Draw the Lewis dot structure for NH3.
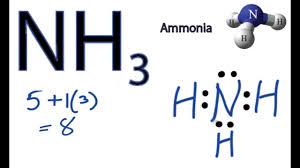
What 3 elements can form hydrogen bonds?
oxygen
fluorine
nitrogen
What is the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond.
ionic = metal + nonmetal
covalent = nonmetal + nonmetal
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule of Br2?
linear
Condensation is the phase change from _____________ to ____________.
+200 points if you can provide an example!
gas; solid
morning dew, breathing on glass, steam on a pot cover/mirror, a cold glass of water
What is wrong with Lewis dot structure "B"?
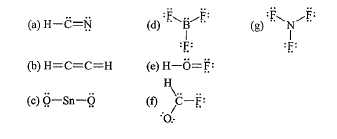
Each hydrogen has too many bonds.
Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why water has a lower boiling point than sodium.
Water has weaker intermolecular forces than sodium.
Sodium has stronger intermolecular forces than water.
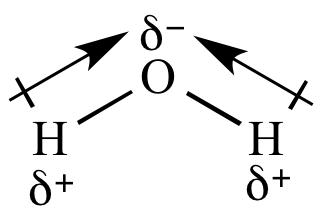
Draw all dipoles in a molecule of H2O.
What is the molecular geometry of BF3. Draw the Lewis dot structure to help you!
trigonal planar
Boron is one of the exceptions! Only 6 valence electrons!
On a cooling curve, what phase of matter does the curve start with? How is this different from a heating curve?
cooling curve = start with gas
heating curve = start with solid
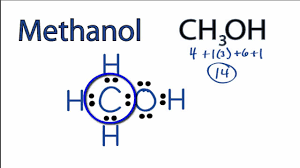
Methanol is an alcohol that can be used to produce acetic acid found in vinegar. Draw the Lewis dot structure for methanol (CH3OH).
Compare the intermolecular forces of the substance at Point "3" and Point "5."
The intermolecular forces at Point "3" are stronger than at Point "5."
The intermolecular forces at Point "5" are weaker than at Point "3."
Magnesium (Mg) will readily react with bromine (Br) to for magnesium bromide (?). Magnesium bromide is commonly used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder. Draw the Lewis dot structure for magnesium bromide.
Why do we say that the polarity of a tetrahedral molecule "depends"?
The polarity depends on what surrounds the central atom.
If all of the surroundings atoms are the same, the dipoles cancel, and the molecule is nonpolar (symmetrical).
If the surrounding atoms are different, the dipoles do NOT cancel, and the molecule is polar (asymmetrical).
On a heating curve, how do you determine the melting point?

What is wrong with Lewis dot structure "F"?

Carbon does not have 4 bonds.
Carbon has 1 lone pair.
Oxygen does not have 2 bonds.
Image that you have a beaker of HBr. What intermolecular forces holds all of the molecules together?
dipole-dipole force
BONUS (400 x 2 = 800 points)
Are diatomic particles ionic or covalent compounds? How do you know?
Covalent. They are all nonmetals.
H N O F Cl Br I
What molecular geometry is demonstrated in the following image? Is this molecule polar or nonpolar? 
trigonal pyramidal (3 groups, 1 lone pair)
polar
What is happening to water's kinetic energy at 12 minutes? What phase is water at 12 minutes?
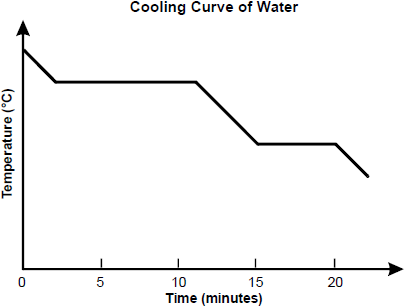
Water is a liquid at 12 minutes. It is cooling down. It's kinetic energy is decreasing.
Draw the lewis dot structure for hydroxylamine (NH2OH).
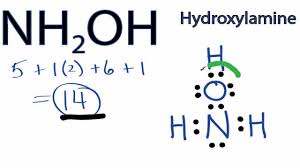
State an intermolecular force that exists between HI molecules, but does not exist between CO2 molecules.
dipole-dipole
How many calcium atoms need to combine with 4 bromine atoms to produce a stable compound?
2 calcium atoms (4+)
4 bromine atoms (4-)
Observe the following molecule. Based on the molecular geometry, is this molecule polar or nonpolar? How would you change the polarity?
nonpolar
change one of the oxygens to something else; that will change the symmetry, making the molecule polar
Which substance is a solid at room temperature (25oC)?
phenol

