electrons are shared
What is wrong with Lewis dot structure "B"?
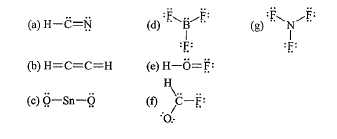
Each hydrogen has too many bonds.
intermolecular forces are the forces _______ molecules
The bond between sodium and chlorine in NaCl
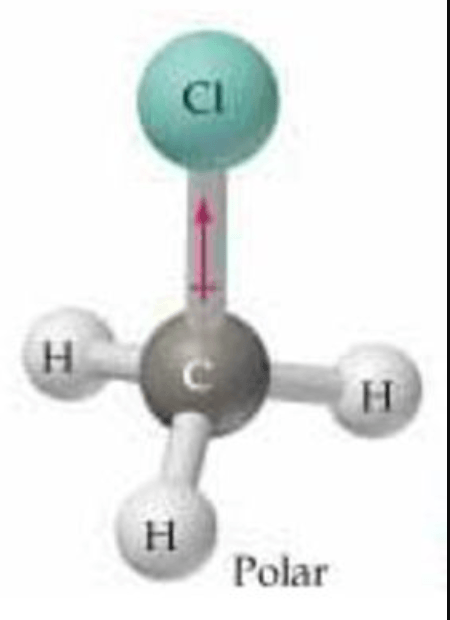
Polar

What is the molecular geometry of a molecule of Br2?
linear
luster and ductility
metallic
What is wrong with Lewis dot structure "F"?

Oxygen does not have an octet.
Which is is the strongest IMF: dipole-dipole, H-bonding, or London Dispersion forces?
dipole-dipole
The molecule H2O
Polar

What molecular geometry is demonstrated in the following image?

trigonal pyramidal (3 atoms, 1 lone pair)
high melting and boiling points
ionic
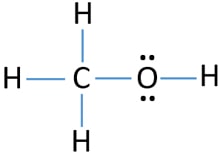
Methanol is an alcohol that can be used to produce acetic acid found in vinegar. Draw the Lewis dot structure for methanol (CH3OH).
Which is the weakest intermolecular force: dipole-dipole, H-bonding, or London Dispersion forces?
London Dispersion forces
The bond between Carbon and Oxygen in CO2
Polar
Which compound below has a molecular geometry that is tetrahedral?
SiO2 BF3 HCl CCl4
CCl4
nonconductors in the solid, molten, and dissolved state
Ammonia is a substance used in creating fertilizers to use on farms. Draw the Lewis structure for ammonia (NH3).

Hydrogen bonding occurs between molecules with bonds between Hydrogen and what three other atoms?
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine (NOF)
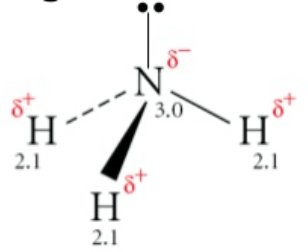
The molecule NH3
Polar!
What is the molecular geometry of SO3. Draw the Lewis dot structure to help you!
trigonal planar (3 atoms, 0 lone pairs)
electrons delocalized
metallic
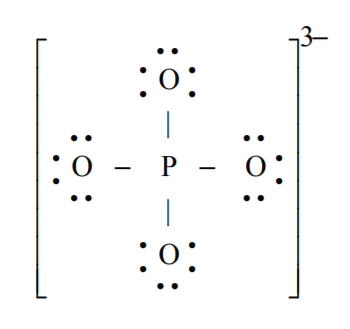
Phosphate is a polyatomic ion present in bones, genes, teeth. Draw the Lewis structure for phosphate (PO43-).
London Dispersion forces come from the random motion of...
electrons
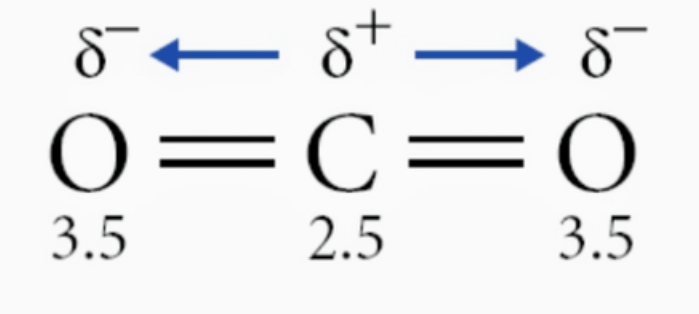
The molecule CO2
Non-polar.
Why do we say that the polarity of a tetrahedral molecule "depends"?
The polarity depends on what surrounds the central atom.
If all of the surroundings atoms are the same, the dipoles cancel, and the molecule is nonpolar (symmetrical).
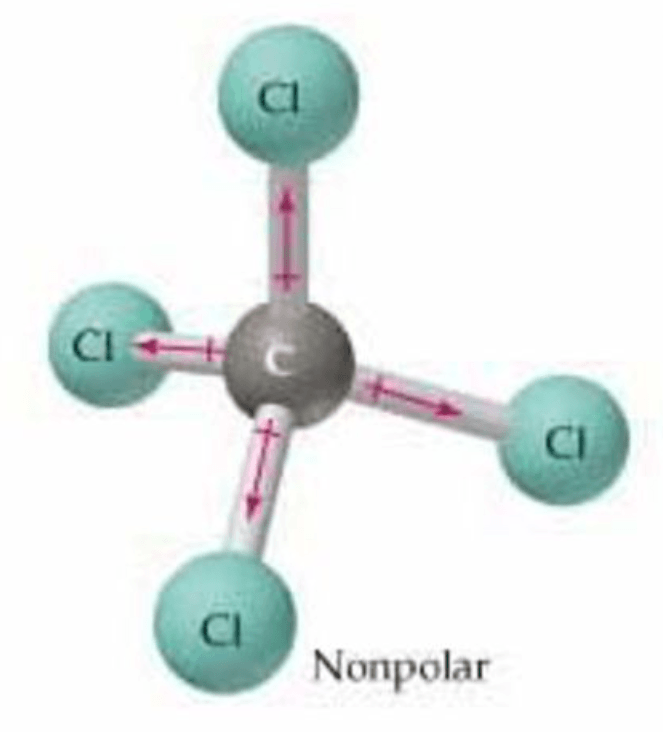
If the surrounding atoms are different, the dipoles do NOT cancel, and the molecule is polar (asymmetrical).