A transfer of electrons from nonmetal to a metal.
What is an ionic bond?
Attractive forces between polar ends of a molecule.
What is dipole-dipole bonding?
A compound that contains carbon.
What is an organic compound?
An intramolecular force that only occurs in metals and delocalizes valence electrons.
What is a metallic bond?
The rules by which substances are named.
What is nomenclature?
The sharing of electrons between two nonmetals.
What is a covalent bond?
A powerful bond between a hydrogen atom and another atom.
What is hydrogen bonding?
A compound only containing carbon and hydrogen.
What is a hydrocarbon?
A homogenous mixture of metals.
What is an alloy?
Name of the cation+name of the anion+ide
What is the ionic bond nomenclature formula?
A pure substance with H2O inside the crystal.
What is a hydrate?
Temporary forces that form between two temporary dipoles. They are the weakest molecular force.
What are London Dispersion forces?
A compound with the same molecular formula as another compound but a different structural formula.
What is a structural isomer?
The regular pattern in which metals are arranged.
What is a lattice?
Are categorized as alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes depending on the number of bonds between carbons.
Alkane=single bonds
Alkene=double bonds
Alkyne=triple bonds
What are hydrocarbons?
Shows how molecules share electrons to gain a filled valence level.
What is the Lewis Plot Diagram?
What intermolecular forces are present in covalent compounds containing hydrogen?
What are hydrogen bonding and London Dispersion forces?
A section of a molecule that has a special arrangement of atoms creating specific chemical behavior for the parent molecule.
What is a functional group?
Free electrons are shared among a lattice of metals.
What is the reason the charge is positive?
Each element's prefix corresponds with the number of atoms.
What is the meaning of the prefix in covalent nomenclature?
The rule that states the number of electrons required in the valence shell to keep the bond stable.
What is the octet rule?
What intermolecular forces are present in ionic compounds?
What are dipole-dipole bonds and London Dispersion forces?
Name the compound:
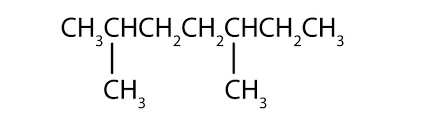
What is 2,5-dimethylheptane?
The effects of mobile valence electrons.
What are metallic properties?
Count the number of carbons, then find the carbons where the functional groups are bonded. Then, count the number of bonds between the carbons.
What is nomenclature of structural formulas for organic compounds?