Why do atoms bond?
To achieve a stable electron configuration/octet.
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for Fr+
[Fr]+
Describe the movement of electrons in a bond between LiF.
Li transfers an electron (1 electron) to F.
When an electron is equally attracted to the nuclei of two atoms at the same time
Nonpolar covalent bond
The greater the boiling point, _________ the strength of the intermolecular force.
GREATER
When a bond is formed what happens to energy in the reaction?
Energy is released.
Or
PE is decreased.
Determine which element becomes a cation and which becomes an anion in the following ionic compound. Determine their correlating charges.
CaCl2
Ca becomes a cation with a 2+ charge.
Cl becomes an anion with a 1- charge.
Describe the movement of electrons in CH4 and determine what kind of general bonds are present.
Electrons are shared in CH4 and there are covalent bonds.
How do you determine the bond polarity of a substance?
Finding the difference in electronegativity of the elements.
Name the three types of intermolecular forces in order of increasing strength.
1. London Dispersion/Dispersion Force
2. Dipole-Dipole
3. Hydrogen Bonding
Describe the energy change based on the following chemical reaction. Determine if bonds are forming or breaking.
2H2O → 2H2 + O2
Bonds breaking and energy is absorbed.
Draw the Lewis Dot for H2
H:H
Why are metals able to conduct electricity?
Metals are able to conduct electricity because they have a sea of mobile electrons (delocalized valence electrons).
Which element has the greatest tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond?
a. Francium
b. Oxygen
c. Neon
d. Chlorine
d. Chlorine
Explain in terms of strength of intermolecular forces why a substance is a solid at STP and another substance a gas.
The substance that is a gas has very weak intermolecular forces as opposed to the solid with very strong IMFs.
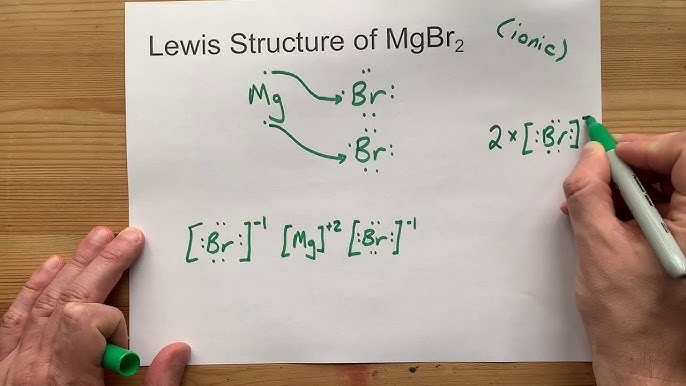
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for MgBr2
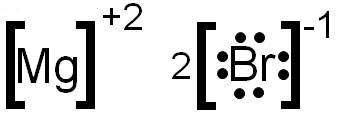
Describe the kind of bonds in sand and diamond and the name of these solids.
Covalent bonds and network solids.
A solid substance was tested in the laboratory. The test results are listed below.
• dissolves in water
• is an electrolyte
• melts at a high temperature
Based on these results, the solid substance could be
a salt/ionic compound
Describe what must be present in order for hydrogen bonding to occur between molecules.
A H of one molecule must be attracted to a F, O, or N of another molecule.
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for C2H2

Which type of bonding is found in all molecular substances?
Covalent bonding
How is the polarity of a substance determine?
Bonus (extra 100): Why is CH4 nonpolar? What is its shape?1. Difference in electronegativity
2. Distribution of charges
There is a symmetrical distribution of charge and it is tetrahedral.
Describe in terms of polarity why HCl dissolves in NH3. Determine the types of forces between these molecules.
They are both polar substances and like dissolves like.
Hydrogen bonds and dispersion forces.