry's Law constant is 7.8 × 10^-4 mol/L·atm. What is the partial pressure?
3141.03 atm
Why are ionic intermolecular forces stronger than hydrogen bonding?
It involves a complete transfer of electrons
If I decrease temperature of a gas or solid, what happens to solubility (for both)?
It is more soluble for a gas, and less soluble for a solid
What would we use if we wanted to heat a solution?
Molarity or molality
molality
What are the Van't Hoff Factor for these molecules?
a) NaNO2
b) C6H12O6
c) NaCl
a) 3
b) 1
c) 2
ln(P2/P1) = -ΔHvap/R * (1/T2 - 1/T1)
R= 8. 3143 J/mol
Determine ΔHvap for a compound that has a measured vapor pressure of 24.3 torr at 273 K and 135 torr at 325 K.
x = 24327 J/mol = 24.3 kJ/mol
List the IMFs with the strongest being last
London Dispersion Forces, Dipole-Dipole Interactions, Hydrogen Bonding, Ionic
Would this molecule be soluble in water? Why?
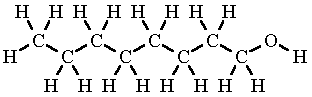
No, it only has a small polar end. The nonpolar part is much larger, so the water cannot react with the overall nonpolar molecule
0.100 mole of NaCl is dissolved into 100.0 grams of pure H2O. What is the mole fraction of NaCl?
H2O= 18 g/mol
0.982
Why do we add salt to roads and sidewalks when it is supposed to freeze?
It decreases the freezing point, therefore the ground would have to be colder to freeze
Calculate the vapor pressure in torr of a solution that is made by dissolving 59.51 grams of glucose (C6H12O6) in 112.2 mL of water at 26.7 oC. The vapor pressure of pure water at 26.7 oC is 26.271 torr and the density of water at that temperature is 0.99669 g/mL.
Psolution = 24.94 torr
It induces a dipole, it is associated with nonpolar molecules
Would caffeine (molecule below) be miscible in water or hexane (c-c-c-c-c-c)? Why?
Water, because like dissolves like
Caffeine is polar, so it would dissolve
What is the molarity of 4.5 m NaCl in solution with ethanol?
Molar mass of NaCl: 58.44 g/mol
Molar mass of ethanol: 46.07 g/mol
Density of solution: 1.078 g/mL
3.84 M
First, find grams of solute, then grams of solution, then find volume (divide by density), lastly convert to L instead of mL and plug in values
How would we decrease osmotic pressure?
What does isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic mean?
Increase the volume of the solution
Isotonic- same concentration
Hypotonic- lower concentration of solute
Hypertonic- higher concentration of solute
What is the ppmm of MgCl2 if you have 500 µg of MgCl2 in a solution of 235g of ethanol?
2.128

What are the IMFs used if the molecule below bonds to itself?
H2S
Dipole-Dipole
Draw and explain an energetics of solution graph
∆Hsol’n = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3
∆H1 = energy needed for breaking solute’s IMFs
∆H2 = energy needed for breaking solvent’s IMFs
∆H3 = energy released by creating solvent-solute IMFs
∆HLat represents-Breaking solute bonds
∆Hhyd represents- Breaking solvent bonds and forming solute-solvent bonds
We have 20g of a solute with a molar mass of 235.6 g/mol. We have 200g of water as our solvent with a molar mass of 18.01528 g/mol. Our solution has a density of 0.95 g/mL. Find molarity, molality, mol fraction of solute and solvent, mass percent of solute and solvent, and mass fraction of solute and solvent.
Molarity- 0.367, molality- 0.42, mol frac (solute)- 0.0076, mol frac (solv)- 0.9924, mass percent (solute)- 9.091, mass percent (solv)- 90.91, mass frac (solute)- 0.09091, mass frac (solv)- 0.9091
Solute mol- 0.085, solvent mass kg- 0.2, solvent mol- 11.102, solution mass- 220g, solution vol mL- 231.6
What would increasing solute concentration due to:
- Boiling point
- Freezing point
- Vapor pressure
a) increase
b) decrease
b) decrease
Draw and Label a Non-normal Phase Diagram
What is an example of a non-normal substance? Give one example of how we know?
Water is a non-normal substance
Its solid is less dense than its liquid
