What subatomic particle(s) is/are found outside of the nucleus?
electrons (protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus)
Solutions, Suspension, Solutes, and Solvents:
If coffee grounds are fully dissolved in water, then the coffee grounds are the ______________ and the water is the _______________.

If coffee grounds are fully dissolved in water, then the coffee grounds are the solute and the water is the solvent.
What monomer is this? (or you can say, "one building block of ______________________")

Nucleotide
Building block of nucleic acids

What macromolecule is used for short-term energy, and what macromolecule is used for long-term energy?
Carbohydrates -- short term energy
Lipids -- long term energy
What enzyme is responsible for breaking down the disaccharide sugar found in milk?
lactase

What type of bond forms between two nonmetal atoms?
a covalent bond
The pH of your stomach is typically around what number?
around 2
I will accept 1, 2, or 3

Which macromolecule is least likely to dissolve in water?
lipids because they are mostly non-polar
What polysaccharide is responsible for forming rigid cell walls in plants, like celery?
Cellulose
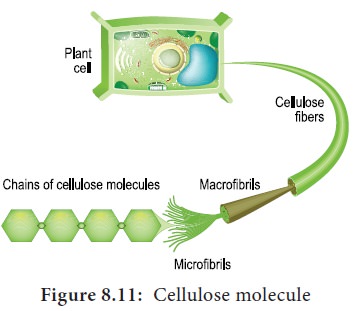
The part of an enzyme where the substrate binds is called the: __________________
Active Site
What type of bond is formed by the attraction of positively and negatively charged atoms?
Ionic Bond
positive and negatively charged atoms are called ions

(hydrogen bonding is a weak bond between molecules formed by the attraction of partial positive side of one molecule to the partial negative side of another molecule)
In this reaction, how many oxygen atoms are present on the products side?

4 oxygen atoms

Out of the 6 most common elements in living things, which element would be found in proteins only (not lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids)
sulfur
Why are some amino acids called the essential amino acids?
Because our body does not produce them, so it is essential that we get them from our diet.
What is the optimum pH for the enzyme pepsin? In which part of the body do you think this enzyme would be present?
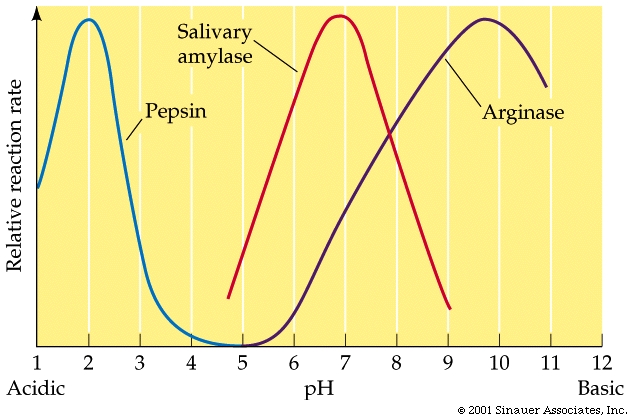
optimum pH is 2
pepsin is present in the stomach
An atom with 12 protons and 10 electrons would be an ion with a charge of what?
+2
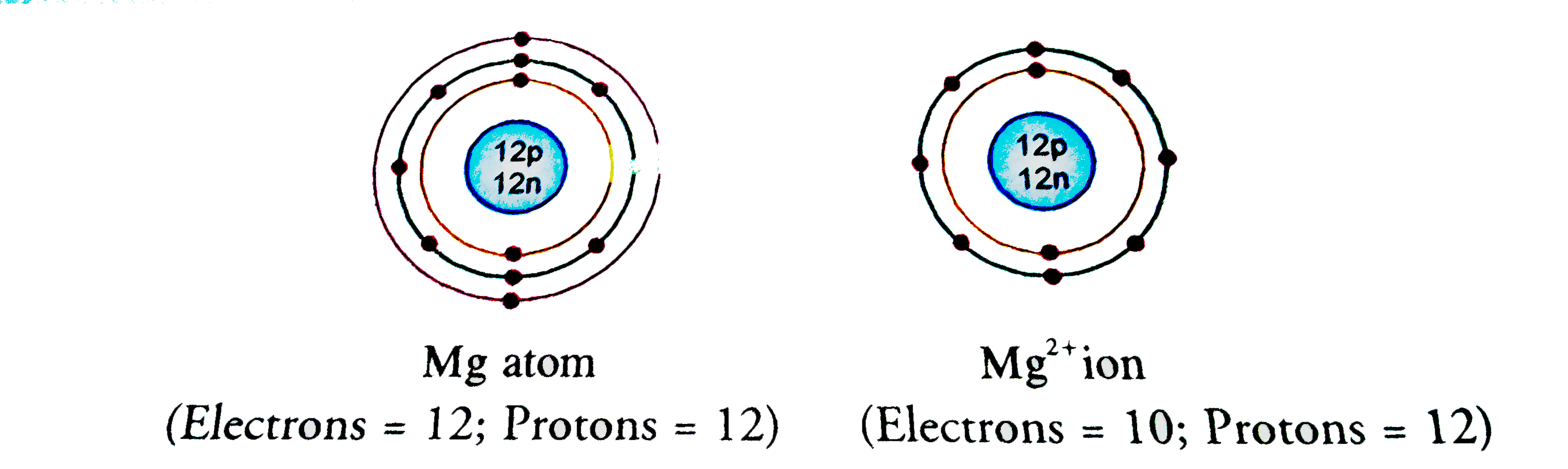
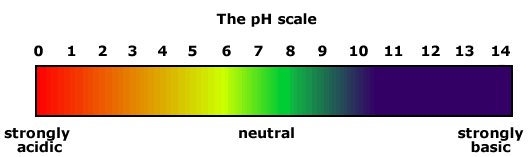
The pH of a solution is 11. Is this solution acidic, basic, or neutral?
Basic
pH below 7 is acidic
pH of 7 is neutral
pH above 7 is basic
Draw the structure of a triglyceride, labelling the glycerol and fatty acids.
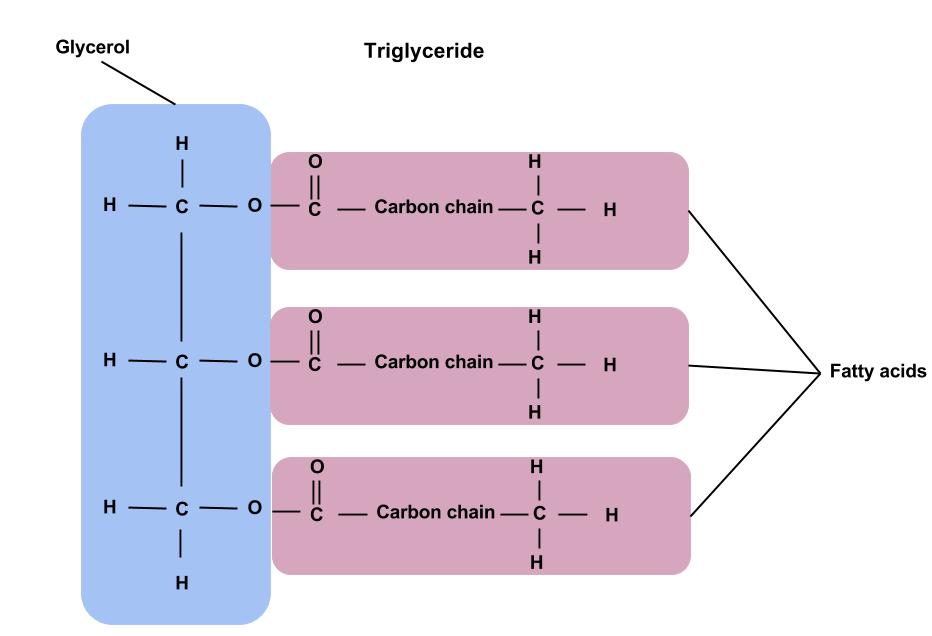
What is the name of the reaction that breaks down polymers into monomers?
What is the name of the reaction that connects monomers to build polymers?
Both need to be correct to receive the points
Hydrolysis breaks polymers down into monomers
Dehydration or Condensation connect monomers to build polymers
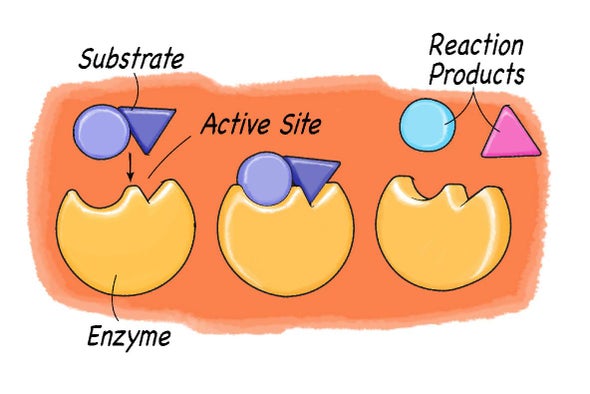
In the image shown, label the:
- enzyme
- substrate(s)
- active site
- enzyme-substrate complex
- product(s)

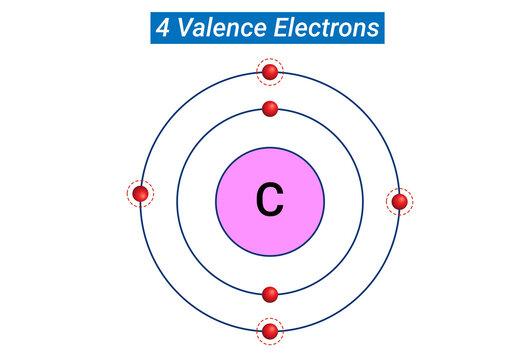
What part of an atom is being shared or transferred in a bond?
Answer is 2 Words: _____________ _____________
Valence Electrons
Define the properties of water:
- cohesion
- adhesion
- specific heat
Cohesion -- the ability of water to stick (or be attracted to) to other water molecules, like raindrops forming bigger drops when meeting up
Adhesion -- the ability of water to stick (or be attracted to) to other polar or charged molecules, like raindrops on a windshield
Specific Heat -- the amount of energy needed to increase the temperature of water
What macromolecule has 4 levels of structural organization? How is this relevant to functions? (must get both parts correct to get points)
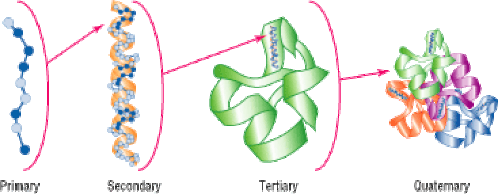
Proteins
These 4 levels of organization are important because the specific shape determines what specific function the protein has.
What are 3 examples of functions that proteins do in the body? (I taught you at least 6)
Hair, skin, and nails
Build and repair muscle and tissues
Movement
Chemical Messengers (neurotransmitters)
Transportation of substances out of cells
Immune System (antibodies)
Enzymes- proteins that speed up chemical reactions
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions in living things?
By lowering the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur.
