The scientist whose work allowed for the reorganization of the periodic table.
Who is Moseley?
The experiment conducted by Rutherford
What is the gold-foil experiment (who did it and what did it prove)?
55% of a sample is found to have a mass of 28. The rest has a mass of 29. What is the average atomic mass of this sample?
28.45 amu
The Lewis Dot Structure for CH4 and shape name.
___________ tetrahedral
What is decreases and increases?
A charged element
What is an ion?
The number of electrons in a neutral atom of silicon.
What is 14?
Shorthand electron configuration for Mg
[Ne]3s2
The scientist who discovered the neutral particle in an atom
Who is Sir James Chadwick?
the experiment done by J. J. Thomson, in which a beam of electrons was sent through a glass container, proving atoms have negative, mobile charges
What is the cathode-ray tube experiment (who did it and what did it prove)?
An element has an average mass of 74.922 amu. If there are only isotopes with a mass of 76 and a mass of 74 for this element, which isotope has the higher abundance?
76
The Lewis Dot Structure for NCl3 and shape name.
Trigonal pyramidal
Electronegativity ________________ going across the periodic table, and _______________ going down the periodic table.
What is increases, decreases?
The distance of the outermost valence electrons to the center of the nucleus.
What is atomic radius?
How many protons, neutrons and electrons are present in an ion of oxygen with a -2 charge and a mass of 14 amu?
P: 8
N: 6
E: 10
Full electron configuration for Al
1s22s22p63s23p1
Used atomic spectra to defend electrons existing in 'energy levels' and energy change results in emission and absorption of energy, often as light.
Who is Niels Bohr?
The discovery made by the oil-drop experiment conducted by Millikan.
What is the charge of an electron?
The average atomic mass for boron based on the information below
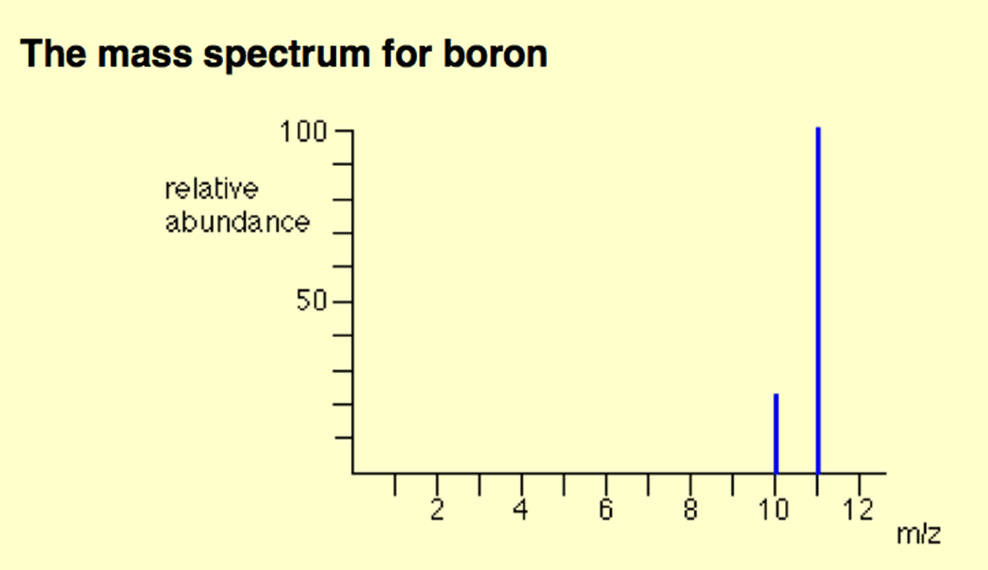
10.8 amu
The Lewis Dot Structure for SO3 and shape name.
trigonal planar/trigonal pyramidal depending on LDS
The most electronegative element
F
Two or more of the same element with different masses.
What are isotopes?
Write the protons, neutrons, electrons, atomic number and mass number for 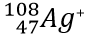
P: 47
N: 61
E: 46
AN: 47
MN: 108
The full electron configuration for Ga
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p1
With Hans Jensen discovered nuclear spin, helped to explain stability of nuclei despite large numbers of charges
Who is Maria Goeppert Mayer?
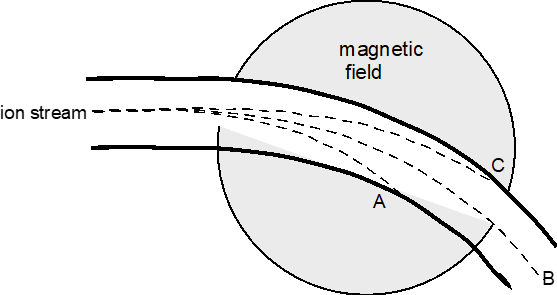 Explain the above schematic of a mass spectrometer.
Explain the above schematic of a mass spectrometer.
ions go through field, influenced by magnetic field, particles whose paths change the fastest are the lightest, detector on other side determines how much of each isotope the sample contains.
Give the average atomic mass and atomic symbol for the most common isotope of the element represented below.
Chlorine.
3517Cl
Draw the LDS for NO2-1 and shape name.
bent
The electron that Miss Zange needed to put the most energy in in order to remove it, when she removed three electrons from a Beryllium atom.
The last one removed (the 2p6 electron)
What is ionization energy?
Write the atomic symbol for an atom that has an atomic number of 27, 33 neutrons and is neutrally charged.
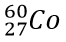
The valance electron configuration for Pb2+
6s24f145d10
discovered that electrons exist mostly in orbitals, or 'probability clouds'
Who is de Broglie and Erwin Schrodinger?
Gold-foil - alpha particles bombarded thin sheet of gold, were expected to all bounce off but most went through, indicating that atoms are mostly made of empty space.
The average atomic mass and identity of an element of which 78.7% has a mass of 24, 10.1% has a mass of 25 and 11.2% has a mass of 26 amu.
Mg, 24.33 amu
The Lewis Dot Structure for BF3
trigonal planar
An explanation of the relationship between ionization energy and atomic radius. (the why in addition to the what, points to best answer)
A smaller atomic radius will have a larger ionization energy. A smaller atomic radius means the electrons are closer to the attractive, positively charged nucleus, which therefore has a stronger pull on them that needs to be overcome in order for an electron to be removed.
The ability of an element to attract shared electrons.
What is electronegativity?
Write the protons, neutrons, electrons, atomic number and mass number for 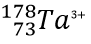
P: 73
N: 105
E: 70
AN: 73
MN: 178
The shorthand electron configuration for Cd3+
[Kr]4d9