What type of bond is formed between a metal and a nonmetal?
Ionic
Define electronegativity.
A) The amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom
B) The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a bond
C) The number of valence electrons in an atom
D) The total positive charge of the nucleus
What does VSEPR stand for?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion — it predicts the shape of a molecule based on the repulsion between electron pairs around the central atom.
This element shown has 7 valence electrons. Which group on the periodic table does it belong to?
Group 17 (Halogens)
What type of bond shares electrons?
Covalent
Which bond is more polar:
A) H–Cl
B) H–Br
C) Both are equally polar
D) Neither is polar
A. H–Cl is more polar because chlorine has a higher electronegativity than bromine, creating a greater difference between the two atoms.
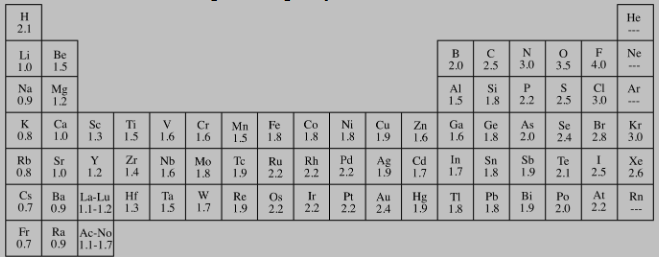
How many total electron domains (bonding + lone pairs) are around the central atom in NH₃?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
C. Four total domains — three bonding pairs and one lone pair.
How many valence electrons does each atom have, and what will happen when these two react?


A) They share electrons equally to form a nonpolar molecule.
B) Sodium will gain an electron from chlorine to form Na⁻ and Cl⁺.
C) Sodium will transfer its electron to chlorine, forming an ionic bond.
D) They will share electrons unequally to form a polar covalent bond.
C.
Na has 1 valence e⁻, Cl has 7; Na will transfer its electron to Cl forming Na⁺ and Cl⁻ (ionic bond).
What type of bond holds copper atoms together in a wire?
Metallic
How can you tell if a molecule is polar or nonpolar?
A) By counting the number of atoms in the molecule
B) By checking if the molecule has an uneven charge distribution due to shape and electronegativity differences
C) By measuring its mass
D) By identifying if it contains hydrogen atoms
B.
Bond polarity — are bonds polar?
Molecular geometry — are dipoles balanced or canceled?
If dipoles cancel → nonpolar; if they don’t → polar.
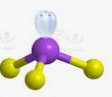
Using VSEPR, what is the molecular geometry of CO₂?
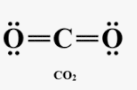
A) Bent
B) Trigonal planar
C) Linear
D) Tetrahedral
C. Linear.
Two electron domains around the central carbon; no lone pairs → atoms spread 180° apart.
Based on the diagram, how many electron pairs will be shared between these atoms?
A) 1 pair
B) 2 pairs
C) 3 pairs
D) 4 pairs
2 shared pairs (double bond).
Why are ionic compounds brittle while metals are malleable?
Ionic lattice shifts cause repulsion; metallic bonds have delocalized electrons.
Explain how polarity affects solubility.
A) Polar substances dissolve only in nonpolar solvents.
B) Nonpolar substances dissolve best in polar solvents.
C) Polar substances dissolve best in polar solvents, and nonpolar substances dissolve best in nonpolar solvents.
D) Solubility is not affected by polarity.
C.
Polar substances dissolve in polar solvents (“like dissolves like”).
Nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
👉 Example: Salt (polar) dissolves in water; oil (nonpolar) does not.
Both CH₄ and H₂O have four electron domains around the central atom. Why do they have different shapes?
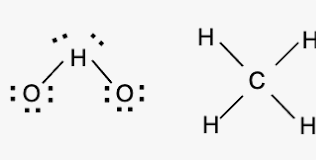
A) H₂O has lone pairs on the central atom, while CH₄ does not.
B) CH₄ has more electrons than H₂O.
C) The hydrogen atoms in CH₄ are larger than in H₂O.
D) H₂O forms ionic bonds while CH₄ forms covalent bonds.
A.
CH₄ has 4 bonding pairs → tetrahedral, while H₂O has 2 bonding + 2 lone pairs → bent.
Lone pairs push harder, changing the angle from 109.5° to ~104.5°.
Which structure is correct, and why?
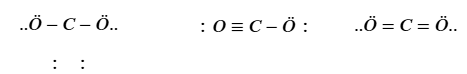
A) O–C–O with single bonds only, because single bonds are always correct.
B) O=C=O with double bonds, because it satisfies the octet rule and has no formal charges.
C) O≡C–O⁻, because carbon forms a triple bond with one oxygen.
D) O–C≡O, because one triple and one single bond is always preferred.
B.
The one with carbon in the center; carbon forms 4 bonds and achieves an octet while oxygen forms two.
Explain why NaCl has a high melting point while H₂O does not.
A) NaCl has stronger ionic bonds, while H₂O has weaker hydrogen bonds.
B) NaCl molecules are smaller than H₂O molecules.
C) H₂O has more atoms than NaCl.
D) H₂O contains only covalent bonds, so it cannot melt.
Predict the bond type (ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent) for each pair:
H–H, H–Cl, Na–Cl
A) H–H: Polar covalent H–Cl: Nonpolar covalent Na–Cl: Ionic
B) H–H: Nonpolar covalent H–Cl: Polar covalent Na–Cl: Ionic
C) H–H: Ionic H–Cl: Polar covalent Na–Cl: Nonpolar covalent
D) H–H: Nonpolar covalent H–Cl: Ionic Na–Cl: Polar covalent
B.
Predict the molecular geometry and polarity of NF₃ using VSEPR theory.
A) Tetrahedral; Nonpolar
B) Trigonal pyramidal; Polar
C) Trigonal planar; Nonpolar
D) Linear; Polar

B.
Geometry: Trigonal pyramidal (3 bonding + 1 lone pair)
Polarity: Polar — because the lone pair creates an uneven charge distribution, giving the molecule a net dipole.
A student drew NH₃ with nitrogen bonded to three hydrogens but no lone pair on nitrogen. What is the mistake and the correction?
A) Mistake: Too many electrons; Correction: Remove a bond.
B) Mistake: Missing lone pair on nitrogen; Correction: Add one lone pair to nitrogen.
C) Mistake: Hydrogen has too many electrons; Correction: Remove a hydrogen.
D) Mistake: Nitrogen has a double bond; Correction: Change to single bonds only.
Nitrogen should have three bonds and one lone pair (not four bonds). The given structure violates the octet rule.